Assessment of the lifestyle risk factors of cognitive impairment among community-dwelling older adults using decision tree and random forest model
-
摘要:
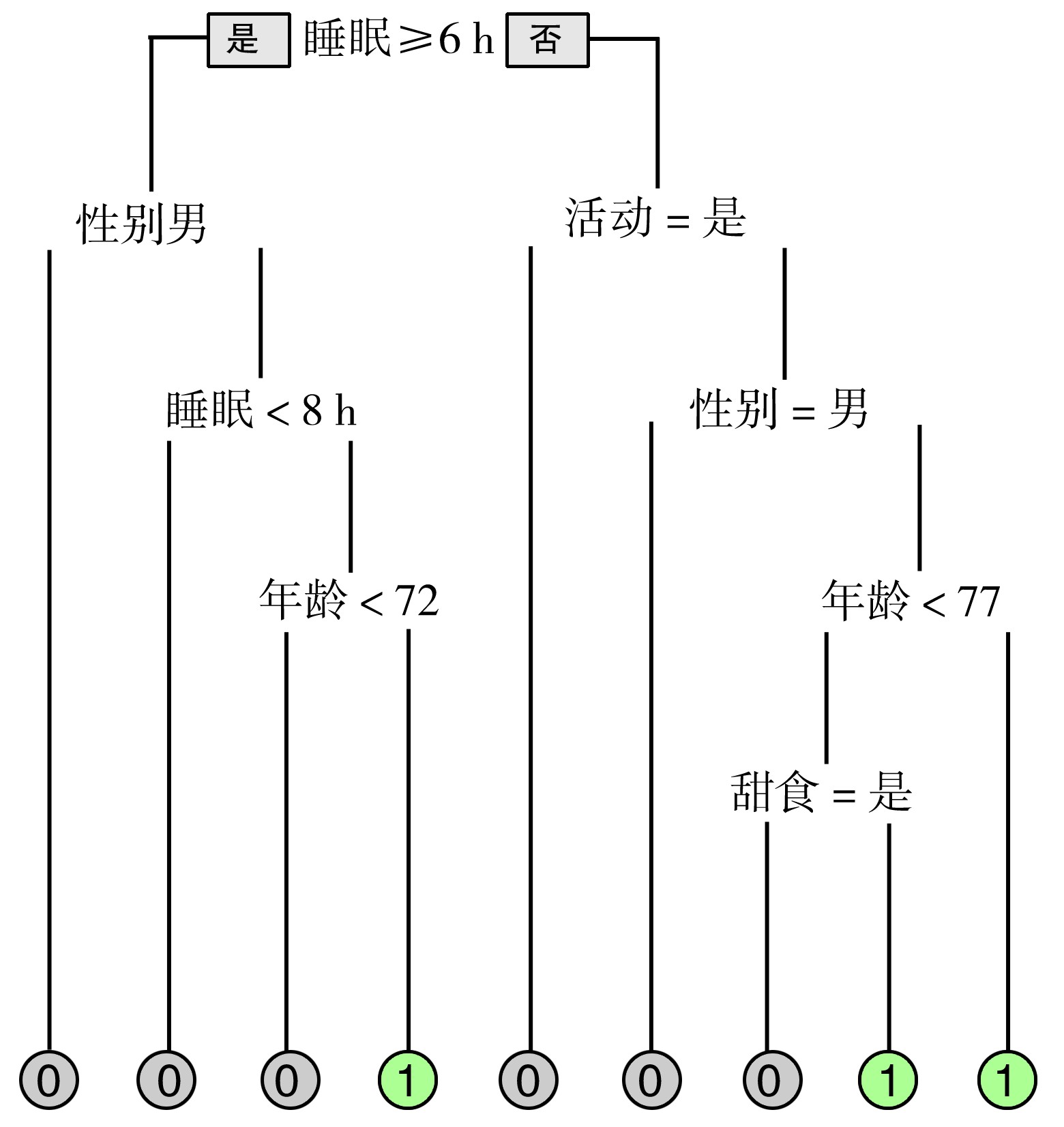
目的 利用分类模型决策树和随机森林探讨社区老年人认知障碍的生活方式影响因素, 为采取有效的预防措施提供科学依据。 方法 在北京、合肥和兰州3座城市整群抽样选取3个社区1 200名60岁以上健康或有慢性病的老人进行问卷调查。调查内容包括一般情况、生活行为方式、认知情况等。采用决策树和随机森林模型分析生活方式与认知障碍相关性。 结果 共1 115人完成全部调查项目, 应答率为92.9%, 287人(25.7%)存在不同程度的认知障碍, 女性认知障碍风险高于男性(P < 0.001), 年龄越大认知障碍风险越高(P=0.002)。决策树和随机森林模型中, 年龄、性别、运动和睡眠与认知障碍相关, 吸烟、饮酒、喝茶等对认知障碍的影响不显著。决策树ROC曲线下面积为0.64, 随机森林为0.94。 结论 分类模型可以帮助识别认知障碍和生活行为方式风险因素之间的关联。认知障碍危险因素的早期识别和积极干预, 可延缓及预防老年人认知障碍的发生, 对提高老年人生活质量有重大的意义。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the associations between lifestyle factors and social network and cognitive impairment among the elderly in three communities in China using decision tree and random forest. Methods 1 200 elderly individuals were selected from three communities in Beijing, Hefei, and Lanzhou by using a random cluster sampling method. Data was collected on lifestyle, social network and cognition. Decision tree and random forest analysis were conducted to identify the associations between lifestyle and cognitive impairment. Results A total 1 115 participants(92.9%) were administered questionnaires. The prevalence of cognitive impairment was 25.7%(n=287). Females exhibited a higher risk compared to males(P < 0.001), and there is a positive association between the risk of cognitive impairment and age(P=0.002). In the decision tree and random forest models, age, sex, activities, and sleep were associated with cognitive impairment, while the associations of smoking, alcohol and tea consumption were not significant in this study. The areas under the ROC curves were 0.64 for the decision tree, and 0.94 for the random forest model. Conclusions Classification models can help identify associations between cognitive impairment and lifestyle risk factors. Identification and intervention of risk factors are crucial in delay and prevention of cognitive impairment and in the improvement of quality of life among the elderly. -
Key words:
- Cognition /
- Risk factors /
- Elderly /
- Lifestyle /
- Decision tree
-
表 1 1 115名社区老年人认知障碍的人口学分布及生活方式危险因素
Table 1. The distribution of demographic and life-style risk factors among 1 115 community-dwelling older adults
调查人数 认知障碍[n (%)] χ2值 P值 年龄(岁) 12.372 0.002 60~ 471 99 (21.0) 70~ 354 94 (26.6) ≥80 290 94 (32.4) 性别 28.429 < 0.001 男性 435 74 (17.0) 女性 680 213 (31.3) 生活方式 吸烟 151 21 (13.9) 13.520 < 0.001 饮酒 150 19 (12.9) 16.198 < 0.001 喝茶 480 94 (19.6) 15.007 < 0.001 常吃甜食 370 97 (26.2) 0.051 0.821 口味偏咸 197 36 (18.3) 6.904 0.009 经常锻炼 373 66 (17.7) 20.317 < 0.001 睡眠时间(h) < 6 184 85 (46.2) 6~ 566 115 (20.3) > 8 365 87 (23.8) 49.677 < 0.001 -
[1] Ohara T, Ninomiya T, Hata J, et al. Midlife and late-life smoking and risk of dementia in the community: the hisayama study[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2015, 63(11): 2332-2339. DOI: 10.1111/jgs.13794. [2] 苏向妮, 化前珍, 陈建华, 等.社区老年人认知障碍与生活方式的相关性研究[J].护理学报, 2016, 23(9): 30-33. DOI: 10.16460/j.issn1008-9969.2016.09.030.Su XN, Hua QZ, Chen JH, et al. Correlation between lifestyle and mild cognitive impairment among community-dwelling seniors[J]. Journal of Nursing(China), 2016, 23(9): 30-33. DOI: 10.16460/j.issn1008-9969.2016.09.030. [3] Handing EP, Andel R, Kadlecova P, et al. Midlife alcohol consumption and risk of dementia over 43 years of follow-up: a population-based study from the swedish twin registry[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2015, 70(10): 1248-1254. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glv038. [4] Scarmeas N. Physical activity, diet, and risk of alzheimer disease[J]. JAMA, 2009, 302(6): 627. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2009.1144. [5] 李晋磊, 金平阅, 王紫娟, 等.城市社区老人生活方式与社交网络对认知障碍的影响[J].中华健康管理学杂志, 2019, 13(3): 220-224. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-0815.2019.03.008.Li JL, Jin PY, Wang ZJ, et al. Associations between lifestyle and social network and cognitive impairment among the elderly in three communities in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Management, 2019, 13(3): 220-224. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-0815.2019.03.008. [6] Folstein MF, Folstein SE, Mchugh PR. "Mini-mental state": a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician[J]. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 1975, 12(3): 0-198. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [7] 李苑, 林寰.决策树在非精神科病人抑郁症患病危险因素筛选中的应用[J].中国卫生事业管理, 2008, 25(7): 501-502. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4663.2008.07.028.Li Y, Lin H. The application of decision tree on risk factors of depressive patients in non-neurology departments[J]. Chinese Health Service Management, 2008, 25(7): 501-502. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4663.2008.07.028. [8] Li J, Ogrodnik M, Kolachalama VB, et al. Assessment of the mid-life demographic and lifestyle risk factors of dementia using data from the framingham heart study offspring cohort[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2018, 63(3): 1119-1127. DOI: 10.3233/JAD-170917. [9] 纪南南, 王玉环.国外老年人轻度认知功能障碍影响因素研究现况[J].中国老年学杂志, 2016, 36(10): 2560-2562. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.10.117.Ji NN., Wang YH. Researches of mild cognitive impairment risk factors in the elderly[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2016, 36(10): 2560-2562. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.10.117. [10] Verdelho A, Madureira S, Ferro JM, et al. Physical activity prevents progression for cognitive impairment and vascular dementia: results from the LADIS(Leukoaraiosis and Disability)study[J]. Stroke, 2012, 43(12): 3331-3335. DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.661793. [11] Potvin O, Lorrain D, Forget, et al. Sleep quality and 1-year Incident cognitive Impairment in community-dwelling older adults[J]. Sleep, 2012, 35(4): 491-499. DOI: 10.5665/sleep.1732. [12] Ramos AR, Dong C, Elkind MSV, et al. Association between sleep duration and the mini-mental score: the northern manhattan study[J]. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 2013, 9(7): 669-673. DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.2834. [13] Gudala K, Bansal D, Schifano F, et al. Diabetes mellitus and risk of dementia: a meta‐analysis of prospective observational studies[J]. Journal of Diabetes Investigation, 2013, 4(6): 640-650. DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12087. -





 下载:
下载: