The spatio-temporal characteristics of hand-foot-mouth disease in Shaanxi Province, 2013-2017
-
摘要:
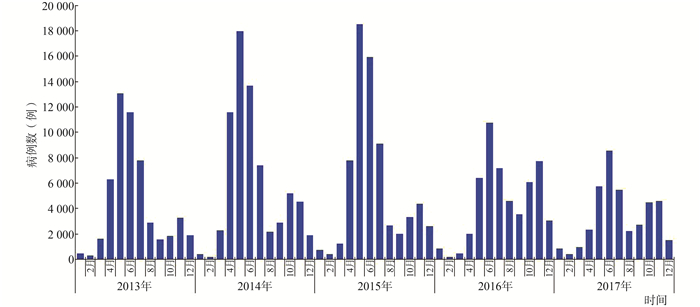
目的 探讨陕西省手足口病疫情的时空演变规律,为优化手足口病的防控策略提供科学依据。 方法 陕西省2013-2017年手足口病疫情个案数据来源于中国疾病预防控制信息系统,同期人口数据来源于陕西省统计年鉴,采用R 3.4.1、ArcGIS 10.2和SaTScan 9.2软件进行时空流行病学特征分析。 结果 陕西省2013-2017年累计报告手足口病284 225例,年均发病率150.45/10万;历年4-7月病例数占总病例数的70.69%,高发病率区县主要分布在关中地区的中东部区域。重症病例、死亡病例分布与总病例的空间分布基本一致。时空扫描分析显示,全省2013-2017年手足口病存在4个高发热点区域;疫情的一类聚集区固定在以西安市为中心的全省中部和东南部区县(RR=2.25, 95% CI: 2.18~3.11, P < 0.001),但二类聚集区位置不固定。全省2013-2017年手足口病的优势流行病原为其他肠道病毒。 结论 陕西省手足口病疫情存在显著的时空聚集性特征,近年来病原以其他肠道病毒为主,呈现多病原交替流行;应针对不同时段和地区采取针对性的措施,以有效控制发病。 Abstract:Objective To obtain the spatial-temporal dynamical features of hand-foot-mouth disease(HFMD) in Shaanxi Province, so as to provide evidence for the development of relative prevention and control programs on HFMD. Methods Surveillance data of HFMD was collected from the China Information System for Diseases Control and Prevention from 2013 to 2017. Related data on population was obtained from Shaanxi Statistical Yearbook. Statistical tools as R 3.4.1, ArcGIS 10.2 and Satscan 9.2 software were used to analyse the spatial-temporal characteristics of the disease. Results A total of 284 225 cases of HFMD were reported in Shaanxi Province from 2013 to 2017, with an average annual incidence as 150.45 per 100 000. 70.69% of the total cases were identified between April and July. Counties with high incidence were mainly distributed in the mid-east parts of Guanzhong area(Central Shaanxi Plain). The spatial distribution of severe as well as death cases were basically consistent with the total cases. Through temporal and spatial scan statistics, we identified that there were four hot spots in Shaanxi Province, the most likely clustering area was fixed to the central and southeast counties of Shaanxi province which were around Xi'an City from 2013 to 2017 (RR=2.25, 95% CI: 2.18-3.11, P < 0.001), but the location of the secondary clustering area was not fixed. The predominant epidemic pathogen of HFMD was other enteroviruses from 2013 to 2017. Conclusions Significant spatial-temporal aggregation of HFMD was seen in Shaanxi Province. In recent years, other enteroviruses have became the main pathogeny, and multiple pathogens have been circulating alternately. Specific measures should be taken for different periods and regions to control the disease effectively. -
表 1 2013-2017年陕西省手足口病疫情概况
Table 1. The overall prevalence of HFMD in Shaanxi Province from 2013 to 2017
指标 2013年 2014年 2015年 2016年 2017年 合计/平均 总病例数 52 610 70 215 68 738 52 827 39 835 284 225 重症数 545 1 327 700 416 374 3 362 死亡数 9 20 6 9 2 46 发病率(/10万) 140.18 186.53 182.08 139.28 104.2 150.45 重症构成比(%) 1.04 1.89 1.02 0.79 0.94 1.18 死亡率(/10万) 0.02 0.05 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.02 病死率(%) 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.02 表 2 2013-2017陕西省年手足口病时空聚集性扫描结果
Table 2. The results of space-time scanning of HFMD in Shaanxi Province from 2013 to 2017
年份(年) 聚集区类型 聚集中心 半径(km) 位置 聚集时间段 包含区县个数 RR值 P值 2013 一类聚集区 阎良 93.30 关中中部 4月10日-6月7日 43 2.57 < 0.001 二类聚集区 - - 不固定 5月10日-6月3日 4 1.94 < 0.001 2014 一类聚集区 华阴 41.70 全省中东部 4月25日-5月31日 21 2.73 < 0.001 二类聚集区 - - 不固定 4月30日-5月30日 9 1.46 < 0.001 2015 一类聚集区 商州 40.90 全省东南部 4月18日-6月11日 27 3.08 < 0.001 二类聚集区 - - 不固定 4月30日-5月11日 4 2.13 < 0.001 2016 一类聚集区 莲湖 15.60 关中中部 4月11日-6月12日 16 2.80 < 0.001 二类聚集区 - - 不固定 4月23日-6月8日 5 1.68 < 0.001 2017 一类聚集区 华阴 39.30 全省东南部 4月8日-6月6日 26 2.18 < 0.001 二类聚集区 - - 不固定 4月29日-6月10日 10 2.20 < 0.001 表 3 2013-2017年陕西省手足口病病原学检测结果
Table 3. The results of pathogenic test of HFMD in Shaanxi Province from 2013 to 2017
年份(年) 实验室诊断病例数 EV71 CoxA16 其他肠道病毒 病例数 占比(%) 病例数 占比(%) 病例数 占比(%) 2013 3 707 856 23.09 1 887 50.91 964 26.00 2014 2 998 1064 35.49 921 30.72 1 013 33.79 2015 3 906 1 297 33.21 791 20.25 1 818 46.54 2016 3 754 1 387 36.95 1 053 28.05 1 314 35.00 2017 2 484 1 001 40.30 666 26.81 817 32.89 合计 16 849 5 605 33.27 5 318 31.56 5 926 35.17 -
[1] 中国疾病预防控制中心. 手足口病预防控制指南(2009年版)[ EB/OL]. (2009-06-12)[2018-09-30]. http://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/bl/szkb/jszl_2275/200906/t20090612_24707.html.Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Guide of prevention and control for hand-foot and mouth disease (2009)[EB/OL]. (2009-06-12)[2018-09-30]. http://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/bl/szkb/jszl_2275/200906/t20090612_24707.html. [2] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 手足口病诊疗指南(2018年版)[EB/OL]. (2018-05-15)[2019-04-12]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s3594q/201805/5db274d8697a41ea84e88eedd8bf8f63.shtml.National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guide of diagnosis and treatment for hand-foot and mouth disease (2018)[EB/OL]. (2018-05-15)[2019-04-12]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s3594q/201805/5db274d8697a41ea84e88eedd8bf8f63.shtml. [3] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 手足口病聚集性和暴发疫情处置工作规范(2012版)[EB/OL]. (2012-06-21)[2013-01-01]. http://www.moh.gov.cn/zwgkzt/pjbkz/201206/55215.shtml.Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. Epidemic disposal standard for the aggregation and outbreak of hand, foot and mouth disease (2012 edition)[EB/OL]. (2012-06-21)[2013-01-01]. http://www.moh.gov.cn/zwgkzt/pjbkz/201206/55215.shtml. [4] 食药讯. 全球首个肠道病毒71型灭活疫苗在我国获批上市[J]. 首都食品与医药, 2016, 23(5): 43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSD201605025.htmFood and Medicine News. The World's First Enterovirus type 71 inactivated vaccines approved listed in China[J]. Capit Food Med, 2016, 23(5): 43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSD201605025.htm [5] Xing W, Liao Q, Viboud C, et al. Hand, foot, and mouth disease in China, 2008-12: an epidemiological study[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2014, 14(4): 308-318. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70342-6. [6] 张静. 2008-2017年中国手足口病流行趋势和病原变化动态数列分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2019, 40(2): 147-154. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.02.005.Zhang J. Trend of epidemics and variation of pathogens of hand, foot and mouth disease in China: a dynamic series analysis, 2008-2017[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2019, 40(2): 147-154. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.02.005. [7] 陕西省统计局, 国家统计局陕西调查总队. 陕西统计年鉴2019[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2019.Shaanxi Provincial Bureau of Statistics, Shaanxi Investigation Corps of National Bureau of Statistics. Shaanxi Statistical Yearbook 2019[M]. Beijing: China Statistic Press, 2019. [8] 王彦霞, 许汴利, 陈豪敏, 等. 河南省2008-2010年手足口病流行趋势及病原学分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2012, 46(8): 761-762. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2012.08.020.Wang YX, Xu BL, Chen HM, et al. Analysis of epidemiological trends and etiology of hand-foot-mouth disease in Henan Province from 2008 to 2010[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2012, 46(8): 761-762. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2012.08.020. [9] 孙春云, 林琳, 刘渠, 等. 深圳市龙岗区2008-2011年手足口病流行趋势分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2013, 17(8): 674-676. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201308009Sun CY, Lin L, Liu Q, et al. Analysis of epidemiology on hand-foot-mouth disease in Longgang District of Shenzhen City, 2008-2011[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2013, 17(8): 674-676. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201308009 [10] Verguet S, Johri M, Morris SK, et al. Controlling measles using supplemental immunization activities: a mathematical model to inform optimal policy[J]. Vaccine, 2015, 33(10): 1291-1296. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.11.050. [11] Wang C, Li X, Zhang YJ, et al. Spatiotemporal cluster patterns of hand, foot, and mouth disease at the county level in mainland China, 2008-2012[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0147532. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147532. [12] 相然, 樊旭成, 高枫, 等. 2013-2017年乌鲁木齐市手足口病病原学监测结果分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2019, 46(7): 1298-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF201907038.htmXiang R, Fan XC, Gao F, et al. Etiologic characteristics of hand-foot-mouth disease in Urumqi, 2013-2017[J]. Mode Prev Med, 2019, 46(7): 1298-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF201907038.htm -





 下载:
下载: