ARIMA乘积季节模型和LSTM深度神经网络对石家庄市手足口病疫情预测效果的比较
doi: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.01.015
Comparison on predictive capacity of ARIMA model and LSTM model for incidence of hand, foot and mouth disease in Shijiazhuang
-
摘要:
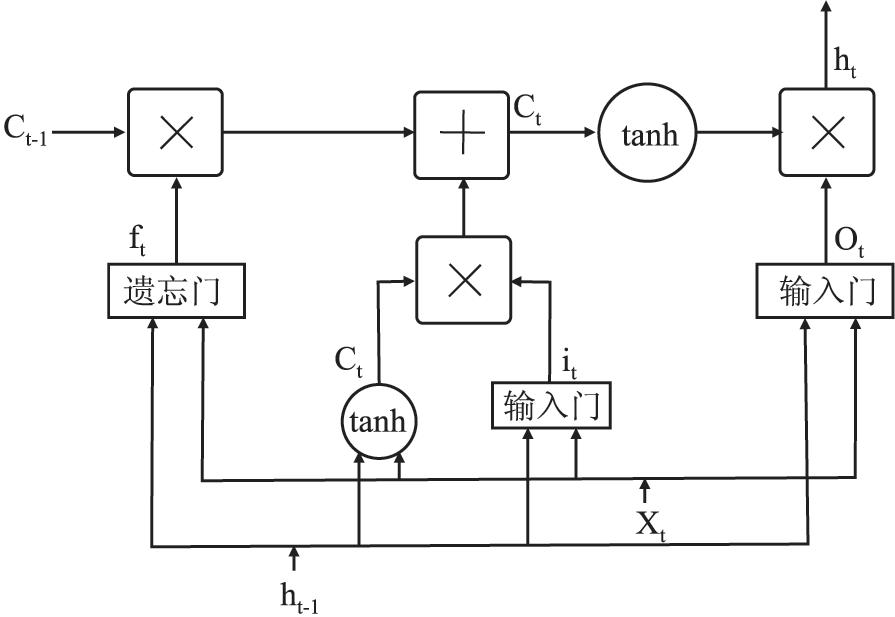
目的 运用自回归移动平均(autoregressive integrated moving average model, ARIMA)乘积季节模型和长期短期记忆网络(long short term memory, LSTM)对石家庄市手足口病(hand, foot and mouth disease, HFMD)的发病趋势进行预测, 为疫情防控工作提供理论依据。 方法 利用Eviews 8.0和python 3.7.1软件对2013年1月-2018年5月石家庄市HFMD逐月发病数据分别建立ARIMA乘积季节模型和LSTM神经网络, 以2018年6月-2019年5月的发病资料检验模型预测精度, 最后应用模型预测2019年6月-2019年8月的月发病数。 结果 最优模型ARIMA(1, 0, 0)×(1, 1, 2)12和LSTM神经网络外推预测2018年6月-12月的MAPE分别为22.14和10.03, 而外推预测2018年6月至2019年5月的MAPE分别为43.84和25.26, 提示LSTM神经网络的拟合效果和预测精度优于ARIMA模型, 预测结果与实际情况基本一致。 结论 LSTM神经网络对石家庄市HFMD发病趋势的拟合度和预测效果较好, 能够为手足口病疫情的预测预警工作提供指导。 Abstract:Objective To predict the incidence of hand, foot and mouth disease(HFMD) in Shijiazhuang using the multiple seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average model(ARIMA) and long short term memory(LSTM) model, lay theoretical foundation for the prevention and control of HFMD. Methods Multiple seasonal ARIMA model and LSTM model were established separately by using Eviews 8.0 and python 3.7.1 according to the data of monthly incidence of HFMD from January 2013 to May 2018 in Shijiazhuang, and the data from June 2018 to May 2019 were used to verify the prediction precision of model. Finally, the monthly incidence from June to August 2019 was predicted. Results Based on the monthly incidence from January 2013 to May 2018, the optimal models, ARIMA(1, 0, 0)×(1, 1, 2)12 and LSTM model were established. Mean absolute percentage of error(MAPE) of ARIMA and LSTM model were 22.14 and 10.03 respectively based on the monthly incidence from June to December 2018, while MAPE of ARIMA and LSTM model were 43.84 and 25.26 respectively based on the monthly incidence from June 2018 to May 2019. These results indicated that LSTM model was superior to ARIMA model in model fitting degree and predicting accuracy, which was relatively consistent with the actual situation. Conclusions LSTM model is able to fit and predict the incidence trend of HFMD well in Shijiazhuang. It can provide guidance to HFMD epidemic prediction and alerting. -
Key words:
- Hand /
- foot and mouth disease /
- ARIMA /
- LSTM /
- Monthly incidence
-
表 1 ARIMA(1, 0, 0)×(1, 1, 2)12模型参数估计和拟合优度统计量结果
Table 1. Parameter estimation and goodness-of-fit statistics for ARIMA(1, 0, 0)×(1, 1, 2)12 models
指标 系数 t值 P值 Rj2 AIC SC AR(1) 0.532 5.154 < 0.001 0.838 0.069 0.238 SAR(1) -0.478 -3.531 0.001 SMA(1) 1.603 35.652 < 0.001 SMA(2) 0.828 28.210 < 0.001 表 2 2018年6月-2019年5月石家庄市手足口病发病数实际值与预测值的比较
Table 2. Comparison of HFMD monthly incidence between the predicted and observed cases in Shijiazhuang from June 2018 to May 2019
ARIMA模型 LSTM模型 年份
(年)月份
(月)观察值
(人)预测值
(人)绝对误差
(人)相对误差
(%)95%置信限 预测值
(人)绝对误差
(人)相对误差
(%)LCL UCL 2018 6 920 1 240 320 34.78 452 3 401 1 037 117 12.72 2018 7 909 1 117 208 22.88 419 2 973 1 029 120 13.20 2018 8 791 882 91 11.50 333 2 337 829 38 4.80 2018 9 578 438 140 24.22 165 1 166 559 19 3.29 2018 10 410 383 27 6.59 142 1 032 368 42 10.24 2018 11 351 365 14 3.99 139 960 285 66 18.80 2018 12 196 96 100 51.02 36 253 210 14 7.14 2019 1 63 8 55 87.30 2 24 61 2 3.17 2019 2 12 25 13 108.33 8 77 25 13 108.33 2019 3 30 19 11 36.67 6 54 11 19 63.33 2019 4 54 112 58 107.41 41 302 78 24 44.44 2019 5 388 266 122 31.44 100 710 441 53 13.65 表 3 ARIMA和LSTM模型对2019年6-8月石家庄市手足口病月发病数的预测结果
Table 3. The predicted results of HFMD monthly incidence by the ARIMA and LSTM from June to August 2019 in Shijiazhuang
ARIMA模型 LSTM模型 月份
(月)预测值
(人)95%置信区间 预测值(人) LCL UCL 6 720 251 2 064 1 079 7 623 235 1 649 1 213 8 574 218 1 513 976 -
[1] 郭建花, 刘立, 张世勇, 等.石家庄市手足口病疫情短期预测模型[J].医学动物防制, 2011(11): 1001-1002. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6245.2011.11.009.Guo JH, Liu L, Zhang SY, et al. Short term forecasting model of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Shijiazhuang[J]. J Med Pest Control, 2011(11): 1001-1002. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6245.2011.11.009. [2] Yu L, Zhou L, Tan L, et al. Application of a new hybrid model with seasonal auto-regressive integrated moving average(ARIMA)and nonlinear auto-regressive neural network(NARNN)in forecasting incidence cases of HFMD in Shenzhen, China[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(6): e98241. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098241. [3] Zhuang Z, Kou Z, Bai Y, et al. Epidemiological research on hand, foot and mouth disease in mainland China[J]. Viruses, 2015, 7(12): 6400-6411. DOI: 10.3390/v7122947. [4] Li Y, Huang M, Peng L. A multi-group model for estimating the transmission rate of hand, foot and mouth disease in mainland China[J]. Math Biosci Eng, 2019, 16(4): 2305-2321. DOI: 10.3934/mbe.2019115. [5] 朱宝增, 赵文娜, 刘莹莹, 等.河北省2008—2017年手足口病流行和病原特征分析[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(3): 356-359. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.03.023.Zhu BZ, Zhao WN, Liu YY, et al. Epidemiologic characteristics and pathogen surveillance of hand, foot and mouth disease in Hebei province from 2008 to 2017[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(3): 356-359. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.03.023. [6] 李杰, 顾月. ARIMA模型在预测手足口病发病中的应用[J].预防医学, 2016, 28(10): 987-991.Li J, Gu Y. The application of ARIMA model in predicting the incidence of hand-foot-mouth disease[J]. Prev Med, 2016, 28(10): 987-991. [7] Liu L, Luan RS, Yin F, et al. Predicting the incidence of hand, foot and mouth disease in Sichuan province, China using the ARIMA model[J]. Epidemiol Infect, 2016, 144(1): 144-151. DOI: 10.1017/S0950268815001144. [8] 王永斌, 柴峰, 李向文, 等. ARIMA模型与残差自回归模型在手足口病发病预测中的应用[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2016, 20(3): 303-306. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.03.022.Wang YB, Cai F, Li XW, et al. Application of ARIMA model and auto-regressive model in prediction on incidence of hand-foot-mouth disease[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2016, 20(3): 303-306. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.03.022. [9] 李琳, 王哲, 张学良, 等.基于LSTM深度神经网络的月门诊量预测精度研究[J].中国数字医学, 2019, 14(1): 14-17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7571.2019.01.004.Li L, Wang Z, Zhang XL, et al. The accuracy of monthly outpatient volume prediction based on LSTM deep neural network[J]. China Digital Medicine, 2019, 14(1): 14-17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7571.2019.01.004. [10] 韩天齐, 宋波.基于LSTM神经网络的麻疹发病率预测[J].电脑与电信, 2018, 5: 54-57. DOI: 10.15966/j.cnki.dnydx.2018.05.016.Han TQ, Song B. The prediction of incidence of measles based on LSTM neural network[J]. Computer and Telecommunication, 2018, 5: 54-57. DOI: 10.15966/j.cnki.dnydx.2018.05.016. [11] 张光, 孙良, 谢金贵, 等. ARIMA模型在阜阳市手足口病发病数预测中的应用[J].安徽预防医学杂志, 2015, 21(4): 231-234.Zhang G, Sun L, Xie JG, et al. Application of autoregressive integrated moving average model in forecasting the incidence of hand-foot-mouth disease in Fuyang[J]. Anhui J Prev Med, 2015, 21(4): 231-234. [12] 王永斌, 许春杰, 尹素凤, 等.中国手足口病发病率ARIMA、RBF及ARIMA-RBF组合模型拟合及预测效果比较[J].中国公共卫生, 2017, 33(5): 760-763. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws2017-33-05-19.Wang YB, Xu CJ, Yin SF, et al. Comparison on predictive capacity and fitting efficiency of ARIMA, RBF, and ARIMA-RBF combination model for incidence of hand-foot-mouth disease[J]. Chin J Public Health, 2017, 33(5): 760-763. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws2017-33-05-19. [13] Duan Y, Lv Y, Wang F. Travel time prediction with LSTM neural network[J]. 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems(ITSC), 2016. DOI: 10.1109/ITSC.2016.7795686. [14] 杨文姣, 肖俊玲, 丁国武. ARIMA模型和BP神经网络模型在甘肃省结核病发病率预测中的应用[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(6): 728-732. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.06.021.Yang WJ, Xiao JL, Ding GW, et al. Application of ARIMA model and BP neural network model in prediction of tuberculosis incidence in Gansu Province[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(6): 728-732. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.06.021. -





 下载:
下载: