Study on the relationship between meteorological factors and the number of hypertension outpatients based on CNN-LSTM
-
摘要:
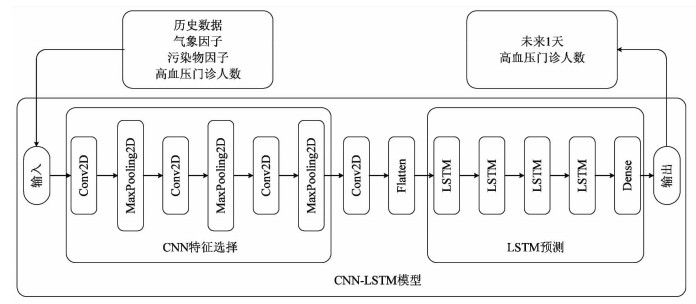
目的 探讨甘肃省不同地区气象因素对高血压门诊人数的影响,并对高血压门诊人数的变化趋势进行预测分析,从而为高血压疾病的预防和控制提供参考依据。 方法 在控制了高血压门诊相关特征因素的基础上,利用Python编程语言对白银、成县、庆城和凉州四个地区的高血压门诊人数建立卷积神经网络(convolutional neural networks,CNN)和长短期记忆神经网络(long short-term memory,LSTM)混合模型(CNN-LSTM)。 结果 CNN-LSTM模型对甘肃四个地区预测的高血压门诊人数的均方根误差分别为6.330 9、6.814 2、6.393 6和6.867 6,平均绝对百分比误差分别为74.082 2、78.508 2、56.618 3、50.235 4,平均绝对误差分别为4.875 7、5.431 1、4.542 0和6.460 8,结果均优于支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)、整合移动平均自回归模型(autoregressive integrated moving average model,ARIMA)、随机森林(random forest,RF)、CNN和LSTM。 结论 CNN-LSTM模型可以对甘肃四个地区高血压门诊人数进行较准确的短期预测,医院可以根据不同时间高血压就医需求合理配置医疗资源。 -
关键词:
- 高血压 /
- 气象要素 /
- 空气污染物 /
- 时间序列分析 /
- CNN-LSTM模型
Abstract:Objective To study the effect of meteorological factors on the number of hypertension outpatients in four areas of Gansu Province, then predict and analyze the trend of the number of hypertension outpatients, so as to provide reference for the prevention and control of hypertension diseases. Methods On the basis of controlling the confounding factors such as long-term trends, date effects, meteorological information and contaminant influence, a mixed model of convolutional neural network (CNN) and long-short term memory (LSTM) was constructed for the number of hypertension outpatients in the four regions of Baiyin, Chengxian, Qingcheng and Liangzhou by Python programming language. Results The root mean square errors of the CNN-LSTM model for the number of hypertensive outpatients in the four regions was 6.330 9, 6.814 2, 6.393 6 and 6.867 6. The mean absolute percentage error was 74.082 2, 78.508 2, 56.618 3 and 50.235 4. And the average absolute errors was 4.875 7, 5.431 1, 4.542 0 and 6.460 8. All the results was superior to those of support vector machine (SVM), autoregressive integrated moving average model (ARIMA), random forest (RF), CNN and LSTM. Conclusion The CNN-LSTM model can accurately predict the number of hypertension outpatients in Gansu. The hospital can rationally allocate medical resources according to the needs of hypertension for medical treatment at different times. -
Key words:
- Hypertension /
- Meteorological elements /
- Air pollutants /
- Time series analysis /
- CNN-LSTM
-
表 1 四种模型在甘肃四地区数据集上的预测性能比较
Table 1. Comparison of prediction performance of four models on datasets in four regions of Gansu
地区 模型 RMSE MAPE MAE 白银 SVM 13.070 4 93.114 9 12.628 9 ARIMA 8.361 1 90.396 1 5.671 5 RF 8.095 4 82.423 6 6.042 9 CNN 7.426 9 77.546 9 5.375 6 LSTM 6.347 5 74.276 5 5.112 9 CNN-LSTM 6.330 9 74.082 2 4.875 7 成县 SVM 16.132 8 95.602 8 14.067 5 ARIMA 14.342 1 86.769 2 10.883 0 RF 10.370 4 84.720 1 7.083 3 CNN 7.932 8 80.806 3 5.988 0 LSTM 7.834 8 80.266 8 5.695 4 CNN-LSTM 6.814 2 78.508 2 5.431 1 庆城 SVM 13.199 9 95.874 5 11.764 5 ARIMA 8.060 5 82.971 6 6.040 3 RF 7.497 8 77.840 4 6.065 7 CNN 7.490 6 76.695 6 5.007 7 LSTM 6.410 4 65.635 5 4.763 0 CNN-LSTM 6.393 6 56.618 3 4.542 0 凉州 SVM 16.242 9 71.635 0 16.734 5 ARIMA 13.771 0 67.389 3 10.454 4 RF 8.881 3 63.637 1 6.087 6 CNN 7.986 9 60.423 5 7.123 2 LSTM 7.888 3 57.702 3 6.775 1 CNN-LSTM 6.867 6 50.235 4 6.460 8 -
[1] Wright JT, Williamson JD, Whelton PK, et al. A randomized trial of intensive versus standard blood-pressure control[J]. N Engl J Med, 2016, 42(8): e141-e143. DOI: 10.1016/j.semerg.2015.12.009. [2] Liu B, Wu J, Zhang J, et al. Characterization and source apportionment of PM 2.5, based on error estimation from EPA PMF 5.0 model at a medium city in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 222: 10-22. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.005. [3] 周璐, 仝爽, 张慧, 等. 我国寒地与非寒地地区高血压影响因素的系统综述与Meta分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(3): 287-292, 297. DOI:10.16462/j.cnki. zhjbkz.2018.03.017.Zhou L, Tong S, Zhang H, et al. Factors of hypertension in cold and non-cold area of China: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(3): 287-292, 297. DOI:10.16462/j.cnki. zhjbkz.2018.03.017. [4] 闵晶晶, 丁德平, 李津, 等. 北京急性脑血管疾病与气象要素的关系及预测[J]. 气象, 2014, 40(1): 108-113. DOI: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2014.01.013.Min JJ, Ding DP, Li J, et al. Relationship between acute cerebrovascular disease and meteorological factors in Beijing and its forecast[J]. Meteor Mon, 2014, 40(1): 108-113. DOI: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2014.01.013. [5] 魏俊妮, 薛淑莲, 路殿英, 等. 高血压日入院人数与空气污染物浓度相关性研究[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2018, 19(2): 101-105. DOI: 10.16506/j.1009-6639.2018.02.005.Wei JN, Xue SL, Lu DY, et al. Association between daily admission of patients with hypertension and air pollutants[J]. Chin Prev Med, 2018, 19(2): 101-105. DOI: 10.16506/j.1009-6639.2018.02.005. [6] Blanes-Vidal V, Cantuaria M L, Nadimi E S. A novel approach for exposure assessment in air pollution epidemiological studies using neuro-fuzzy inference systems: Comparison of exposure estimates and exposure-health associations[J]. Environmental Research, 2017, 154: 196-203. DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2016.12.028. [7] 陈杰, 孙耕耘. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病频繁加重的多因素分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(3): 341-344. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.03.020.Chen J, Sun GY. Analysis of the indicators of frequent exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(3): 341-344. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.03.020. [8] 丁亚萍, 虞明星, 郝海燕, 等. 石家庄市空气PM2.5浓度与儿童呼吸系统疾病门诊量的关系[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(7): 672-676. DOI:10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz, 2018.07.005.Ding YP, Yu MX, Hao HY, et al. The relationship between fine particulate matter and hospital outpatients with pediatric respiratory diseases in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(7): 672-676. DOI:10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz, 2018.07.005. [9] Zhai G, Chai G, Zhang H. Study on the medical meteorological forecast of the number of hypertension inpatient based on SVR[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2017, 69: 012059. DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/69/1/012059. [10] 任君, 王建华, 王传美, 等. 基于正则化LSTM模型的股票指数预测[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2018, 35(4), 44-48, 108. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2018.04.008.Ren J, Wang JH, Wang CM, et al. Stock index forecast based on regularized LSTM model[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2018, 35(4), 44-48, 108. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2018.04.008. [11] 宋俊萱. 浅谈白银市生态环境现状与保护对策[J]. 环境研究与监测, 2016, 29(4): 62-65.Song JX. The present situation and protection countermeasures of ecological environment in Baiyin[J]. Environ Stud Monitor, 2016, 29(4): 62-65. [12] 哈文舸, 台会选. 成县暴雨山洪泥石流灾害的成因分析与对策[J]. 水利规划与设计, 2016(7): 32-34. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2469.2016.07.012.Ha WG, Tai HX. Analysis of the causes and countermeasures of the storm and flood disasters in Cheng County[J]. Water Resour Plan Dsign, 2016(7): 32-34. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2469.2016.07.012. [13] 张天锋. 庆阳县经济发展中主要气候要素分析[J]. 甘肃农业, 2002(8): 50-51. DOI: 10.15979/j.cnki.cn62-1104/f.2002.08.026.Zhang TF. Analysis of main climate factors in economic development of Qingyang county[J]. Gansu Agr, 2002(8): 50-51. DOI: 10.15979/j.cnki.cn62-1104/f.2002.08.026. [14] 袁祥, 张小燕, 郭威, 等. 甘肃省武威市凉州区病媒生物监测分析[J]. 疾病预防控制通报, 2018, 33(2): 15-17. DOI: 10.13215/j.cnki.jbyfkztb.1712011.Yuan X, Zhang XY, Guo W, et al. Analysis of vectors surveillance in Liangzhou district, Wuwei city[J]. Endemic Dis Bull, 2018, 33(2): 15-17. DOI: 10.13215/j.cnki.jbyfkztb.1712011. [15] 张文增, 甄国新, 陈东妮, 等. 北京市顺义区大气污染物对呼吸系统疾病门诊量的影响[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2017, 34(2): 275-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201702026.htmZhang WZ, Zhen GX, Chen DN, et al. Influence of atmospheric pollutants on the outpatient volume of respiratory diseases in Shunyi District, Beijing[J]. Chinese J Health Stats, 2017, 34(2): 275-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201702026.htm [16] 陆继翔, 张琪培, 杨志宏, 等. 基于CNN-LSTM混合神经网络模型的短期负荷预测方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43(8): 131-137. DOI: 10.7500/AEPS20181012004.Lu JX, Zhang QP, Yang ZH, et al. Short-term load forecasting method based on hybrid CNN-LSTM neural network model[J]. Automat Electron Power Sys, 2019, 43(8): 131-137. DOI: 10.7500/AEPS20181012004. [17] 厍向阳, 王邵鹏. 基于卷积-LSTM网络的广告点击率预测模型研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(2): 193-197. DOI: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1806-0044.She XY, Wang SP. Research on advertising click through rate prediction model based on CNN-LSTM network[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2019, 55(2): 193-197. DOI: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1806-0044. [18] 翁俊, 韦性富, 聂永红, 等. 颗粒物污染对高血压门急诊就诊人数的影响-时间序列研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(7): 2751-2757. DOI: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2018.0288.Weng J, Wei XF, Nie YH, et al. Time series study on the effect of air particulate pollution on emergency admissions for hypertension[J]. China Environ Sci, 2018, 38(7): 2751-2757. DOI: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2018.0288. [19] 吴玉攀, 韦柳意, 王双, 等. 武冈市农村地区心脑血管住院病例的时间序列预测分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(2): 223-227. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.02.020.Wu YF, Wei LY, Wang S, et al. A time-series prediction and analysis on rural inpatient with cardio-cerebrovascular disease in Wugang[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(2): 223-227. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.02.020. -





 下载:
下载: