Path analysis of the relationships among health knowledge of chronic diseases, lifestyle and utilization of workplace health services of teachers in a district of Beijing
-
摘要:
目的 了解北京市某区教师健康知识、行为生活方式、工作场所健康服务利用情况对慢性病的影响路径。 方法 采用自行设计问卷进行调查, 通过通径方法进行数据分析。 结果 该地区教师慢性病患病率为51.5%, 排名前三位的疾病分别是腰或脊椎疾病(19.0%)、高血压(12.5%)和胃肠炎(11.1%)。调查对象随着年龄增长超重肥胖率逐渐升高, 且男性教师超重肥胖率高于女性, 差异有统计学意义(χ2=119.313, P < 0.001)。超重肥胖、健康相关知识和工作场所健康服务利用对慢性病产生直接作用。健康生活行为与方式以超重肥胖为中间变量对慢性病产生间接作用。 结论 该地区教师健康水平一般。今后应关注教师这一类职业人群, 特别是将男性作为该工作场所健康教育重点干预对象, 预防与控制其超重肥胖发生率, 提高其健康知识水平, 培养健康生活习惯, 同时加大工作场所健康资源的投入。 Abstract:Objective To understand the influence path of occupational health knowledge, behavior and lifestyle, and utilization of workplace health service on chronic diseases of teachers in a district of Beijing. Method A self-designed questionnaire was used among teachers in a district of Beijing through path analysis. Results The prevalence rate of chronic diseases in occupational population was 51.5%. The top three diseases were lumbar or spinal diseases(19.0%), hypertension(12.5%) and gastroenteritis(11.1%). The rate of overweight and obesity increased with age, and male teachers were higher than that of female teachers which was statistically significant(χ2=119.313, P < 0.001).Overweight-obesity, health related knowledge and utilization of workplace services made direct effects on chronic diseases. Healthy behaviors and lifestyles made indirect effects on chronic diseases by overweight-obesity. Conclusions The teachers' health in this district was not bad. It is recommended that we should pay attention to the population of teachers, especially the male so that to prevent and control the incidence of overweight and obesity, improve their health knowledge level and develop healthy habits, and increase the input of health resources in the workplace. -
Key words:
- Teachers /
- Health knowledge /
- Lifestyle /
- Utilization of workplace health services /
- Chronic diseases /
- Path analysis
-
由于人们生活水平与生活方式的转变, 慢性病的发病率呈逐年上升的发展趋势, 已成为中国公共卫生的首要问题[1]。世界卫生组织指出, 职业人群是经济和社会发展的主要贡献者, 其身体健康直接影响国家经济发展[2]。教师是学校的灵魂, 他们的素质与工作质量直接关系到学校的生存与发展。根据国家发改委调查结果[3]显示教师的平均年龄只有58岁, 随着年龄的增长, 高血压、高脂血症等慢性病患病率也逐渐升高, 且超重及肥胖率高于其他年龄段的人群, 慢性病风险因素广泛流行。同时教师的行为生活方式对学生也会产生一定的影响。本文通过通径分析方法, 探索健康知识、行为生活方式和工作场所服务利用对教师人群慢性病的影响路径, 从而为今后有针对性的开展工作场所健康教育活动提供依据。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
以北京市延庆区全体教师为调查对象。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 调查方法
本研究依托“健康北京人十年行动”评估, 于2018年6-9月由延庆区教育部门布置调查任务, 各中小学相关负责人通过会议、内部网络和微信群等形式, 向本校教职员工推送问卷二维码(或链接), 员工扫码阅读知情同意书后开始答题, 即视为知情同意。采用自行设计的问卷, 主要内容包括个人基本情况、健康知识、行为生活方式和工作场所健康服务利用情况四部分, 经检验Cronbach’s α系数为0.70, 信效度良好。
1.2.2 判定标准与赋值
(1) 慢性病患病:指职工自报的、经专业医疗机构诊断的慢性病患病人数(本研究慢性病涵盖高血压、高血脂、糖尿病、胃肠炎、腰椎疾病、缺血性心脏病、癌症肿瘤、脑血管病、胆结石及慢阻肺十类常见慢性病, 满足一项则为慢性病, 加和总分进入通径模型)。(2)体重判定[4]:以身体体重指数(body mass index, BMI)作为标准, BMI < 24.0 kg/m2为体重正常或偏低, 24.0 kg/m2≤BMI < 28.0 kg/m2为超重, BMI≥28.0 kg/m2为肥胖。(3)健康相关知识包含4道单选题, 回答正确计1分, 回答错误计0分; 4道多选题, 每个正确选项回答对计1分, 回答错误计0分; 所有知识题得分相加为健康知识得分, 得分范围在0~25分。(4)行为生活方式包含11道题, 每道题根据其程度分别计0~4分, 得分范围在0~38分。(5)工作场所健康服务:工作场所中对职工身体和心理健康有益的服务。本研究包含提供健康体检、健康培训、职业安全培训, 发放健康宣传资料, 配备医务室及健身场所六项服务, 利用该项服务计1分, 没有利用计0分, 得分范围在0~6分。
1.2.3 质量控制
问卷经平台回收后由经过统一培训的调查员进行数据整理核对, 对不合格问卷进行剔除。
1.3 统计学方法
采用EpiData 3.1软件建立数据库, 使用SPSS 19.0软件和Amos 22.0软件进行统计学分析。计量资料符合正态分布, 采用均数和标准差(x±s)描述, 两组间比较采用t检验, 多组间比较采用方差分析。分类变量组间频率比较采用χ2检验; 变量间因果关联分析采用通径分析。检验水准α=0.05。
2. 结果
2.1 基本情况
参加调查教职员工共有1 799人, 平均年龄为(39±8)岁。男性389人(21.6%), 女性1 410人(78.4%); < 35岁525人(29.2%), 35~44岁701人(39.9%), ≥45岁573人(31.9%); 高中/职高/中专/大专/本科1 760人(97.8%), 硕士及以上39人(2.2%)。
2.2 教师行为生活方式及工作场所服务利用调查
调查对象的慢性病患病率为51.1%(919/1 799), 其中排前三位分别是腰或脊椎疾病(19.0%)、高血压(12.5%)和胃肠炎(11.1%)。超重肥胖占45.0%(809/1 799)。不同性别、年龄的调查对象健康生活行为与生活方式和超重肥胖差异均有统计学意义(均有P < 0.05), 女性教师健康生活行为与生活方式得分高于男性, 并且随着年龄增长得分呈上升趋势; 男性教师超重肥胖率高于女性, 随着年龄增长超重肥胖率逐渐升高, 患慢性病率升高, 差异有统计学意义(χ2=119.313, P < 0.001)。见表 1。
表 1 不同特征调查对象慢性病状况、知识行为及工作场所服务利用状况分析(x±s)Table 1. Analysis of chronic disease status, knowledge behavior and service utilization in the workplace(x±s)变量 健康相关知识 健康生活行为与方式 工作场所服务利用 超重肥胖[n(%)] 慢性病[n(%)] 性别 男 14.399±4.791 30.152±3.610 3.237±1.151 273(70.2) 215(55.3) 女 14.027±4.707 32.667±3.000 3.162±1.122 536(38.0) 704(49.9) χ2/t值 1.073 16.782 1.130 127.469 3.480 P值 0.300 < 0.001 0.259 < 0.001 0.067 年龄(岁) < 35 13.770±4.966 31.547±3.234 3.211±1.108 151(28.8) 166(31.6) 35~ 14.021±4.595 32.314±3.195 3.133±1.113 325(46.4) 391(55.8) ≥45 14.107±4.726 32.417±3.455 3.204±1.167 333(58.1) 362(51.5) χ2/F值 3.671 11.516 0.949 96.291 119.313 P值 0.026 < 0.001 0.387 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 2 各连续变量间的Pearson相关性分析Table 2. Person correlation analysis of continuous variable变量 健康相关知识 健康生活方式与行为 工作场所服务利用 超重肥胖 慢性病 健康相关知识 1.000 健康行为与生活方式 0.094a 1.000 工作场所健康服务利用 0.053a 0.022 1.000 超重肥胖 0.087a -0.090a -0.019 1.000 慢性病 0.069a -0.210 -0.021 0.175a 1.000 注:a表示P < 0.05。 2.3 调查对象慢性病状况与健康知识、行为生活方式及工作场所服务利用相关性分析
从Pearson相关性分析可以看出, 工作场所健康服务利用和健康相关知识存在相关关系; 健康相关知识与健康行为与生活方式和超重肥胖存在相关关系; 健康相关知识、超重肥胖和慢性病存在相关关系。
2.4 调查对象慢性病状况、健康知识、行为生活方式及工作场所健康服务利用通径分析
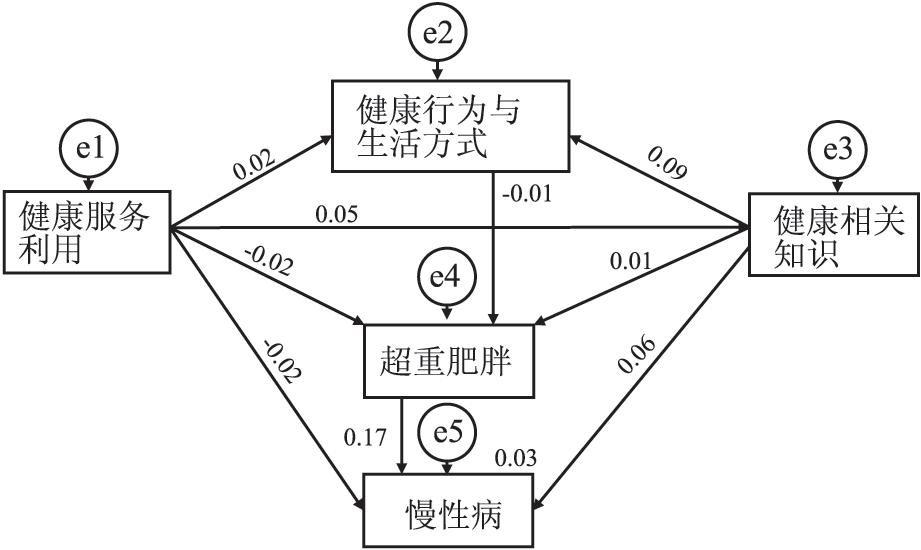
通过查阅相关文献[5]和上述相关性分析, 结合统计学检验结果, 并以健康相关知识、健康生活行为与方式、工作场所健康服务利用、超重肥胖和慢性病总得分为进入模型, 构建出通径图。通过逐步修改路径, 最终获得拟合良好的通径模型, 见图 1。结果显示, 模型各项拟合优度指标较好, χ2 =0.643, CFI(comparative fit index)=1.00, NFI(normed fit index)=0.99, IFI(incremental fit index)=0.98, RMSEA(root mean square error of approximation)=0.01。
通过模型提示和影响总效应可以看出, 超重肥胖、健康相关知识和工作场所服务利用对慢性病直接产生作用, 且超重肥胖的影响最大, 标准化总效应为0.170。健康生活行为与方式以超重肥胖为中介对慢性病产生间接作用。见表 3。
表 3 慢性病影响因素的效应分解Table 3. Effect decomposition of influencing factors of chronic diseases影响因素 直接效应 间接效应 总效应 总效应排序 超重肥胖 0.170 - 0.170 1 健康相关知识 0.055 0.015 0.070 2 健康行为与生活方式 - -0.017 -0.017 3 工作场所健康服务利用 -0.021 - -0.021 4 3. 讨论
职业人群作为国家生产力发展和社会文明进步的主要推动力量, 其健康状况和存在的健康问题逐渐成为社会关注的焦点之一[6]。健康生活方式与行为是影响健康的四大因素之一, 不良生活方式, 如吸烟、缺乏体育锻炼等, 与肥胖、心脑血管疾病等发生有密切关系[7]。因此, 关注职业人群健康生活方式与行为是预防慢性病、改善职业人群健康的关键。
教师是学校得以长远发展的关键保障。教师作为一个从事教学、以智力劳动为主的社会群体, 由于近年来繁重的教学工作及其习惯于久坐、熬夜, 疏于体育运动, 睡眠不足等不良工作生活习惯, 该群体的整体身体健康状况堪忧[8-9]。而教师自身对知识的认识和行为对学生有重要传递作用, 因此从学校入手, 重视教师对健康的认知对于提高学生的健康行为显得尤为重要[10]。
本次调查的北京市某地区教师慢性病患病率为51.5%, 高于中国城市居民水平[11]。随着年龄增加, 慢性病患病率整体呈上升趋势。这与既往研究[12]结果相一致。在本次研究中, 女性健康生活行为与生活方式得分高于男性, 比男性拥有更高的健康行为水平, 这可能与性激素水平, 同时男性日常应酬多, 不注重控制饮食、培养健康生活方式有关[13]。
以往研究[14]通常采用多元线性回归等分析方法, 该方法仅揭示对因变量有直接影响的自变量, 而忽略了一些通过中间变量起作用的间接因素。本研究采用通径分析方法, 从模型的角度出发, 定量描述系统内各变量间复杂的因果关系, 包括直接效应和间接效应, 进一步探讨相关因素对职业人群慢性病的作用, 弥补了既往研究方法的不足。社会认知理论提出, 个体的行为是行为、个人的认知和其他内部因素、环境三者之间交互作用所决定的。环境作为个体存在的外部条件会影响个体行为, 但个体也能影响环境并调节自己的行为[15]。通径分析结果显示, 超重肥胖是慢性病产生的重要因素(通径系数为0.17), 同时不良的行为与生活方式通过超重肥胖间接导致慢性病。既往研究[3]显示, 超重肥胖是由许多因素引起的慢性代谢疾病, 并且其本身是许多慢性病的危险因素, 提示教师这类职业人群要对此重视。
研究结果显示, 调查对象健康知识得分升高对于慢性病的产生有正向作用(通径系数为0.07), 这一结果提示该人群知行没有达成一致, 调查对象仅停留在掌握较高水平的健康知识阶段, 没有将其转变成健康相关行为。工作场所健康服务利用对于慢性病的产生有一定影响(通径系数为-0.021), 提示今后在对学校进行干预的过程中, 应加大健康资源(如健康宣传材料、健康相关培训、健身场所)的投入, 提高教师健康服务利用。
教师的健康是保证教学质量的前提, 本次研究显示北京市某地区教师健康状况不容乐观, 应引起相关部门的重视, 有针对性采取应对措施。首先, 相关部门要关注教师这类职业人群, 以学校健康教育为平台, 预防与控制教师群体的超重与肥胖发生率。其次, 倡导教师“知行统一”, 将知识转为行动, 加大对男教师的重视, 改善其不良生活习惯, 树立健康的生活方式。同时加大学校健康资源的投入, 包括人力资源、财力资源、物力资源和信息资源, 增设从事职工健康管理工作的专职人员, 对上岗职工进行职业培训, 加大职业安全防护经费的投入, 配备健康设施; 同时改变传统单一的健康资料发放模式, 利用手机、网络等被职工喜爱的新媒体模式[16], 充分调动员工阅读积极性, 通过提高工作场所健康服务利用, 促进职业人群健康行为产生, 进而提高职工整体健康水平。
-
表 1 不同特征调查对象慢性病状况、知识行为及工作场所服务利用状况分析(x±s)
Table 1. Analysis of chronic disease status, knowledge behavior and service utilization in the workplace(x±s)
变量 健康相关知识 健康生活行为与方式 工作场所服务利用 超重肥胖[n(%)] 慢性病[n(%)] 性别 男 14.399±4.791 30.152±3.610 3.237±1.151 273(70.2) 215(55.3) 女 14.027±4.707 32.667±3.000 3.162±1.122 536(38.0) 704(49.9) χ2/t值 1.073 16.782 1.130 127.469 3.480 P值 0.300 < 0.001 0.259 < 0.001 0.067 年龄(岁) < 35 13.770±4.966 31.547±3.234 3.211±1.108 151(28.8) 166(31.6) 35~ 14.021±4.595 32.314±3.195 3.133±1.113 325(46.4) 391(55.8) ≥45 14.107±4.726 32.417±3.455 3.204±1.167 333(58.1) 362(51.5) χ2/F值 3.671 11.516 0.949 96.291 119.313 P值 0.026 < 0.001 0.387 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 2 各连续变量间的Pearson相关性分析
Table 2. Person correlation analysis of continuous variable
变量 健康相关知识 健康生活方式与行为 工作场所服务利用 超重肥胖 慢性病 健康相关知识 1.000 健康行为与生活方式 0.094a 1.000 工作场所健康服务利用 0.053a 0.022 1.000 超重肥胖 0.087a -0.090a -0.019 1.000 慢性病 0.069a -0.210 -0.021 0.175a 1.000 注:a表示P < 0.05。 表 3 慢性病影响因素的效应分解
Table 3. Effect decomposition of influencing factors of chronic diseases
影响因素 直接效应 间接效应 总效应 总效应排序 超重肥胖 0.170 - 0.170 1 健康相关知识 0.055 0.015 0.070 2 健康行为与生活方式 - -0.017 -0.017 3 工作场所健康服务利用 -0.021 - -0.021 4 -
[1] 刘敏, 李英华, 陶茂萱, 等.北京市职业人群健康状况自评及其影响因素研究[J].中国健康教育, 2014, 30(3): 198-201. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2014.03.002.Liu M, Li YH, Tao MX, et al. Study on self-rated health status and its influencing factors among occupational populations in Beijing[J]. Chin J Health Ed, 2014, 30(3): 198-201. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2014.03.002. [2] Bertazzi PA, Colombi A, Spallanzani A. Proposal for a global plan of action on workers' health from 2008 to 2017[J]. Med Lav, 2007, 98(3): 255-260. [3] 肖喜娥, 蒋宝泉, 钟丕洪, 等.重庆市某区中小学教师人群常见慢性病动态分析[J].公共卫生与预防医学, 2019, 30(4): 132-135. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FBYF201904033.htmXiao XE, Jiang BQ, Zhong PH, et al. Dynamic analysis of common chronic diseases among primary and middle school teachers in a district of Chongqing[J]. Public health and Prevent Med, 2019, 30(4): 132-135. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FBYF201904033.htm [4] 邢慧媛, 刘琰, 赵艾, 等.吸烟、饮酒和膳食因素对高尿酸血症人群中高血压的影响[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(6): 555-559. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.06.004.Xing HY, Liu Y, Zhao A, et al. Effects of smoking, drinking and dietary factors on hypertension in subjects with hyperuricemia[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(6): 555-559. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.06.004. [5] 徐勤, 郭建丽.北京某高校教职工2005-2015年主要慢性病变化趋势分析[J].中国学校卫生, 2017, 38(4): 623-626. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2017.04.044.Xu Q, Guo JL. Analysis on the change trend of major chronic diseases in a university in Beijing from 2005 to 2015[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2017, 38(4): 623-626. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2017.04.044. [6] 申洋, 刘胜兰, 王燕玲, 等.我国四城市部分职业人群慢性病患病及其公平性分析[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2017, 21(8): 758-761. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.08.002.Shen Y, Liu SL, Wang YL, et al. Analysis of chronic disease prevalence and its equity among working population in four cities, China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2017, 21(8): 758-761. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.08.002. [7] 曹仲辉, 钱霞, 谭彩, 等.健康技能在健康知识与健康行为间的中介效应研究[J].中国健康教育, 2011, 27(6): 477-479. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2011.06.016.Cao ZH, Qian X, Tan C, et al. Mesometic effect of health skill between health knowledge and health behavior[J]. Chin J Health Ed, 2011, 27(6): 477-479. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2011.06.016. [8] 蒋林, 王玲, 李小平.普洱市中小学教师慢性病就医行为及其影响因素[J].职业与健康, 2017, 33(4): 526-530. DOI: 10.13329/j.cnki.zyyjk.2017.0157.Jiang L, Wang L, Li XP, et al. Health seeking behavior and its influencing factors of teachers with chronic disease in primary and middle schools of Pu'er City[J]. Occup and Health, 2017, 33(4): 526-530. DOI: 10.13329/j.cnki.zyyjk.2017.0157. [9] 魏开芳.某高校教职工健康状况调查[J].中国学校卫生, 2013, 34(6): 762-763. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2013.06.052.Wei KF. Investigation on the health status of some university staff[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2013, 34(6): 762-763. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2013.06.052. [10] 朱晓磊, 梁靖, 翟屹, 等.我国8省小学教师慢性病防控相关知识与行为分析[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2013, 17(9): 763-766. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JBKZ201309008.htmZhu XL, Liang J, Zhai Y, et al. Analysis on knowledge and practice on the prevention and control of NCDs among primary school teachers in eight provinces, China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2013, 17(9): 763-766. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JBKZ201309008.htm [11] 张群, 王光丽, 陈跃芳, 等.四川省攀枝花市东区成年居民慢性病患病情况调查[J].中国健康教育, 2018, 34(5): 432-436. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2018.05.011.Zhang Q, Wang GL, Chen YF, et al. Investigation on status of chronic disease among adult residents at Dongqu community of Panzhihua City, Sichuan Province[J]. Chin J Health Ed, 2018, 34(5): 432-436. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2018.05.011. [12] 郭建花.北京市某区部分中小学教师健康体检结果分析[J].中国实用医药, 2014, 9(19): 271-272. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsyyy201419206Guo JH. Analysis of the results of health examinations of some primary and middle school teachers in a certain district of Beijing[J]. China Prac Med, 2014, 9(19): 271-272. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsyyy201419206 [13] 彭友悦, 杨洋, 刘小锦, 等.成都市外来务工人员超重和肥胖的流行现况分析[J].现代预防医学, 2018, 45(10): 1800-1803.Peng YY, Yang Y, Liu XJ, et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among migrant workers in Chengdu[J]. Modern Prevent Med, 2018, 45(10): 1800-1803. [14] 梁函, 程静, 沙蕊, 等.皖西村民糖尿病知识、自我效能及健康行为的通径分析[J].中国卫生事业管理, 2016, 33(6): 470-472.Liang H, Cheng J, Sha R, et al. Path analysis of the relationships among diabetes knowledge self-efficacy and health behaviors in rural residents of Western Anhui[J]. Chin Health service management, 2016, 33(6): 470-472. [15] 马骁.健康教育学[M].北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2004, 71-74.Ma X. Health education[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2004, 71-74. [16] 陶丽丽, 韩晓燕, 任佩佳, 等.北京市朝阳区职业人群超重及肥胖影响因素研究[J].中国健康教育, 2018, 34(8): 714-717. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2018.08.009.Tao LL, Han XY, Ren PJ, et al. Study on the associated factors of overweight and obesity among occupational population in Chaoyang District, Beijing[J]. Chin J Health Ed, 2018, 34(8): 714-717. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2018.08.009. 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 莫少敏,陈超. 社会健康决定因素对脊柱手术后30 d和90 d再入院率的影响. 颈腰痛杂志. 2024(01): 14-18+23 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 朱莹莹,董莹,徐倩倩,冯宏伟,李玉红,金秋妍,丁十戈. 基于双重差分模型的健康促进银牌学校创建效果评价. 中国农村卫生事业管理. 2023(10): 755-760 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 麦洁梅,林清霞,陈瑞华,蔡雪莲. 广州市番禺区医务人员生理亚健康影响因素分析. 华南预防医学. 2023(11): 1382-1390 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 王青青,沈泽坤,黄白艳,郭兵兵. 健康教育对郑州地区居民掌握疟疾相关知识、态度与行为情况的影响. 中国地方病防治. 2021(02): 146-147 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 陈翠屏,刘一争,时红梅,陈海燕,谢春英. 中小学教师健康素养知识的调查研究. 开封文化艺术职业学院学报. 2020(11): 199-201 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(3)
-





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:

