Effect of TLR gene polymorphisms on primary immune response to hepatitis B vaccine in Han children of Guangxi
-
摘要:
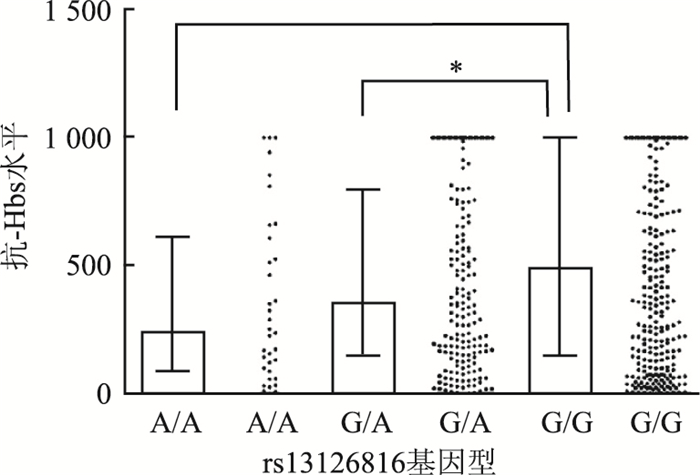
目的 探讨Toll样受体(toll-like receptors,TLR)基因多态性与广西汉族儿童乙型肝炎(以下简称乙肝)疫苗初次免疫应答水平的关联。 方法 收集2014-2016年到广西自治区妇幼保健院、南宁市妇幼保健院儿科就诊的8~9月龄汉族儿童513例为研究对象。采集外周血标本,采用微粒子酶免疫法检测乙肝血清标志物"两对半",用套式聚合酶链式反应法检测乙肝病毒DNA,应用SNPscanTM多重SNP分型技术检测TLR基因10个位点的基因多态性。采用非条件Logistic回归分析TLR等位基因、基因型与儿童乙肝疫苗免疫后应答的关联。 结果 TLR3基因rs13126816的基因多态性与广西汉族儿童初次乙肝疫苗免疫后应答情况有关(OR=1.79,95% CI:1.11~2.89,P=0.018);A/A基因型[238.04(519.75) mIU/L]和G/A基因型[347.96(619.68) mIU/L]儿童的乙肝病毒表面抗体(hepatitis B surface antibody,抗-HBs)水平明显低于G/G基因型[489.08(854.76) mIU/L]的儿童,差异均有统计学意义(均有P < 0.05);携带等位基因A[317.20(608.72) mIU/L]儿童的抗-HBs水平也明显低于携带等位基因G[457.01(852.66) mIU/L]的儿童,差异有统计学意义(Z=-3.055,P < 0.05)。TLR基因其余位点均与乙肝疫苗免疫应答无关(均有P>0.05)。 结论 TLR3基因rs13126816位点等位基因A可能是汉族儿童产生初次乙肝疫苗免疫低应答的影响因素。 Abstract:Objective To explore the association between Toll-like receptors(TLR) gene polymorphisms and the primary immune response level to Hepatitis B Vaccine in Han children in Guangxi. Methods A total of 513 Han children aged 8-9 months were collected from the department of pediatrics in the Maternal and Child Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region and Nanning Maternal and Child Health Hospital from 2014 to 2016. Peripheral venous blood of each study object was collected to detect HBsAg, anti-HBs, HBeAg, anti-HBe, anti-HBc and HBV DNA. The polymorphisms of 10 sites of TLR gene were detected by SNPscanTM multiple SNP typing techniques. The association between allele, genotype of TLR gene and anti-HBs levels were analyzed by non-conditional logistic regression. Results The genetic polymorphism of TLR3 gene rs13126816 was related to immune response after primary Hepatitis B immunization in Han children in Guangxi (OR=1.79, 95% CI: 1.11-2.89, P=0.018). The anti-HBs level of children with A/A genotype[238.04(519.75) mIU/L] and G/A genotype[347.96(619.68) mIU/L] were significantly lower than those with G/G genotype[489.08(854.76) mIU/L], and the differences were statistically significant (all P < 0.05). Anti-HBs level of children carrying allele A[317.20(608.72) mIU/L] was significantly lower than those carrying allele G[457.01(852.66) mIU/L], and the difference was statistically significant (Z=-3.055, P < 0.05). The rest of the TLR genes were not related to the immune response of Hepatitis B Vaccine (all P>0.05). Conclusions The allele A of TLR3 gene rs13126816 may be the influencing factor for the low response of primary immune response to Hepatitis B Vaccine in Han children. -
表 1 本次研究分析的TLR基因10个位点
Table 1. Ten sites of TLR gene for SNPs analysis
基因 位点 区域 TLR2 rs3804100 exonic TLR3 rs11721827 intronic rs3775296 UTR5 rs13126816 intronic rs7657186 intronic rs3775292 intronic rs3775291 exonic rs7668666 intronic TLR4 rs1927911 intronic rs11536889 UTR3 表 2 研究对象的基本情况
Table 2. Base line data of study subjects
变量 合计(n=513) 男童(n=395) 女童(n=118) t/Z/χ2值 P值 年龄(月,x±s) 8.89±0.31 8.90±0.31 8.88±0.33 0.457a 0.648 抗-HBs水平[mIU/L,M(IR)] 403.40(856.53) 363.94(869.87) 544.31(802.48) -1.217b 0.224 抗-HBs构成[n(%)] 9.416c 0.024 无应答 17(3.31) 9(2.28) 8(6.78) 低应答 88(17.16) 75(18.99) 13(11.01) 正常应答 276(53.80) 208(52.66) 68(57.63) 高应答 132(25.73) 103(26.07) 29(24.58) 注:a不同性别年龄比较,资料服从正态分布,采用两独立样本t检验(计算t值);b不同性别抗-HBs水平比较,资料不服从正态分布,采用Mann-Whitney U检验(计算Z值);c不同性别抗-HBs构成比较,为单向有序行列表计数资料,采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验(计算χ2值) 表 3 TLR基因各SNPs与抗-HBs关联Logistic回归分析
Table 3. Analysis for the association between SNPs of TLR gene and anti-HBs levels by Logistic regression
基因 位点 染色体 物理位置 次等位基因/主要等位基因 基因型AA/AB/BB 最小等位基因频率 OR(95% CI)值 P值 TLR2 rs3804100 4 154625409 C/T 13/67/140 0.211 4 0.95(0.60~1.49) 0.814 TLR3 rs11721827 4 186991137 C/A 1/44/175 0.104 5 0.85(0.44~1.64) 0.631 rs7657186 4 186994039 A/G 10/69/141 0.202 3 0.81(0.50~1.30) 0.374 rs13126816 4 186994178 A/G 10/66/144 0.195 5 1.79(1.11~2.89) 0.018 rs3775296 4 186997767 A/C 19/85/116 0.279 5 0.90(0.59~1.37) 0.619 rs3775292 4 187003025 C/G 6/70/144 0.186 4 0.89(0.53~1.47) 0.644 rs3775291 4 187004074 T/C 28/92/100 0.336 4 1.32(0.89~1.95) 0.169 rs11536879 9 120472211 G/A 4/46/170 0.122 7 0.75(0.41~1.37) 0.344 rs1927907 9 120472764 T/C 5/58/157 0.154 5 0.99(0.58~1.68) 0.966 TLR4 rs1927911 9 120470054 A/G 18/91/111 0.288 6 0.90(0.59~1.38) 0.626 rs11536889 9 120478131 C/G 22/98/100 0.322 7 1.01(0.66~1.53) 0.970 表 4 TLR3基因rs13126816基因型抗-HBs水平的分布情况[M(IR)]
Table 4. The distribution of anti-HBs levels of TLR3 gene rs13126816 allele[M(IR)]
抗-HBs水平(mIU/L) 基因型 χ2值 P值 等位基因 χ2值 P值 A/A (n=35) G/A (n=182) G/G (n=296) A (n=252) G (n=774) 男童(n=395) 245.69(561.53) a 305.74(633.47) a 451.18(860.66) 8.124 0.017 290.01(552.69) 408.94(865.33) -2.943 0.003 女童(n=118) 227.11(568.16) 525.70(614.60) 603.29(819.34) 1.410 0.494 463.58(608.73) 557.34(818.34) -1.047 0.295 合计(n=513) 238.04(519.75)a 347.96(619.68) a 489.08(854.76) 8.751 0.013 317.20(608.72) 457.01(852.66) -3.055 0.002 注:a与G/G相比,P<0.05。 -
[1] Zhou YH, Wu C, Zhuang H. Vaccination against hepatitis B: the Chinese experience[J]. Chin Med J(Engl) 2009, 122(1): 98-102. [2] Fang ZL, Harrison TJ, Yang JY, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in a highly endemic area of southern China after catch-up immunization[J]. J Med Virol, 2012, 84(6): 878-884. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.23278. [3] Whittle H, Jaffar S, Wansbrough M, et al. Observational study of vaecin efficacy 14 years after trial of hepstitis B vaccination in Gambian children[J]. BMJ, 2002, 325(7364): 569. doi: 10.1136/bmj.325.7364.569 [4] Newport MJ, Goetghebuer T, Weiss HA, et al. Genetic regulation of immune responses to vaccines in early life[J]. Genes Immun, 2004, 5(2): 122-129. DOI: 10.1038/sj.gene.6364051 [5] Okada Y, Uno N, Sato S, et al. Strong influence of human leukocyte antigen-DP variants on response to hepatitis B vaccine in a Japanese population[J]. Vaccine. 2017, 35(42): 5662-5665. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.08.045. [6] Akcay IM, Katrinli S, Ozdil K, et al. Host genetic factors affecting hepatitis B infection outcomes: Insights from genome-wide association studies[J]. World J Gastroenterol. 2018, 24(30): 3347-3360. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i30.3347. [7] Roh EY, Yoon JH, In JW, et al. Association of HLA-DP variants with the responsiveness to Hepatitis B virus vaccination in Korean Infants[J]. Vaccine, 2016, 34(23): 2602-2607. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.03.090. [8] 李海, 杨进业. 乙肝疫苗免疫应答与免疫分子基因变异关系的研究进展[J]. 广西医学, 2014, 36(3): 354-358. DOI:10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304. 2014.03.26.Li Hai, Yang Jin-ye. Study development between immune response of hepatitis B vaccine and genetic variable of immune molecules gene[J]. Guangxi Medical Journal, 2014, 36(3): 354-358. DOI:10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304. 2014.03.26. [9] 陈珍珍. ATP6AP2基因多态性与2型糖尿病肾病发病及其临床表型的相关性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018.Chen Zhen-zhen. Association study of ATP6AP2 gene polymorphism with type 2 diabetic nephropathy and clinical phenotype[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018. [10] Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity[J]. Nat Immunol, 2001, 2(8): 675-680. DOI: 10.1038/90609. [11] Cooper A, Tal G, Lider O, et al. Cytokine induction by the hepatitis B virus capsid in macrophages is facilitated by membrane heparan sulfate and involves TLR2[J]. J Immun, 2005, 175(5): 3165-3176. DOI:https://doi.org/ 10.4049/jimmunol.175.5.3165. [12] Wei XQ, Guo YW, Liu JJ, et al. The significance of Toll-like receptor 4(TLR4) expression in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Clin Invest Med, 2008, 31(3): 123-130. doi: 10.25011/cim.v31i3.3469 [13] 张之海, 戴垚垚, 陈杰, 等. IL-17、TLR4、P2X7基因多态与慢性阻塞性肺疾病的关联研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(2): 142-146, 152. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.02.010.Zhang ZH, Dai YY, Chen J, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of IL-17, TLR4 and P2X7 in association with the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(2): 142-146, 152. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.02.010. [14] Chen J, Liang Z, Lu F, et al. Toll-like receptors and cytokines/cytokine receptors polymorphisms associate with non-response to hepatitis B vaccine[J]. Vaccine, 2011, 29(4): 706-711. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.11.023. [15] Wang Y, Xu P, Zhu D, et al. Association of polymorphisms of cytokine and TLR-2 genes with long-term immunity to hepatitis B in children vaccinated early in life[J]. Vaccine, 2012, 30(39): 5708-5713. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.07.010. [16] EzzE1-Din, Galal SH, Ahmed AO, et al. Toll Like Receptor 3 Polymorphisms in Hepatitis B Virus Infection[J]. Egyptian Journal of Immunology, 2017, 24(2): 173-178. [17] Huang X, Li H, Wang J, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor 3, gene are associated with the risk of hepatitis B virus-related liver diseases in a Chinese population[J]. Gene, 2015, 569(2): 218-224. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.05.054. -





 下载:
下载: