Spatial epidemiological analysis of measles in Taizhou from 2009 to 2017
-
摘要:
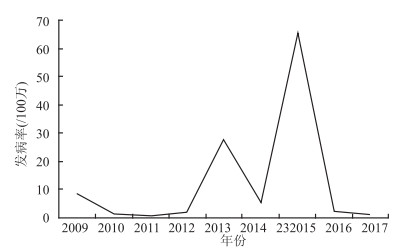
目的 分析泰州市2009-2017年麻疹发病空间流行病学特征,为麻疹防制提供理论依据。 方法 用ArcGIS 10.0软件对泰州市2009-2017年麻疹数据进行空间自相关性分析、趋势面分析,对泰州市麻疹疫情的动态趋势及变化特征进行综合分析。 结果 泰州市2009-2017年麻疹发病率处于0.83~65.43/100万之间。全局自相关分析发现,2012年、2013年、2015年、2016年泰州市麻疹发病率存在空间相关性,且为高值聚集性分布。局部自相关分析发现2009-2017年泰州市麻疹发病热点区域主要集中在泰州市中部乡镇。趋势面分析发现泰州市麻疹疫情2010年南部地区高于北部地区,2013年、2015年中部地区高于东西、南北地区。 结论 根据空间分析,2009-2017年泰州市麻疹发病空间分布存在自相关,中部乡镇存在发病热点区域。针对这些特点,应该采取针对性的预防措施。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the spatial epidemiological characteristics of measles in Taizhou from 2009 to 2017, so as to provide theoretical basis for measles prevention and control. Methods The spatial autocorrelation analysis and trend surface analysis of measles epidemics data from 2009 to 2017 in Taizhou were performed using ArcGIS 10.0 software. The dynamic characteristics of measles epidemics in Taizhou were analyzed. Results Among 2009-2017 years, the incidences of measles in Taizhou ranged from 0.83/1 million to 65.43/1 million. The results of global autocorrelation analysis showed that there were spatial correlations of the incidence of measles among 2012, 2013, 2015, and 2016 in Taizhou with a high-value clustering distribution. Local autocorrelation analysis indicated that the hot spots of measles incidence in Taizhou from 2009 to 2017 were mainly concentrated in the central towns of Taizhou. Trend surface analysis suggested that the measles incidence in the south towns of Taizhou was higher than that in the north in 2010, and the incidence in the central region was higher than those in other regions in 2013 and 2015. Conclusions According to the spatial analysis, autocorrelation was observed for the spatial distribution of measles incidence in Taizhou from 2009 to 2017, and there are hot spots in the central township. Targeted preventive measures should be taken based on these characteristics. -
Key words:
- Measles /
- Spatial analysis /
- Incidence
-
表 1 泰州市2009-2017年发病率最高乡镇统计表
Table 1. List of township with highest measles incidence in each year in Taizhou from 2009 to 2017
年份 发病率最高乡镇 所在市区 2009 茅山镇 兴化市 2010 寺巷街道 高新区 2011 刁铺街道 高港区 2012 大泗镇 高港区 2013 京泰路街道 海陵区 2014 红旗农场 农业开发区 2015 凤凰街道 高新区 2016 九龙镇 海陵区 2017 京泰路街道 海陵区 表 2 泰州市2009-2017年麻疹发病全局自相关分析表
Table 2. Global autocorrelation analysis for measles incidence in Taizhou from 2009 to 2017
年份 Moran′s Index Z值 P值 聚集性 2009年 -0.010 0.003 0.997 - 2010年 0.019 0.506 0.613 - 2011年 -0.027 -0.034 0.738 - 2012年 0.179 3.448 0.001 聚集 2013年 0.496 7.892 <0.001 聚集 2014年 0.066 1.879 0.060 - 2015年 0.566 9.443 <0.001 聚集 2016年 0.149 2.632 0.008 聚集 2017年 -0.027 -0.335 0.738 - 表 3 泰州市2009-2017年麻疹发病全局自相关(high/low Cluster)分析表
Table 3. Global autocorrelation of measles incidence in Taizhou from 2009 to 2017 (high/low Cluster)
年份 Observed General G Expected General G Variance Z值 P值 2009 0.010 3 0.010 5 0.000 0 -0.112 2 0.910 7 2010 0.016 4 0.010 5 0.000 1 0.512 4 0.608 3 2011 0.000 0 0.010 5 0.000 5 -0.460 4 0.645 2 2012 0.052 9 0.010 5 0.000 1 3.660 0 0.000 3 2013 0.022 9 0.010 5 0.000 0 7.522 0 0.000 0 2014 0.020 3 0.010 5 0.000 0 1.930 5 0.053 5 2015 0.027 0 0.010 5 0.000 0 9.462 1 0.000 0 2016 0.028 4 0.010 5 0.000 0 2.584 9 0.009 7 2017 0.000 0 0.010 5 0.000 4 -0.498 0 0.618 5 -
[1] 世界卫生组织. 麻疹[EB/OL]. (2018-11-29)[2019-01-22]. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs286/zh/World Health Organization. Measles[EB/OL]. (2018-11-29)[2019-01-22]. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs286/zh/. [2] 马超, 郝利新, 苏琪茹, 等. 中国2011年麻疹流行病学特征与消除麻疹进展[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2012, 18(3): 193-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201403001.htmMa C, Hao LX, Su QR, et al. Measles epidemiology and progress towards measles elimination in China, 2011[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization, 2012, 18(3): 193-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201403001.htm [3] 马超, 苏琪茹, 郝利新等. 中国2012-2013年麻疹流行病学特征与消除麻疹进展[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2014, 20(3): 193-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201403001.htmMa C, Su QR, Hao LX, et al. Measles epidemiology characteristics and progress toward measles elimination in China, 2012-2013[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization, 2014, 20(3): 193-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201403001.htm [4] 马超, 郝利新, 苏琪茹, 等. 中国2014年麻疹流行病学特征分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2015, 30(10): 818-823. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2015.10.006.Ma C, Hao LX, Su QR, et al. Measles epidemiology in China, 2014[J]. Disease Surveillance, 2015, 30(10): 818-823. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2015.10.006. [5] 苏琪茹, 郝利新, 马超, 等. 中国2015-2016年麻疹流行病学特征分析[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2018, 24(2): 146-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201802006.htmSu QR, Hao LX, Ma C, et al. Epidemiology of measles in China, 2015-2016[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization, 2018, 24(2): 146-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201802006.htm [6] 姚保栋, 周艺彪, 王增亮, 等. 湖沼地区行政村尺度的洲滩阳性钉螺空间分布特征及变化趋势[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2012, 33(7): 702-705. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2012.07.013.Yao BD, Zhou YB, Wang ZL, et al. Study on spatial-temporal variation of infected snail in bottomland areas after an integrated control strategy at village level in the marshland and lake regions based on geographic information system[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2012, 33(7): 702-705. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2012.07.013. [7] 陈胤忠, 李峰, 徐慧, 等. 江苏省盐城市沿海滩涂2005-2014年恙虫病时空分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2016, 37(2): 232-237. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.02.017.Chen YZ, Li F, Xu H, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of scrub typhus and related influencing factors in coastal beach area of Yancheng, China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2016, 37(2): 232-237. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.02.017. [8] 王荣华, 李琼芬, 林燕, 等. 2008-2013年云南省手足口病流行特征和空间分布特点分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2014, 29(11): 857-861. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2014.11.005.Wang RH, Li QF, Lin Y, et al. Epidemiology of hand foot and mouth disease and geographic distribution of the cases in Yunnan, 2008-2013[J]. Disease Surveillance, 2014, 29(11): 857-861. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2014.11.005. [9] Fabro AYR, Avila JGP, Alberich MVE, et al. Spatial distribution of nitrate health risk associated with groundwater use as drinking water in Merida, Mexico[J]. Applied Geography, 2015, 65: 49-57. DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2015.10.004. [10] Dantas AP, Azevedo UN, Nunes AD, et al. Analysis of suicide mortality in Brazil: spatial distribution and socioeconomic context[J]. Braz J Psychiatry, 2018, 40(1): 12-18. DOI: 10.1590/1516-4446-2017-2241. [11] 马涛, 谢国祥, 孙红敏等. 2009-2016年南京市重症手足口病流行特征和时空聚集性分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(11): 1138-1143. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.11.011.Ma T, Xie GX, Sun HM, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and temporal-spatial clustering analysis of severe hand-foot-mouth disease in Nan-jing from 2009 to 2016[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(11): 1138-1143. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.11.011. [12] 刘德钦, 刘宇, 薛新玉. 中国人口分布及空间相关分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2004, 29(7): 78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD2004S1025.htmLiu DQ, Liu Y, Xue XY. Analysis of population distribution and spatial correlation in China[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2004, 29(7): 78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD2004S1025.htm [13] 郭风云, 路紫. 基于空间分析方法的疾病地理研究进展[J]. 地理信息世界, 2009, 7(6): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2009.06.004Guo FY, Lu Z. Disease geography research development based on spatial analysis method[J]. Geomatics World, 2009, 7(6): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2009.06.004 [14] 张晓萌, 郝利新, 王华庆. 中国2005~2014年15~49岁人群麻疹流行病学特征分析[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2015, 21(3): 248-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201503004.htmZhang XM, Hao LX, Wang HQ. Epidemiological characteristics of measles among people 15 to 49 years of age in China, 2005-2014[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization, 2015, 21(3): 248-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201503004.htm [15] 王超, 张翔, 朱中奎等. 2013-2015年泰州市健康人群麻疹免疫水平监测结果分析[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2017, 18(7): 493-496. DOI: 10.16506/j.1009-6639.2017.07.004.Wang C, Zhang X, Zhu ZK, et al. Survey on immune responses to measles among healthy individuals in Taizhou during 2013-2015[J]. Chin Prev Med, 2017, 18(7): 493-496. DOI: 10.16506/j.1009-6639.2017.07.004. [16] 修仕信, 张雪峰, 刘元宝, 等. 2015年无锡市麻疹流行病学特征分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2016, 43(18): 3300-3303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF201618010.htmXiu SX, Zhang XF, Liu YB, et al. Analysis on epidemiological characteristic of measles in Wuxi city in 2015[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2016, 43(18): 3300-3303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF201618010.htm [17] 刘元宝, 胡莹, 邓秀英, 等. 江苏省儿童和成人麻疹传播影响因素的1: 3配比病例对照研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2016, 20(8): 796-800. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.08.011.Liu YB, Hu Y, Deng XY, et al. Risk factor analysis for measles infection in 8 months to 14 years children and older than 15 years adults in Jiangsu Province: a 1: 3 matched case-control study[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2016, 20(8): 796-800. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.08.011. -





 下载:
下载: