The association of overweight and obesity with hypertension among residents aged 35 years or older in Yuhuan county
-
摘要:
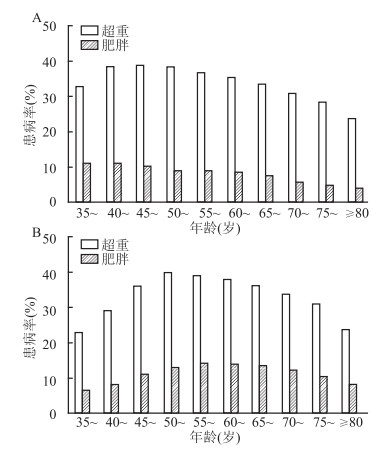
目的 了解浙江省玉环县农村社区≥35岁居民超重和肥胖流行现状,探索超重、肥胖与高血压患病的关系。 方法 2009-2010年,采用整群抽样方法在玉环县所有农村社区中抽取124 693名≥35岁常住居民进行横断面调查,分析超重和肥胖与高血压患病之间的关系。 结果 玉环县农村社区≥35岁居民超重和肥胖率分别为34.53%和10.18%。其中男性超重率(35.56%)高于女性(33.66%),女性肥胖率(11.26%)高于男性(8.90%),差异均有统计学意义(均有P<0.05)。多因素分析显示:年龄、是否务农、教育程度、规律体育锻炼、吸烟、饮酒和高盐饮食等均为超重/肥胖的可能影响因素(均有P<0.05)。在调整可能的混杂因素后,非条件Logistic回归分析结果显示:男性超重和肥胖者患高血压的风险分别是体重正常人群的2.02(95%CI:1.93~2.11)和3.83(95%CI:3.57~4.10)倍;女性分别为1.94(95%CI:1.86~2.02)和3.56(95%CI:3.35~3.77)倍。 结论 玉环县农村社区≥35岁居民超重和肥胖患病率较高,且超重和肥胖可能增加高血压的患病风险。 Abstract:Objective To assess the prevalence of overweight and obesity among residents aged 35 years or older in Yuhuan county of Zhejiang Province and explore the associations of overweight and obesity with hypertension. Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted among 124 693 permanent residents aged 35 years or older, who were randomly selected using cluster sampling method from Yuhuan county. Results The prevalence of overweight and obesity was 34.53% and 10.18% among subjects, respectively. The overweight prevalence for male (35.56%) was higher than that for female (33.66%), whereas the obesity prevalence for female (11.26%) was higher than that for male (8.90%) (all P<0.05). The multivariate analysis showed that age, education, occupation, regular physical exercise, smoking, drinking and high-salt diet were possible factors for overweight and obesity (all P<0.05). After adjustment for covariates, compared to participants with normal weight, the multivariate logistic regression indicated that the adjusted odds ratio (OR) and their 95% confidential interval of overweight and obesity were 2.02 (95% CI: 1.93-2.11) and 3.83 (95% CI: 3.57-4.10) for hypertension in men, and were 1.94(95% CI: 1.86-2.02)and 3.56(95% CI: 3.35-3.77) in women, respectively. Conclusions The prevalence of overweight and obesity was high among residents aged 35 years or older in Yuhuan county, and they may relate to the increasing risk of hypertension. -
Key words:
- Overweight /
- Obesity /
- Hypertension /
- Prevalence
-
表 1 不同BMI水平居民基本特征情况[n(%)]
Table 1. The basic characteristics of residents by different BMI levels[n(%)]
变量 低体重(n=4 293) 正常(n=64 648) 超重(n=43 054) 肥胖(n=12 698) 合计(n=124 693) t/χ2值 P值 年龄(岁,x±s) 57.75±15.81 54.17±13.02 54.35±11.73 54.34±11.55 54.37±12.57 109.24 <0.001 男性 1 667(38.83) 29 853(46.18) 20 183(46.88) 5 050(39.77) 56 753(45.51) 290.07 <0.001 农民a 526(12.27) 9 914(15.39) 5 780(13.52) 1 405(11.18) 17 625(14.21) 198.42 <0.001 初中及以上文化 966(22.50) 14 384(22.25) 8 702(20.21) 2 295(18.07) 26 347(21.13) 211.73 <0.001 规律体育锻炼 269(6.27) 4 480(6.93) 3 742(8.69) 1 185(9.33) 9 676(7.76) 171.70 <0.001 饮酒 569(13.25) 12 598(19.49) 8 714(20.24) 2 226(17.53) 24 107(19.33) 151.86 <0.001 吸烟a 954(22.24) 16 379(25.36) 9 763(22.70) 2 317(18.26) 29 413(23.61) 335.86 <0.001 高盐饮食 747(17.40) 12 301(19.03) 8 790(20.42) 2 788(21.96) 24 626(19.75) 87.29 <0.001 糖尿病a 811(20.06) 14 838(24.42) 13 957(34.27) 5 091(42.24) 34 697(29.51) 2 314.95 <0.001 血脂异常 1 398(32.56) 26 005(40.23) 23 402(54.35) 7 757(61.09) 58 562(46.96) 3 497.17 <0.001 注:a部分数据有缺失。 表 2 农村社区≥35岁居民超重/肥胖影响因素
Table 2. The risk factors of overweight or obesity among rural community population aged 35 years old and above
OR(95% CI)值 P值 aOR(95% CI)a值 P值 年龄 35~ 1.00 - 1.00 - 45~ 1.48(1.44~1.52) < 0.001 1.47(1.43~1.51) < 0.001 55~ 1.48(1.43~1.53) < 0.001 1.44(1.39~1.49) < 0.001 65~ 1.19(1.15~1.23) < 0.001 1.14(1.10~1.19) < 0.001 ≥75 0.82(0.79~0.86) < 0.001 0.79(0.75~0.83) < 0.001 性别 男 0.98(0.96~1.00) 0.104 女 1.00 - 职业 农民 0.83(0.81~0.86) < 0.001 0.81(0.78~0.84) < 0.001 非农民 1.00 - 1.00 - 文化程度 初中及以上 0.86(0.83~0.88) < 0.001 0.87(0.85~0.90) < 0.001 小学及以下 1.00 - 1.00 - 规律体育锻炼 是 1.31(1.26~1.37) < 0.001 1.30(1.24~1.35) < 0.001 否 1.00 - 1.00 - 饮酒 是 1.03(1.01~1.06) 0.020 1.16(1.13~1.20) < 0.001 否 1.00 - 1.00 - 吸烟 是 0.82(0.80~0.85) < 0.001 0.77(0.75~0.80) < 0.001 否 1.00 - 1.00 - 高盐饮食 是 1.12(1.09~1.15) < 0.001 1.14(1.10~1.17) < 0.001 否 1.00 - 1.00 - 注:年龄、职业、文化程度、规律体育锻炼、饮酒、吸烟和高盐饮食等变量同时引入模型。 表 3 不同性别个体BMI水平与高血压患病的相关性[n(%)]
Table 3. The association between BMI levels and hypertension by gender[n(%)]
BMI分组 调查人数 高血压 OR(95%CI) 值 P值 aOR(95% CI)值 P值 男性 低体重 1 667 279(16.74) 0.70(0.61~0.80) < 0.001 0.52(0.45~0.60) < 0.001 正常 29 853 6 654(22.29) 1.00 1.00 超重 20 183 6 965(34.51) 1.84(1.77~1.91) < 0.001 2.02(1.93~2.11) < 0.001 肥胖 5 050 2 377(47.07) 3.10(2.91~3.30) < 0.001 3.83(3.57~4.10) < 0.001 女性 低体重 2 626 537(20.45) 0.93(0.84~1.02) 0.130 0.58(0.51~0.65) < 0.001 正常 34 795 7 554(21.71) 1.00 1.00 超重 22 871 8 096(35.40) 1.98(1.90~2.05) < 0.001 1.94(1.86~2.02) < 0.001 肥胖 7 648 3 780(49.42) 3.52(3.35~3.71) < 0.001 3.56(3.35~3.77) < 0.001 注:aOR为调整年龄、职业、教育程度、饮酒、吸烟、规律体育锻炼、高盐饮食、糖尿病、血脂异常等。 -
[1] Di CM, Bentham J, Stevens GA, et al. Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19·2 million participants[J]. Lancet, 2015, 387(10026): 1377-1396. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30054-X. [2] Pecin I, Samovojska R, Heinrich B, et al. Hypertension, overweight and obesity in adolescents: the CRO-KOP study[J]. Coll Antropol, 2013, 37(3): 761-764. DOI: 10.1016/j.anthro.2013.09.001. [3] Maniecka-Bryla I, Szymocha M, Bryla M. Overweight and obesity as risk factors in hypertension——study of the working population[J]. Med Lav, 2011, 102(6): 523-538. DOI: 10.1007/s10654-011-9602-5. [4] Jafar TH, Chaturvedi N, Pappas G. Prevalence of overweight and obesity and their association with hypertension and diabetes mellitus in an Indo-Asian population[J]. CMAJ, 2006, 175(9): 1071-1077. DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.060464. [5] Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG, Walker M, et al. Lifestyle and 15-year survival free of heart attack, stroke, and diabetes in middle-aged British men[J]. Arch Intern Med, 1998, 158(22): 2433-2440. DOI: 10.1001/archinte.158.22.2433. [6] Zhu YB, Wang Q, Wu CY, et al. Logistic regression analysis on relationships between traditional Chinese medicine constitutional types and overweight or obesity[J]. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao, 2010, 8(11): 1023-1028. DOI: 10.3736/jcim20101104. [7] Dhurandhar NV, Kulkarni PR. Prevalence of obesity in Bombay[J]. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord, 1992, 16(5): 367-375. http://jech.bmj.com/external-ref?access_num=1319972&link_type=MED [8] Deurenbergyap M, Schmidt G, Staveren WAV, et al. The paradox of low body mass index and high body fat percentage among Chinese, Malays and Indians in Singapore[J]. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord, 2000, 24(8): 1011-1017. DOI: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801353. [9] 中国肥胖问题工作组数据汇总分析协作组. 我国成人体重指数和腰围对相关疾病危险因素异常的预测价值: 适宜体重指数和腰围切点的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2002, 23(1): 5-10. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2002.01.003.Coorperative Meta-analysis Group of China Obesity Task Force. Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference to risk factors of related diseases in Chinese adult population[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2002, 23(1): 5-10. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2002.01.003. [10] 肖甜, 陈晓英, 王娜, 等. 中国城市社区COPD患者急性加重的相关因素调查[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2017, 21(2): 110-113. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.02.002.Xiao T, Chen XY, Wang N, et al. Survey on influencing factors related to exacerbation of COPD patients in Chinese urban communities[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2017, 21(2): 110-113. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.02.002. [11] 陈晓英, 吴照帆, 王学才, 等. 2006-2014年德清县农村成人2型糖尿病患病情况及流行趋势[J]. 卫生研究, 2017, 46(6): 868-874. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSYJ201706004.htmChen XY, Wu ZF, Wang XC, et al. Prevalence and change of type 2 diabetes mellitus among rural adults in Deqing County, Zhejiang Province in China during 2006-2014[J]. Journal of Hygiene Research, 2017, 46(6): 868-874. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSYJ201706004.htm [12] 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会. 中国高血压防治指南2010[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2011, 3(5): 701-708. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7372.2011.05.011.Writing Group of 2010 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of hypertension. 2010 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension[J]. Chinese Journal of the Frontiers of Medical Science (Electronic Version), 2011, 3(5): 701-708. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7372.2011.05.011. [13] American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetes Care, 2013, 36(Supplement 1): S67-S74. DOI: 10.2337/dc13-S067. [14] 中国成人血脂异常防治指南制订联合委员会. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南[J]. 中国实用乡村医生杂志, 2012, 19(16): 390-419. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7185.2012.16.002.Joint Committee for the Development of guidelines for prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in adults. Chinese adult guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia[J]. Chinese Practical Journal of Rural Doctor, 2012, 19(16): 390-419. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7185.2012.16.002. [15] 方顺源, 施世锋, 刘庆敏, 等. 杭州市城乡居民超重及肥胖与相关疾病关系[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2006, 22(7): 852-853. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws2006-22-07-51.Fang SY, Shi SF, Liu QM, et al. Relationship between overweight, fat and relative diseases in residents of Hangzhou city[J]. Chin J Public Health, 2006, 22(7): 852-853. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws2006-22-07-51. [16] 陈其龙, 华春芬, 周伯华, 等. 平湖市成人超重肥胖现状及与糖尿病、高血压、血脂异常的关系[J]. 上海预防医学, 2016(6): 361-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHYI201606003.htmChen QL, Hua CF, Zhou BH, et al. Analysis on prevalence of overweight and obesity and their relation with diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia among adults in Pinghu City[J]. Shanghai J Prevent Med, 2016(6): 361-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHYI201606003.htm [17] 崔红月. 海淀区居民超重、肥胖现状及危险因素分析[J]. 中国公共卫生管理, 2008, 24(5): 529-530. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9561.2008.05.047.Cui HY. Current situation and analysis on risk factors of overweight and obesity in residents of Haidian District of Beijing[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health Management, 2008, 24(5): 529-530. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9561.2008.05.047. [18] 宋孟娜, 程潇, 孔静霞, 等. 我国中老年人超重、肥胖变化情况及影响因素分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(8): 804-808. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.08.010.Song MN, Cheng X, Kong JX, et al. Prevalence and influencing factors of overweight and obesity among middle-aged and elderly people in China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(8): 804-808. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.08.010. [19] 屈亚莉, 沈俊, 梁小云, 等. 三峡农村地区人群超重肥胖的流行现状及其影响因素[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2012, 27(3): 204-207. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2012.03.014.Qu YL, Shen J, Liang XY, et al. Current Epidemic Status with Related Factors for Overweight and Obesity in Rural Area of Three Gorges[J]. Chinese Circulation Journal, 2012, 27(3): 204-207. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2012.03.014. [20] 刘小蓉, 黄晓波, 刘剑雄, 等. 西南地区中老年人群超重及肥胖流行状况与影响因素分析[J]. 重庆医学, 2016, 45(8): 1056-1058. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.08.016.Liu XR, Huang XB, Liu JX, et al. Prevalence status of overweight and obesity among middle age and elderly people in southwest area and their influence factors[J]. Chongqing Med J, 2016, 45(8): 1056-1058. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.08.016. [21] 陈捷, 赵秀丽, 武峰, 等. 我国14省市中老年人肥胖超重流行现状及其与高血压患病率的关系[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2005, 85(40): 2830-2834. DOI: 10.3760/j:issn:0376-2491.2005.40.007.Chen J, Zhao XL, Wu F, et al. Epidemiology of obesity and overweight and relation thereof to the prevalence of hypertension in 14 provinces/municipality in China[J]. Natl Med J China, 2005, 85(40): 2830-2834. DOI: 10.3760/j:issn:0376-2491.2005.40.007. [22] Wu Y, Zhou B, Tao S, et al. [Prevalence of overweight and obesity in Chinese middle-aged populations: Current status and trend of development][J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2002, 23(1): 11-15. DOI: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290131. [23] 李琦, 张国福, 张绍芬. 绝经后女性体脂分布特点及相关因素[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2010, 26(12): 966-968. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201012032.htmLi Q, Zhang GF, Zhang SF. Distribution characteristics and related factors of body fat in postmenopausal women[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2010, 26(12): 966-968. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSF201012032.htm [24] 韩战红, 王明晓. 高血压与超重和肥胖的关系[J]. 中国心血管病研究, 2006, 4(10): 738-739. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5301.2006.10.007.Han ZH, Wang MX. Relations between hypertension and overweight-and-fatness[J]. Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Review, 2006, 4(10): 738-739. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5301.2006.10.007. [25] Ogah O, Ijezie C, Madukwe O, et al. 722: prevalence and determinants of hypertension in abia state nigeria: results from the abia state non-communicable diseases and cardiovascular risk factors survey. Cardiovascular Journal of Africa[J]. Cardio J Africa, 2013, 23(2): 161-167. http://connection.ebscohost.com/c/articles/86953021/722-prevalence-determinants-hypertension-abia-state-nigeria-results-from-abia-state-non-communicable-diseases-cardiovascular-risk-factors-survey -





 下载:
下载: