Application of ARIMA model and BP neural network model in prediction of tuberculosis incidence in Gansu Province
-
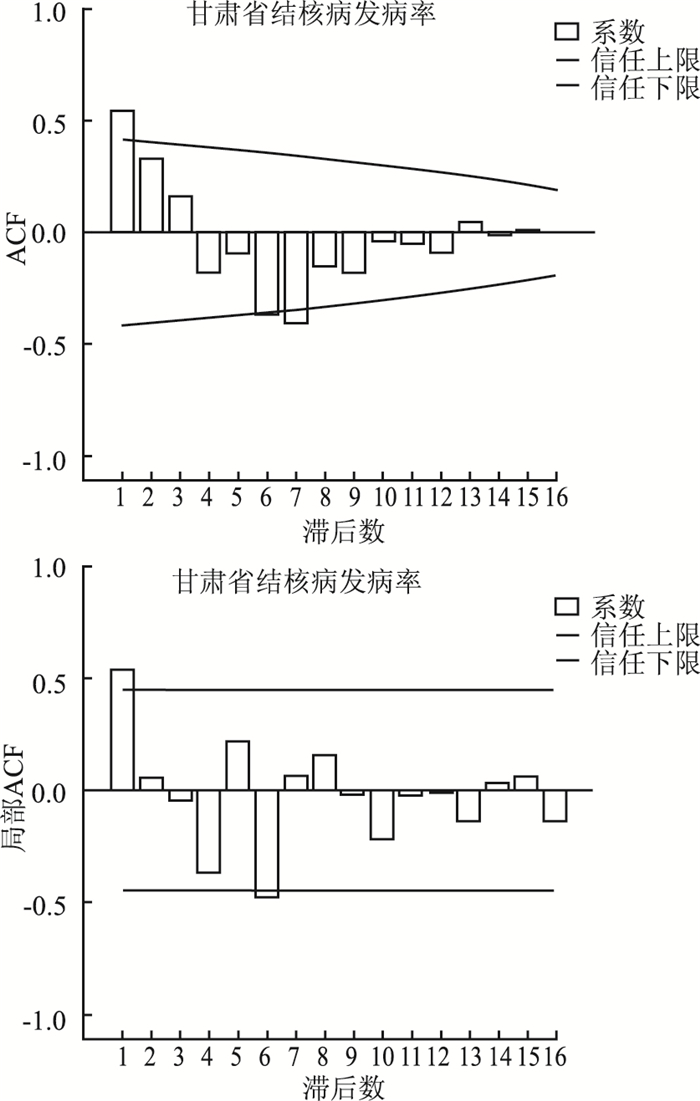
摘要:
目的 探讨自回归滑动平均混合模型(autoregressive integrated moving average,ARIMA)与误差逆传播((back propagation,BP)神经网络模型在甘肃省结核病发病率预测中的预测效果,选取合适的模型预测发病趋势。 方法 以甘肃省1997-2017年结核病数据为基础,建立ARIMA时间序列模型和BP神经网络模型分别预测2018-2019年的发病率,并比较两种模型的预测精度和建模效果。 结果 对于甘肃省2018年和2019年结核病发病率,ARIMA时间序列模型预测结果为55.1075,54.5373,MSE=92.24,MAE=7.5313,MAPE=9.26%;BP神经网络模型预测结果为62.0132,73.4460,MSE=9.6575,MAE=1.1449,MAPE=1.68%。 结论 BP神经网络模型对甘肃省结核病发病率的预测效果更佳,预测得2018-2019年甘肃省结核病发病率将呈小幅上升趋势。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the predictive effect of autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model and back propagation neural network (BPNN)in the prediction of tuberculosis incidence in Gansu Province, and to select appropriate models to predict the incidence. Methods Based on the data of tuberculosis in Gansu Province from 1997 to 2017, the ARIMA time series model and BP neural network model were established to predict the incidence from 2018 to 2019, and the prediction accuracy and modeling effect of the two models were compared. Results For the incidence of tuberculosis in Gansu Province in 2018 and 2019, the ARIMA model predicted results were 55.1075, 54.5373, MSE=92.24, MAE=7.5313, MAPE=9.26%; BP neural network model predicted results were 62.0132, 73.4460, MSE=9.6575, MAE=1.1449, MAPE=1.68%. Conclusions The BP neural network model has a better predictive effect on the incidence of tuberculosis in Gansu Province, and it shows that the incidence of tuberculosis in Gansu Province will increase slightly from 2018 to 2019. -
Key words:
- Tuberculosis /
- ARIMA time series /
- BP neural network /
- prediction
-
表 1 ARIMA及BP神经网络拟合及预测结果
Table 1. Fitting and forecasting results of ARIMA and BP neural network models
时间(年) 观测值 ARIMA 拟合值 1997 56.807 8 1998 60.011 0 56.807 8 1999 56.973 6 61.673 7 2000 53.742 9 55.396 9 2001 52.359 0 52.065 9 2002 52.885 3 51.640 6 65.583 3 2003 69.943 5 53.158 5 70.145 7 2004 76.258 4 78.798 2 76.320 0 2005 89.835 8 79.536 4 89.841 9 2006 108.226 5 96.883 6 108.047 0 2007 119.174 2 117.772 9 115.078 5 2008 128.287 6 124.857 0 128.200 9 2009 111.216 1 133.018 2 111.194 1 2010 90.640 6 102.354 5 90.641 6 2011 88.089 2 79.960 1 88.062 6 2012 75.696 4 86.764 8 73.902 2 2013 69.255 7 69.263 5 69.271 8 2014 64.449 4 65.912 4 64.527 5 2015 54.917 8 61.954 5 54.983 9 2016 58.322 2 49.970 1 62.322 9 2017 56.206 0 60.089 4 57.650 7 2018 55.107 5 62.013 2 2019 54.537 3 73.446 0 表 2 ARIMA时间序列模型与BP神经网络模型预测误差
Table 2. Forecasting errors of ARIMA model and BP neural network model
模型 MSE MAE MAPE(%) ARIMA时间序列 75.5507 6.5175 8.27 BP神经网络 9.6575 1.1449 1.68 -
[1] 马永成, 王兆芬, 李斌, 等. 基于GIS的青海省结核病时空分布特征研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(4): 340-344, 353. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.04.005.Ma YC, Wang ZF, Li B, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of tuberculosis in qinghai province based on GIS[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(4): 340-344, 353. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.04.005. [2] Fogel N. Tuberculosis: A disease without boundaries[J]. Tuberculosis (Edinb), 2015, 95(5): 527-531. DOI:5 10.1016/j.tube.2015.05.017. [3] 王黎霞, 成诗明, 陈明亭, 等. 2010年全国第五次结核病流行病学抽样调查报告[J]. 中国防痨杂志, 2012, 34(8): 485-508. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFLZ201208002.htmWang LX, Cheng SM, Chen MT, et al. The fifth national tuberculosis epidemiological survey in 2010[J]. Chin J Antituberc, 2012, 34(8): 485-508. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFLZ201208002.htm [4] 漆莉, 李革, 李勤. ARIMA模型在流行性感冒预测中的应用[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2007, 29(3): 267-269. DOI: 10.16016/j.1000-5404.2007.03.031.Qi L, Li G, Li Q. Application of ARIMA model on predictive incidence of influenza[J]. Journal of the Third Military Medical University, 2007, 29(3): 267-269. DOI: 10.16016/j.1000-5404.2007.03.031. [5] 胡碧波, 傅克本, 许亮亮, 等. 应用ARIMA模型预测结核病发病率研究[J]. 预防医学, 2018, 30(10): 1011-1015. DOI: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2018.10.009.Hu BB, Fu KB, Xu LL, et al. Prediction of tuberculosis incidence by ARIMA model[J]. Prev Med, 2018, 30(10): 1011-1015. DOI: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2018.10.009. [6] 张彦琦, 唐贵立, 王文昌, 等. ARIMA模型及其在肺结核预测中的应用[J]. 现代预防医学, 2008, 35(9): 1608-1610, 1615. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8507.2008.09.004.Zhang YQ, Tang GL, Wang WC, et al. Application of ARIMA model in tuberculosis prediction[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2008, 35(9): 1608-1610, 1615. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8507.2008.09.004. [7] 陈莉. 探讨ARIMA模型在细菌性痢疾发病预测中的应用[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2011, 28(4): 417-419. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3674.2011.04.021.Chen L. Exploration of the application of ARIMA model in the prediction of bacterial dysentery[J]. Chin J Heal Statist, 2011, 28(4): 417-419. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3674.2011.04.021. [8] 沈波, 王李仁, 陈艳, 等. 中低强度噪声致高频听力损伤的BP神经网络模型研究[J]. 预防医学论坛, 2008, 14(12): 1088-1090. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9153.2008.12.011.Shen B, Wang LR, Chen Y, et al. Study of the model of BP neural network of high frequency hearing loss by low-middle dose noise[J]. Prev Med Trib, 2008, 14(12): 1088-1090. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9153.2008.12.011. [9] 徐学琴, 孙宁, 徐玉芳. 基于BP神经网络的河南省甲乙类法定报告传染病预测研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2014, 18(6): 561-563. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201406023Xu XQ, Sun N, Xu YF. Prediction of the notifiable infectious diseases in henan province based on BP neural network[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2014, 18(6): 561-563. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201406023 [10] 陈婷. ARIMA模型和BP神经网络模型在艾滋病发病率预测应用中的比较研究[D]. 南宁: 广西医科大学, 2015.Chen T. A comparative study on the application of ARIMA model and BP neural network model in the prediction of AIDS incidence[D]. Nanning: Guangxi medical university, 2015. [11] 刘天, 姚梦雷, 黄继贵, 等. 组合预测模型在丙型病毒性肝炎发病率预测中的应用[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2018, 24(6), 674-679. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201806015.htmLiu T, Yao ML, Huang JG, et al. Application of combined prediction model in the prediction of incidence of viral hepatitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccine and Immunization, 2018, 24(6), 674-679. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201806015.htm [12] 王巧智, 龚德华. 结核病疫情现状和控制策略[J]. 实用预防医学, 2017, 24(3): 257-259, 351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYY201703001.htmWang QZ, Gong DH. Current situation and control strategy of tuberculosis[J]. Prac Prev Med, 2017, 24(3): 257-259, 351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYY201703001.htm [13] 王晨, 郭倩, 周罗晶. 基于R语言的ARIMA模型对流感样病例发病趋势的预测[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(9): 957-960. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.020.Wang C, Guo Q, Zhou LJ. ARIMA model based on R language to predict the incidence of influenza-like cases[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(9): 957-960. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.020. [14] 李家琦, 王雷, 宋媛媛, 等. ARIMA模型在湖北省肺结核发病数预测中的应用[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学, 2018, 29(5): 37-40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2018.05.010.Li JQ, Wang L, Song YY, et al. Application of ARIMA model in the prediction of pulmonary tuberculosis incidence in Hubei province[J]. J of Pub Health and Prev Med, 2018, 29(5): 37-40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2018.05.010. [15] 王雅文, 沈忠周, 严宝湖, 等. ARIMA模型和ARIMA-GRNN模型在AIDS发病预测中的应用[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(12): 1287-1290. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.020.Wang YW, Shen ZZ, Yan BH, et al. Application of ARIMA model and ARIMA-GRNN model in the prediction of AIDS[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2008, 22(12): 1287-1290. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.020. [16] 卢洪洲. 艾滋病合并结核病研究进展[C]. //全国第九次中西医结合传染病学术会议暨深圳市医学会肝病专业委员会2018年学术年会, 深圳, 2018: 170-181.Lu HZ. Progress in AIDS combined with tuberculosis research[C]. //The 9th national conference on infectious diseases of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine and the 2018 academic annual meeting of liver disease committee of Shenzhen medical association, Shenzhen, 2018: 170-181. [17] 徐继承, 李磊, 刘桂红, 等. 人工神经网络建立食管癌发病预测模型的比较研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2011, 38(17): 3408-3410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF201117005.htmXu JC, Li L, Liu GH, et al. A comparative study on the prediction model of esophageal cancer using artificial neural network[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2011, 38(17): 3408-3410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF201117005.htm [18] 刘振球, 严琼, 左佳鹭, 等. EMD-BP神经网络在传染病发病趋势和预测研究中的应用[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2018, 35(1): 152-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201801045.htmLiu ZQ, Yan Q, Zuo JL, et al. The application of EMD-BP neural network in the research on the incidence trend and prediction of infectious diseases[J]. Chin J Heal Statist, 2018, 35(1): 152-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201801045.htm -





 下载:
下载: