Association between fasting glucose and branchial-ankle pulse wave velocity among hypertensive population in rural areas of Eastern China
-
摘要:
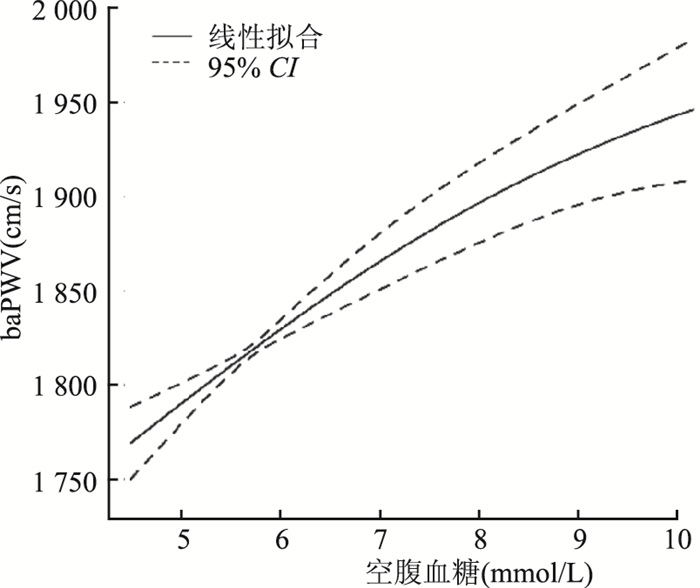
目的 探讨华东地区农村高血压人群空腹血糖水平与臂踝脉搏波传导速度(branchial-ankle pulse wave velocity,baPWV)的关联性。 方法 2013年7月~9月在连云港市的赣榆县和东海县、安庆市的枞阳和望江县开展关于高血压患者合并相关危险因素的横断面研究。以空腹血糖水平作为自变量,以baPWV作为因变量进行多元线性回归分析。 结果 本研究共纳入共3 894例高血压患者,其中血糖正常(normal fasting glucose,NFG)、空腹血糖受损(impaired fasting glucose,IFG)以及糖尿病(diabetes mellitus,DM)的人群分别占44.5%、43.0%和12.5%。分析显示,baPWV与空腹血糖水平存在关联,且空腹血糖水平每增加1 mmol/L,baPWV水平随之升高26.2 cm/s(95%CI:19.6~32.8,P < 0.001)。与NFG人群相比,IFG(β=50.4 cm/s,95%CI:28.4~72.3,P < 0.001)和DM(β=113.4 cm/s,95%CI:80.2~146.5,P < 0.001)人群baPWV水平均呈升高。另外,空腹血糖与baPWV水平在收缩压≥ 140 mmHg的人群中具有更强的关联(β=34.3 cm/s,95%CI:24.5~44.2,P < 0.001 vs.收缩压 < 140 mmHg;β=18.1 cm/s,95%CI:9.1~27.2,P < 0.001;交互P=0.027)。 结论 华东地区农村高血压人群中,空腹血糖水平与baPWV水平呈正相关。 Abstract:Objective To explore the relationship between fasting blood glucose and branchial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) levels among hypertensive population in rural areas of Eastern China. Methods A cross-sectional analysis were conducted among hypertensive population in Lianyungang and Anqing city from July to September 2013. Multivariable linear regression models were used to analyze the association of serum glucose and baPWV. Results A total of 3 894 hypertensive participants were included in the present study. The prevalence of normal fasting glucose (NFG), impaired fasting glucose (IFG) and diagnosed diabetes (DM) were 44.5%, 43.0%, and 12.5%, respectively. Each 1-mmol/L increase in fasting blood glucose levels was significantly associated with a 26.2 cm/s increase in baPWV levels (95% CI: 19.6-32.8, P < 0.001). Consistently, significantly higher baPWV levels were observed in participants with IFG (β=50.4 cm/s, 95% CI: 28.4-72.3, P < 0.001) and DM (β=113.4 cm/s, 95% CI: 80.2-146.5, P < 0.001) when compared to those with NFG. Furthermore, a stronger positive association between fasting blood glucose and baPWV was observed in participants with systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mmHg (β=34.3 cm/s, 95% CI: 24.5-44.2, P < 0.001; vs. < 140 mmHg; β=18.1 cm/s, 95% CI: 9.1-27.2, P < 0.001; Pinteraction=0.027). Conclusion There was a positive association between fasting blood glucose and baPWV levels among hypertensive population in rural areas of Eastern China. -
Key words:
- Serum glucose /
- pulse wave velocity /
- arterial stiffness
-
表 1 研究人群基本信息描述(x±s)
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of study participants(x±s)
变量 血糖(mmol/L) F/χ2值 P值 NFG IFG DM 年龄(岁) 64.6±7.7 65.6±7.3 65.9±7.1 10.154 < 0.001 男性[n(%)] 524(30.2) 485(29.0) 164(33.6) 3.845 0.146 BMI(kg/m2) 24.2±3.8 25.0±4.0 25.7±4.1 35.931 < 0.001 BaPWV(cm/s) 1 778.0±372.1 1 847.6±375.1 1 923.9±407.6 33.073 < 0.001 收缩压(mmHg) 141.4±18.5 142.2±18.0 143.7±19.4 2.991 0.050 舒张压(mmHg) 83.9±11.3 83.2±10.9 82.4±10.7 3.838 0.022 目前吸烟[n(%)] 320(18.5) 259(15.5) 86(17.7) 10.184 0.037 目前饮酒[n(%)] 281(16.6) 304(18.7) 86(18.1) 6.134 0.189 自述高脂血症史[n(%)] 30(1.7) 28(1.7) 12(2.5) 1.413 0.493 总胆固醇(mmol/L) 5.0±1.1 5.4±1.0 5.6±1.3 69.254 < 0.001 甘油三酯(mmol/L) 1.6±1.2 1.8±1.2 2.2±1.6 39.283 < 0.001 同型半胱氨酸(μmol/L) 13.8±7.2 13.9±7.0 14.9±9.4 4.210 0.015 叶酸(ng/mL) 12.3±4.5 13.1±4.9 13.2±4.4 2.824 0.060 肌酐(μmol/L) 67.2±27.1 66.2±18.2 66.7±21.3 0.735 0.479 服用降压药[n(%)] 1 294(74.71) 1 344(80.3) 396(81.1) 19.419 < 0.001 服用降脂药[n(%)] 25(1.4) 31(1.9) 7(1.4) 0.979 0.613 例数[n(%)] 1 733(44.5) 1 673(43.0) 488(12.5) 表 2 空腹血糖与baPWV的多元线性回归分析(x±s)
Table 2. Multiple linear regression analysis of fasting blood glucose and baPWV levels(x±s)
血糖(mmol/L) 例数 baPWV(cm/s) 粗模型 调整模型 OR (95% CI)值 P值 OR (95% CI)值 P值 连续性 3 894 1 826.2±381.1 31.2(23.7~38.6) < 0.001 26.2(19.6~32.8) < 0.001 临床切点 < 5.6 1 733 1 778.0±372.1 0.0 0.0 5.6~ 1 673 1 847.6±375.1 69.6(44.2~95.0) < 0.001 50.4(28.4~72.3) < 0.001 ≥7.0 488 1 923.9±407.6 145.9(108.0~183.9) < 0.001 113.4(80.2~146.5) < 0.001 趋势性检验 < 0.001 < 0.001 注: 调整变量为年龄、性别、BMI、吸烟、饮酒、研究中心、收缩压、总胆固醇、甘油三酯、同型半胱氨酸、肌酐、降压药。 表 3 空腹血糖与baPWV的分层回归分析(x±s)
Table 3. Multiple linear regression analysis of fasting blood glucose and baPWV levels in various subgroups(x±s)
变量 例数 baPWV (cm/s) OR(95% CI)值 交互P值 性别 0.958 男 1 173 1 828.3±393.8 24.7(12.9~36.5) 女 2 721 1 825.3±375.6 26.1(18.1~34.1) 年龄(岁) 0.533 < 65 1 907 1 679.3±314.2 27.8(19.1~36.4) ≥65 1 987 1 967.2±386.4 27.4(17.2~37.7) BMI(kg/m2) 0.775 < 24 1 713 1 877.7±392.3 24.2(13.3~35.1) 24~ 1 422 1 812.7±386.8 24.2(13.2~35.3) ≥28 742 1 733.3±320.2 24.7(12.7~36.7) 目前吸烟 0.980 否 3 217 1 829.3±373.3 26.4(19.1~33.7) 是 665 1 812.5±418.2 22.3(6.2~38.4) 收缩压(mmHg) 0.027 < 140 1 786 1 702.2±332.3 18.1(9.1~27.2) ≥140 2 067 1 933.2±387.8 34.3(24.4~44.2) 总胆固醇(mmol/L) 0.325 < 5.2 1 975 1 805.7±372.8 29.8(20.4~39.2) ≥5.2 1 918 1 847.3±388.6 23.4(14.2~32.5) 降压药 0.754 是 3 034 1 844.8±385.7 27.5(19.7~35.3) 否 809 1 759.3±356.3 22.7(10.7~34.6) 注: 调整变量为年龄、性别、BMI、吸烟、饮酒、研究中心、收缩压、总胆固醇、甘油三酯、同型半胱氨酸、肌酐、降压药。 -
[1] 陈伟伟, 高润霖, 刘力生, 等. 《中国心血管病报告2017》概要[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2018, (1): 1-8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2018.01.001.Chen WW, Gao RL, Liu LS, et al. Summary of China cardiovascular disease report 2017[J]. Chinese Circulation Journal, 2018, (1): 1-8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2018.01.001. [2] Cohn JN. Arterial stiffness, vascular disease, and risk of cardiovascular events[J]. Circulation, 2006, 113(5): 601-603. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.600866. [3] Verwoert GC, Franco OH, Hoeks AP, et al. Arterial stiffness and hypertension in a large population of untreated individuals: the Rotterdam Study[J]. J Hypertens, 2014, 32(8): 1606-1612. DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000237. [4] Munakata M. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity in the measurement of arterial stiffness: recent evidence and clinical applications[J]. Curr Hypertens Rev, 2014, 10(1): 49-57. doi: 10.2174/157340211001141111160957 [5] Pan XR, Yang WY, Li GW, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and its risk factors in China, 1994. National Diabetes Prevention and Control Cooperative Group[J]. Diabetes Care, 1997, 20(11): 1664-1669. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.11.1664 [6] Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China[J]. N Engl J Med, 2010, 362(12): 1090-1101. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0908292. [7] Xu Y, Wang L, He J, et al. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults[J]. JAMA, 2013, 310(9): 948-959. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2013.168118. [8] American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetes Care, 2008, 31: S55-60. DOI: 10.2337/dc08-S055. [9] Slezák D, Mayer O, Bruthans J, et al. The prognostic importance of impaired fasting glycemia in chronic coronary heart disease patients[J]. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes, 2018. DOI: 10.1055/a-0684-9601. [10] 陈忠龙, 戴龙, 张金华, 等. 厦门市2002-2009年糖尿病死亡趋势及寿命损失年分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2011, 15(11): 935-938. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201111005Chen ZL, Dai L, Zhang JH, et al. Analysis on the trend of mortality and years of life lost of diabetes mellitus in Xiamen City, Fujian Province from 2002 to 2009[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2011, 15(11): 935-938. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201111005 [11] 方志峰, 朱婷, 刘展华, 等. 2010-2012年广西5市县≥ 18岁城乡居民心血管疾病危险因素及聚集状况分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2017, 21(1): 80-83. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.01.019.Fang ZF, Zhu T, Liu ZH, et al. Clustering status and risk factors analysis of cardiovascular disease among residents aged 18 and above from five cities and counties in Guangxi Province[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2017, 21(1): 80-83. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.01.019. [12] Ando T, Okada S, Niijima Y, et al. Impaired glucose tolerance, but not impaired fasting glucose, is a risk factor for early-stage atherosclerosiss[J]. Diabet Med, 2010, 27(12): 1430-1435. DOI: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03144.x. [13] Li CH, Wu JS, Yang YC, et al. Increased arterial stiffness in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and newly diagnosed diabetes but not isolated impaired fasting glucose[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 97(4): E658-E662. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2011-2595. [14] Liu ZK, Wu KY, Dai XT, et al. Grading effect of abnormal glucose status on arterial stiffness and a new threshold of 2-h post-load glucose based on a Chinese community study[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2018, 9(3): 616-622. DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12741. [15] Mazzone T, Chait A, Plutzky J. Cardiovascular disease risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus: insights from mechanistic studies[J]. Lancet, 2008, 371(9626): 1800-1809. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60768-0. [16] Fiorentino TV, Prioletta A, Zuo P, et al. Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and its role in diabetes mellitus related cardiovascular diseases[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2013, 19(32): 5695-5703. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319320005 [17] 李震花, 张涛, 葛志明. 高血糖加速动脉粥样硬化的分子生物学机制[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2006, 14(7): 633-635. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3949.2006.07.024.Li ZH, Zhang T, Ge ZM. Molecular mechanisms of hyperglycemia in the acceleration of atherosclerosis[J]. Chin J arterioscler, 2006, 14(7): 633-635. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3949.2006.07.024. [18] Chen G, McAlister FA, Walker RL, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes in framingham participants with diabetes: the importance of blood pressure[J]. Hypertension, 2011, 57(5): 891-897. DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.162446. [19] de Oliveira Alvim R, Santos PCJL, Musso MM, et al. Impact of diabetes mellitus on arterial stiffness in a representative sample of an urban Brazilian population[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2013, 5(1): 45. DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-45. [20] Tedesco MA, Natale F, Di Salvo G, et al. Effects of coexisting hypertension and type Ⅱ diabetes mellitus on arterial stiffness[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2004, 18(7): 469-473. DOI: 10.1038/sj.jhh.1001690. -





 下载:
下载: