Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of NSCLP in Gansu Province from 2010 to 2016
-
摘要:
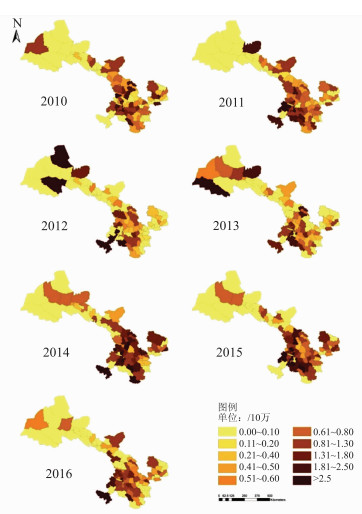
目的 探讨甘肃省2010-2016年出生的非综合征性唇腭裂(non-syndromic cleft lip with or without palate,NSCLP)的时空分布特征并建立预测模型,为甘肃省NSCLP的防控工作提供依据。 方法 采用空间流行病学研究方法及地理信息系统(geographic information system,GIS)进行专题制图、空间自相关分析、高/低聚类分析、热点分析和克里金(Kirging)插值预测。 结果 甘肃省2010-2016年各年度89个县区NSCLP发病率聚集趋势为东南高、西北低;2010-2016年甘肃省NSCLP累积发病率的空间分布呈现空间正相关(Moran’I=0.274,Z=7.814,P < 0.001),且聚集类型为高聚类(Getis Gi=0.000 003,Z=4.381,P < 0.001),存在22个发病热点县区。Kirging插值预测结果显示NSCLP主要流行趋势由甘肃的陇东往陇西、陇南方向延伸。 结论 甘肃省2010-2016年NSCLP地理分布呈现空间正相关,主要聚集类型为高-高聚集,高聚集区集中在甘肃陇东、陇西和陇南区域,需要重点防控。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of non-syndromic cleft lip with or without palate (NSCLP) who born in Gansu Province from 2010 to 2016, and to establish a predictive model for developing the strategies for the prevention and control of NSCLP. Methods Spatial epidemiological research method and geographical information systems (GIS) were used to conduct thematic mapping, spatial correlation analysis, high/low clustering analysis, hotspot analysis and Kirging interpolation prediction for NSCLP patients in Gansu Province from 2010 to 2016. Results From 2010 to 2016, the aggregation trend of NSCLP incidence in 89 counties in Gansu Province was different obviously, the southeast area was high and the northwest was low. Based on the data of the cumulative incidence of NSCLP from 2010 to 2016 in Gansu, the spatial distribution of NSCLP presented positive spatial correlation (Moran'I=0.274, Z=7.814, P < 0.001) and the aggregation type was high-high cluster(Getis Gi=0.000 003, Z=4.381, P < 0.001), with 22 hot spots. The Kirging interpolation prediction results showed that the main prevalence trend of NSCLP in Gansu extended from Longdong to Longxi and Longnan areas. Conclusions The geographical distribution of NSCLP had a positive spatial correlation and a high-high aggregation type in Gansu from 2010 to 2016. The high aggregation area is concentrated in Longdong, Longxi and Longnan of Gansu, which suggest that it is essential to focus on prevention and control in these areas. -
Key words:
- NSCLP /
- GIS /
- Space-time clustering
-
表 1 2010-2016年甘肃省NSCLP全局空间自相关分析
Table 1. Global spatial autocorrelation analysis of NSCLP in Gansu Province from 2010 to 2016
年份 Moran’ I Z值 P值 聚集 2010 0.040 1.398 0.162 否 2011 0.159 4.886 < 0.001 是 2012 0.051 1.813 0.070 否 2013 0.022 1.238 0.216 否 2014 0.125 3.742 < 0.001 是 2015 0.166 4.915 < 0.001 是 2016 0.106 3.422 < 0.001 是 7年累积 0.274 7.814 < 0.001 是 表 2 2010-2016年甘肃省NSCLP空间自相关分析产生的热点区域
Table 2. Hot spots generated by autocorrelation analysis of NSCLP space in Gansu Province from 2010 to 2016
年份 高-高聚集的热点县区 2010 广河县、合作市、康乐县、临潭县、永靖县 2011 迭部县、广河县、合作市、和政县、康乐县、临潭县、夏河县、舟曲县、漳县 2012 迭部县、碌曲县、玛曲县 2013 无高-高聚集的热点县区 2014 东乡县、广河县、积石山县、康乐县、临潭县、永靖县、榆中县、卓尼县 2015 迭部县、宕昌县、东乡县、皋兰县、和政县、康乐县、临洮县、临夏市、临夏县、岷县、夏河县、卓尼县、漳县 2016 定西市安定区、东乡县、积石山县、康乐县、临洮县、夏河县、永靖县、漳县 -
[1] 徐晨, 吕燕, 杨育生. 非综合征型唇腭裂易感基因的研究进展[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志, 2012, 22(1): 68-72. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4979.2012.01.018Xu C, Lv Y, Yang YS. Recent advances on susceptible gene loci involved in nonsyndromic cleft lip and/or palate[J]. Chin J Oral Maxillofacial Surg, 2012, 22(1): 68-72. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4979.2012.01.018 [2] 代维斯, 仇杰, 吴菊, 等. 甘肃省出生缺陷发病趋势分析[J]. 卫生职业教育, 2015, 33(13): 118-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYX201513063.htmDai WS, Qiu J, Wu J, et al. Analysis of the incidence of birth defects in Gansu Province[J]. Health Vocational Education, 2015, 33(13): 118-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYX201513063.htm [3] 静广平, 焦晓辉. 家族性非综合征性唇裂伴或不伴腭裂的基因研究[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2004, 20(2): 216-218. DOI: 10.13701/j.cnki.kqyxyj.2004.02.046.Jing GP, Jiao XH. Gene study of familial non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. [J]. Journal of Oral Science Research, 2004, 20(2): 216-218. DOI: 10.13701/j.cnki.kqyxyj.2004.02.046. [4] Carinci F, Scapoli L, Palmieri A, et al. Human genetic factors in nonsyndromic cleft lip and palate: an update[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2007, 71(10): 1509-1519. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.06.007. [5] 潘永初, 周连, 马兰, 等. 非综合征型唇腭裂发病危险因素的病例对照研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2015, 35(12): 1060-1063. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4020.2018.08.09.Pan YC, Zhou L, Ma L, et al. Case-control study on risk factors of non-syndromic cleft lip and palate[J]. Stomatol, 2015, 35(12): 1060-1063. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4020.2018.08.09. [6] Martelli DR, Coletta RD, Oliveira EA, et al. Association between maternal smoking, gender, and cleft lip and palate[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 81(5): 514-519. DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2015.07.011. [7] 刘维量, 寇增强, 陈宝立, 等. 山东省2014-2016年布鲁氏菌病空间分布特征和空间自相关分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(9): 897-900. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.007.Liu WL, Kou ZQ, Chen BL, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and spatial autocorrelation analysis of brucellosis in Shandong Province from 2014 to 2016[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(9): 897-900. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.007. [8] 魏娜娜, 鲍俊哲, 宇传华, 等. 中国卫生总费用空间分布特征与趋势分析[J]. 中国卫生资源, 2016, 19(1): 47-51. DOI: 10.13688/j.cnki.chr.2016.15198.Wei NN, Bao JZ, Yu CH, et al. Analysis on the spatial distribution characteristics on total expenditure on health and its tendency in China. [J]. Chinese Health Resources, 2016, 19(1): 47-51. DOI: 10.13688/j.cnki.chr.2016.15198. [9] Getis A, Ord JK. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics[J]. Geographical Analysis, 1992, 24(3): 189-206. DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-4632.1992.tb00261.x. [10] Oliver MA, Webster R. Kriging: a method of interpolation for geographical information systems. [J] Int J Geogr Info Sci, 1990, 4(3): 313-332. DOI: 10.1080/02693799008941549. [11] 马永成, 王兆芬, 李斌, 等. 基于GIS的青海省结核病时空分布特征研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(4): 340-344, 353. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.04.005.Ma YC, Wang ZF, Li B, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of tuberculosis in Qinghai Province based on GIS[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(4): 340-344, 353. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.04.005. [12] 刘勇, 刘静, 翟文济, 等. 2008-2011年山东省肾综合征出血热流行状况及其防治对策[J]. 预防医学论坛, 2012, 18(2): 107-109. DOI: 10.16406/j.pmt.issn.1672-9153.2012.02.016.Liu Y, Liu J, Zhai WJ, et al. The prevalence of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and countermeasures in Shandong Province, 2008-2011[J]. Prev Med Trib, 2012, 18(2): 107-109. DOI: 10.16406/j.pmt.issn.1672-9153.2012.02.016. [13] Liao Y, Zhang Y, He L, et al. Temporal and spatial analysis of neural tube defects and detection of geographical factors in Shanxi Province, China. [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e150332. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150332. [14] Tollefson TT, Shaye D, Durbin-Johnson B, et al. Cleft lip-cleft palate in Zimbabwe: estimating the distribution of the surgical burden of disease using geographic information systems[J]. The Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(Suppl 1): S1-S14. DOI: 10.1002/lary.24747. -





 下载:
下载: