Exploration of anti-aging life behavior in middle-aged and elderly people based on PPSHAS scale
-
摘要:
目的 通过分析中老年人衰老相关的生活行为方式,提出抗衰老措施。 方法 采用课题组研制并通过国家级学会认证的《生理-心理-社会三维人体衰老度量表》(简称PPSHAS量表)对老年人展开衰老度测量,同时以问卷和构建logistic模型的方式进行抗衰老因素。 结果 得到有效PPSHAS量表及抗衰老调查表各836份,其中明显年轻和明显衰老有效问卷471份,经Mann-Whitney U检验发现,饱食程度和是否吸烟不具有统计学意义(P饱食=0.295,P吸烟=0.294),将有意义的因素纳入logistic模型得出穿戴打扮、饮酒频率、饮茶习惯等7项相关抗衰老因素。 结论 通过注重穿戴打扮、限酒、充足的睡眠、加强锻炼、保持和睦的家庭氛围、常饮茶的生活行为方式可以延缓衰老 Abstract:Objective To study the aging-related lifestyle and behaviors associated with the middle-aged and elderly so as to propose anti-aging strategies. Methods The aging degree of the elderly was measured by PPSHAS scale, which was certified by the national society. At the same time, the anti-aging factors were studied by questionnaire and logistic model. Results There were 836 effective PPSHAS scales and anti-aging questionnaires, 471 of which were significantly younger or older. Mann-Whitney U test showed that there was no significant difference in satiety and smoking between the two groups (Psatiety=0.295, Psmoking=0.294). By incorporating meaningful factors into logistic model, seven related anti-aging factors, such as dressing, drinking frequency and tea drinking habits, were obtained. Conclusions Aging can be delayed by paying attention to dressing, limiting alcohol, getting enough sleep, strengthening exercise, maintaining a harmonious family atmosphere, and drinking tea regularly. -
Key words:
- PPSHAS scale /
- lifestyle /
- anti-aging /
- mathematical model
-
表 1 PPSHAS量表衰老度总分测量及人群分布
Table 1. Aging Score Measurement and Population Distribution of PPSHAS Scale
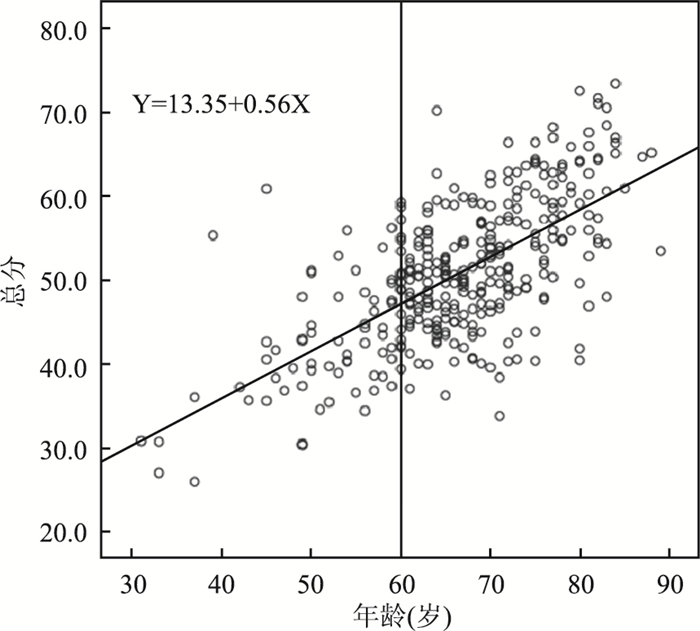
年龄(岁) 男 女 人数 明显衰老 明显年轻 相符 衰老度总分(x±s) 人数 明显衰老 明显年轻 相符 衰老度总分(x±s) 45~ 22 5 6 11 38.37±8.59 18 10 6 2 43.05±8.95 50~ 17 4 5 8 43.40±6.20 49 17 12 20 45.82±7.11 55~ 24 6 12 6 44.23±5.74 73 20 32 21 47.52±5.93 60~ 77 21 10 46 49.43±5.87 97 46 16 35 50.45±6.62 65~ 68 11 25 32 47.52±5.93 93 38 31 24 51.80±6.68 70~ 55 13 19 23 52.61±7.07 71 29 22 20 47.52±5.93 75~ 41 14 11 16 57.73±6.36 38 16 11 11 57.16±7.51 80~93 35 9 10 16 60.45±8.51 58 12 16 30 59.24±10.41 合计 339 83 98 158 50.71±8.67 497 188 146 163 51.06±8.28 F值 36.289 130.79* P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 注:*基于Levene检验方差不齐,选用Welch法近似F分布^衰老度总分值±标准差。 表 2 两组人群抗衰老因素调查结果比较
Table 2. Statistical comparison of anti-aging factors between two groups
因素 选项 明显衰老 明显年轻 合计 U*值 P值 穿戴打扮 ①非常注重 42 106 148 33 499.50 < 0.001 ②一般 51 62 113 ③不注重 156 54 210 家庭情感 ①非常和谐 59 128 187 36 056.00 < 0.001 ②一般 150 38 188 ③不和谐,不够满意 40 56 96 饱食程度 ①饱足 52 53 105 28 946.50 0.295 ②中等 161 146 307 ③吃不饱 36 26 62 饮酒频率 ①从不喝酒 32 143 175 40 507.00 < 0.001 ②偶尔喝酒 168 26 194 ③经常喝酒 49 53 102 是否吸烟 ①不吸烟 212 196 408 28 554.50 0.294 ②偶尔吸烟 15 13 28 ③每天都吸烟 22 13 35 锻炼频率 ①每天都锻炼 48 82 130 24 717.00 0.033 ②每周都会运动 66 61 127 ③很少,几乎不锻炼 108 106 214 锻炼强度 ①以低强度为主 128 92 220 24 084.00 0.009 ②以中等强度为主 57 48 105 ③以高强度运动为主 64 82 146 锻炼时长(h) ① < 1 148 86 234 20 489.50 < 0.001 ②1~2 47 35 82 ③ > 2 54 101 155 饮茶情况 ①不饮茶 157 52 209 14 792.00 < 0.001 ②偶尔喝茶 58 66 124 ③经常喝茶 34 104 138 睡眠时长(h) ① < 2或失眠 28 11 39 24 248.00 0.016 ②2~4 19 22 41 ③4~6 100 71 171 ④6~8 77 93 170 ⑤ > 8 25 25 50 注:*Mann-Whitney U检验。 表 3 变量赋值表
Table 3. Variable assignment table
变量 赋值 衰老程度(Y) 0=明显年轻;1=明显衰老 穿戴打扮(X1) 1=非常注重;2=一般;3=不注重 饮酒频率(X2) 1=从不喝酒;2=偶尔喝酒;3=经常喝酒 饮茶习惯(X3) 1=不喝茶;2=偶尔喝茶;3=经常喝茶 睡眠时长(h, X4) 1=<2或失眠;2=2~4;3=4~6;4=6~8;5=≥8 锻炼频率(X5) 1=每天都锻炼;2=每周都会运动;3=很少,几乎不锻炼 锻炼强度(X6) 1=以低强度为主;2=以中等强度为主;3=以高强度运动为主 锻炼时长(h, X7) 1=<1;2=1~2;3=≥2 家庭情感(X8) 1=非常和谐;2=一般;3=不和谐,不够满意 表 4 logistic回归模型分析结果
Table 4. Logistic regression model analysis results
影响因素 β sx Wald χ2 P值 OR (95% CI)值 穿戴打扮 0.618 0.152 16.588 < 0.001 1.865(1.378~2.500) 饮酒频率 1.275 0.222 32.860 < 0.001 3.579(2.314~5.534) 饮茶习惯 -0.848 0.155 30.012 < 0.001 0.428(0.316~0.580) 睡眠时长 -0.343 0.123 7.823 0.005 0.710(0.558~0.902) 锻炼强度 -0.792 0.164 23.434 < 0.001 0.453(0.329~0.624) 锻炼时长 -0.835 0.170 24.230 < 0.001 0.434(0.311~0.605) 家庭情感 0.479 0.168 8.086 0.004 1.614(1.160~2.246) -
[1] 胡杰成. 我国人口老龄化现状、趋势与建议[J]. 中国经贸导刊, 2017, (12): 59-62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9777.2017.12.020.Hu JC. Current situation, trends and suggestions of population aging in china. [J]. Chin Econmic & Trude Heralol, 2017, (12): 59-62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9777.2017.12.020. [2] 黄河浪, 刘星, 李翔, 等. 人体衰老认识与测试指标(量表)构建的理论思维与方法[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(1): 85-88. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.01.019.Huang HL, Liu X, Li X, et al. Theoretical thinking and method of cognition of human aging and test index(scale) construction[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(1): 85-88. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.01.019. [3] Tudorache E, Fildan AP, Frandes M. Aging and extrapulmonary effects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2017, 12: 1281-1287. DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S145002. [4] Gennuso KP, Thraenborowski KM, Gangnon RE, et al. Patterns of sedentary behavior and physical function in older adults[J]. Aging Clin Exp Res, 2016, 28(5): 943-950. DOI: 10.1007/s40520-015-0386-4. [5] Seals DR, Edward F. Adolph Distinguished lecture: the remarkable anti-aging effects of aerobic exercise on systemic arteries[J]. J App Physiol, 2014, 117(3): 425-439. DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00362.2014. [6] 李翔, 林菲, 刘星等. 女性衰老度测量分值水平及分布特点与规律[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2018, 38(6): 1399-1402. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.06.051.Li X, Lin F, Liu X. Measurement of female aging score and its distribution characteristics and regularities[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2018, 38(6): 1399-1402. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.06.051. [7] 刘星, 曾妮, 叶兴, 等. 三维人体衰老量表检测城市社区男性衰老状态及其变化特点[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2018, 43(7): 94-99. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2018.07.014.Liu X, Zeng N, Ye X, et al. Evaluation of the aging status and distribution characteristics for male population by three-dimensional human aging scale[J]. J Cent South Univ(Med Sci), 2018, 43(7): 94-99. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2018.07.014. [8] 曾妮, 邓鹏飞, 林菲, 等. 我国健康人社会功能衰老测量量表构建研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2017, 21(4): 383-386. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.04.015.Zeng N, Deng PF, Lin F, et al. Study on the construction and evaluation of social function of aging measurement scale (SFAMS) in healthy Chinese[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2017, 21(4): 383-386. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.04.015. [9] 武姣, 罗艳虹, 郭兴萍, 等. 母亲孕早期患病对出生缺陷的随机效应Logistic模型分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2016, 20(2): 146-148. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.02.010.Wu J, Luo YH, Guo XP, et al. Analysis of the impact of the diseases during the pregnancy on birth defects with random effects Logistic model[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2016, 20(2): 146-148. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.02.010. [10] World Health Ornization. International classification of functioning, disability and health (ICF)[M]. Br J Gen Pract, 2008. [11] 朱凤梅, 苗子强. 老龄化背景下"医养结合"的内涵、现状及其困境[J]. 中国卫生经济, 2018, 37(3). DOI: 10.7664/CHE20180303.Zhu FM, Miao ZQ. Study on the conception, existing problem and dilemma of "the combination of medical-nursing and health care service" under the background of aging[J]. Chin Health Econ, 2018, 37(3). DOI: 10.7664/CHE20180303. [12] 童坦君, 张宗玉. 从分子水平看适度限食、适量运动对衰老进程的影响[J]. 老年医学与保健, 2010, 16(6): 321-322. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8296.2010-06-01.Tong TJ, Zhang ZY. Effects of moderate caloric restriction and exercise on the aging process at the molecular level[J]. Geriatr Health Care, 2010, 16(6): 321-322. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8296.2010-06-01. [13] 周璇, 胡炜华, 黄河浪. 南昌市社区老年人心理年龄与实际年龄差异比较及其原因分析[J]. 南昌大学学报(医学版), 2015, 55(4): 71-74. DOI: 10.13764/j.cnki.ncdm.2015.04.020.Zhou X, Hu WH, Huang HL, et al. Difference between psychological age and chronological age and its reasons in community elderly in nanchang[J]. J Nanchang Univ (Med Sci), 2015, 55(4): 71-74. DOI: 10.13764/j.cnki.ncdm.2015.04.020. [14] Wood AM, Kaptoge S, Butterworth AS, et al. Risk thresholds for alcohol consumption: combined analysis of individual-participant data for 599912 current drinkers in 83 prospective studies[J]. The Lancet, 2018, 391(10129): 1513-1523. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=13834c8f34f6a5acbcb89229becbe7e7 [15] 郑棒, 林丽玲, 余灿清, 等. 中国成年人睡眠时长、午睡与失眠症状的分布及关联研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(4): 452-456. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.04.008.Zheng B, Lin L L, Yu C Q, et al. Distributions and associations between duration of sleep, daytime naps and insomnia symptoms among Chinese adults[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(4): 452-456. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.04.008. [16] Cameron ID, Fairhall N, Langron C, et al. A multifactorial interdisciplinary intervention reduces frailty in older people: randomized trial[J]. BMC Med, 2013, 11: 65-74. DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-65. [17] Fei T, Fei J, Huang F, et al. The anti-aging and anti-oxidation effects of tea water extract in caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2017, 97: 89-96. DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.07.015. -





 下载:
下载: