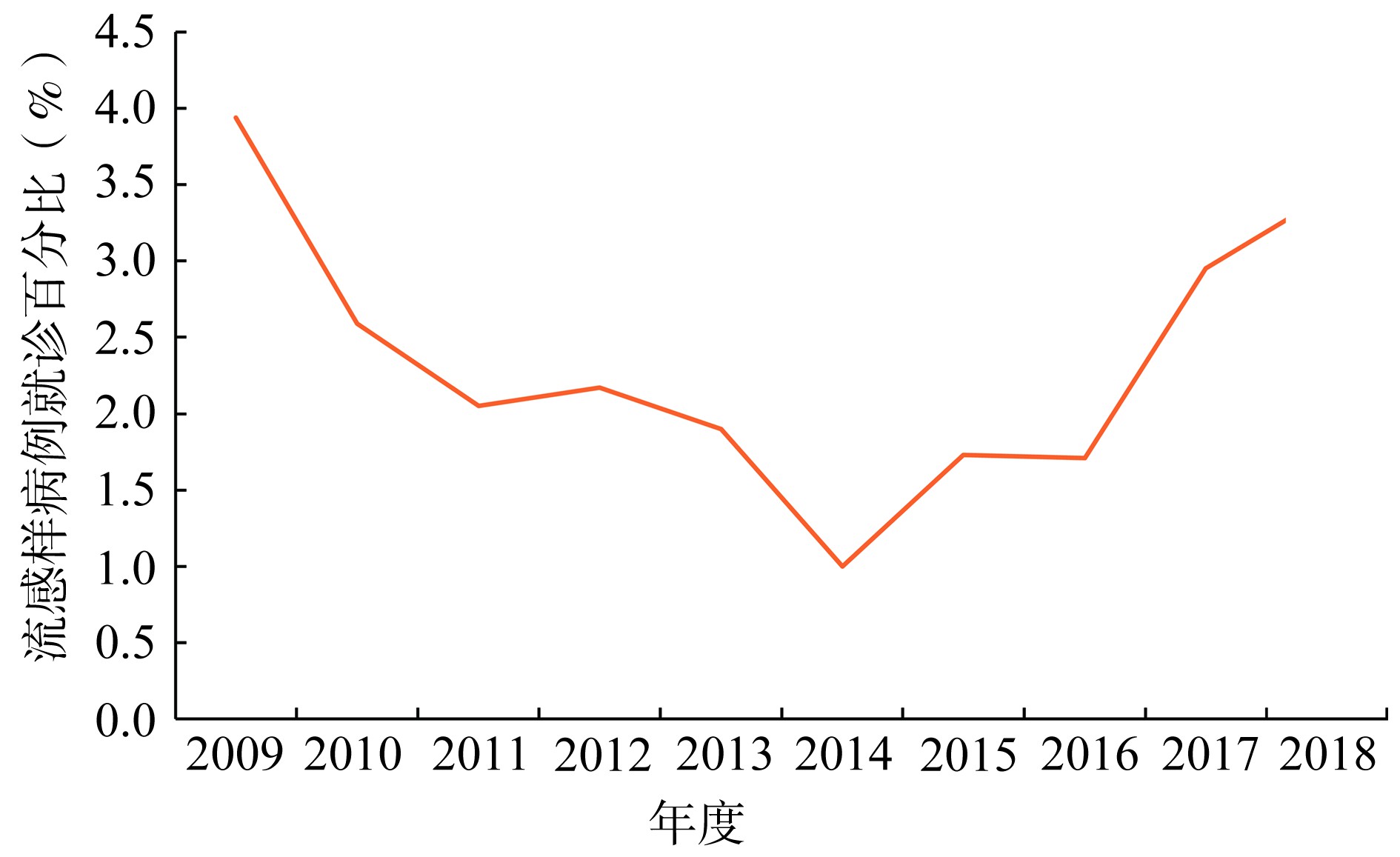
-
摘要:
目的 分析2009年14周-2019年13周青海省流行性感冒(简称流感)病毒变迁规律, 为高原地区科学防控流感提供依据。 方法 从中国流感监测信息系统中, 导出流感样病例数据、病例样本核酸检测阳性数据及病毒分离数据。使用描述流行病学方法, 分析2009年14周-2019年13周流感病毒在高原地区青海省的变化特征。 结果 青海省2009、2011、2014和2015年均以H1N1 (pdm09)为主, 2010和2012年以H3N2为主, 2013年以B型为主, 2016年和2017年以H3N2、B型和H1N1 (pdm09)为主, 2018年以H1N1 (pdm09)、H3N2和B型为主。青海省西北部地区(海西和海北)检测到的流感病毒以H3N2、H1N1 (pdm09)和BV这3种为主, 其他地区则以H3N2、H1N1 (pdm09)、BY和BV这4种病毒为主。其中春季流感病毒阳性检出率为8.73%, 乙型居多; 夏季为1.35%, 秋季为15.33%, 均以H1N1 (pdm09)居多; 冬季为23.17%, H3N2和H1N1 (pdm09)居多。 结论 青海省西北区域流感病毒型别和活跃程度与青海省其他地区不同; 冬、春季流感病毒型别和活跃程度更为丰富, 可在此前做好流感预警预测等防控措施; 14岁以下人群更易感染乙型病毒, 可针对重点人群和重点地区接种流感疫苗, 并做好学校流感疫情的监测与防控。 Abstract:Objective Toexplore the transitional patterns of influenza virus in Qinghai province between 14 weeks of 2009 and 13 weeks of 2018 for the scientific prevention and control of influenza in the plateau region. Methods The samples and virus isolation data with influenza-like cases and positive nucleic acid test of case were derived from the Chinese influenza surveillance information system. The characteristics of influenza viruses in Qinghai province between 2009 and 2018 were analyzed by descriptive epidemiological method. Results HNN1(pdm09) was dominated influenza of seasonof 2009, 2011, 2014 and 2015 in Plateau area of Qinghai province. H3 N2 was dominated in influenza of seasonof 2010 and 2012. The major is olate in 2013 was type B. H3 N2, type B and HNN1(pdm09) had account for a large proportion in 2016 and 2017, and in 2018, the HNN1(pdm09), H3 N2 and B type were dominant. H3 N2, H1 N1 influenza virus(pdm09) and BVwere mainly prevalent in the northwest region of Qinghai province(hercynian and distance from the north sea).Main types in other areas were H3 N2, H1 N1(pdm09), BY and BV4 viruses. Among which the positive detection rate of influenza virus was 8.73% in spring and 1.35% in summer and autumn. Conclusions The types and activity of influenza virus in northwest Qinghai province are different from other parts of Qinghai province. Under 14 years old are more likely to be infected with the b virus.There fore, they can be vaccinated against influenza in key groups and key areas, and the influenza epidemic in schools should be monitored and prevented. -
Key words:
- The plateau area /
- Influenza virus /
- Changes rule
-
表 1 2009-2018年青海省流感病毒主要阳性型别
Table 1. The positive types of virus in Qinghai province from 2009 to 2018
变量 病原主要型别 χ2值 P值 季H1a 季H3b H1N1 (pdm09)c BVd BYe 混合型 地区(CDC) 428.80 < 0.001 格尔木 1 103 51 36 11 0 海北州 1 448 459 216 100 0 海东市 0 299 349 79 96 0 海南州 0 121 247 115 69 0 海西州 1 125 136 41 23 0 黄南州 2 143 181 61 57 1 果洛州 0 31 62 71 31 0 青海省 1 596 1 968 182 231 0 西宁市 0 760 1 108 321 224 1 玉树州 0 44 30 48 12 0 季节(月) 921.64 < 0.001 春(3-5) 0 253 155 799 152 0 夏(6-8) 0 76 8 2 23 0 秋(9-11) 4 424 2 021 28 55 0 冬(12-次年2) 2 1 917 2 407 341 624 0 年龄(岁) 2 891.12 < 0.001 ﹤5 1 1 112 1 134 363 275 0 5~ 3 613 1 701 495 283 1 15~ 1 254 840 92 80 0 25~ 1 513 768 191 163 1 ≥60 0 178 148 29 53 0 注:a季H1:H1N1;b季H3:H3N2;cH1NI (pdm09):新甲型H1N1;dBV:乙型Victoria系; eBY:乙型Yamagata系。 表 2 2009-2018年青海省流感病毒阳性检出率[n(%)]
Table 2. The positive detection rates of influenza virus in Qinghai province from 2009 to 2018[n(%)]
变量 总计 阳性 阴性 χ2值 P值 地区(CDC) 946.14 < 0.001 格尔木 4 590(7.29) 202(4.40) 4 388(95.60) 海北州 6 898(10.95) 1 224(17.74) 5 674(82.26) 海东市 4 438(7.04) 823(18.54) 3 615(81.46) 海南州 3 931(6.24) 552(14.04) 3 379(85.96) 海西州 3 474(5.51) 326(9.38) 3 148(90.62) 黄南州 4 391(6.97) 445(10.13) 3 946(89.87) 果洛州 2 333(3.70) 195(8.36) 2 138(91.64) 青海省 15 137(24.03) 2 978(19.67) 12 151(80.33) 西宁市 16 415(26.05) 2 414(14.71) 14 001(85.29) 玉树州 1 395(2.21) 134(9.61) 1261(90.39) 季节(月) 1 800.34 < 0.001 春(3-5) 15 582(24.73) 1 360(8.73) 14 222(91.27) 夏(6-8) 8 058(12.79) 109(1.35) 7 949(98.65) 秋(9-11) 16 520(26.22) 2 532(15.33) 13 988(84.67) 冬(12-次年2) 22 842(36.26) 5 292(23.17) 17 550(76.83) 年龄(岁) 4 054.60 < 0.001 ﹤5 29 210(46.36) 2 885(9.88) 26 325(90.12) 5~ 12 981(20.60) 3 096(23.85) 9 885(76.15) 15~ 5 271(8.37) 1 267(24.04) 4 004(75.96) 25~ 12 306(19.53) 1 637(13.30) 10 669(86.70) ≥60 3 234(5.13) 408(12.62) 2 826(87.38) -
[1] 郭元吉, 王敏, 王平, 等.流感病毒变异规律的一些新发现及其在流感监测和生态学研究中的应用[J].医学研究通讯, 1990, (8): 18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=892541Guo YJ, Wang M, Wang P, et al. Some new findings of influenza virus mutation and its application in influenza surveillance and ecology research[J]. J Med Res, 1990, (8): 18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=892541 [2] 焦鹏涛, 范文辉, 孙业平, 等. B型流感病毒研究进展[J].生物工程学报. 2018, 34(6): 821-831.DOI: 10. 13345/j. cjb. 180138.Jiao PT, Fan WH, Sun YP, et al. Research advance of influenza B viruses[J]. Chin J Biotech, 2018, 34(6): 821-831. DOI: 10. 13345/j. cjb. 180138. [3] 赵杰夫, 吕中科, 赵燕妮.流行性感冒与气象条件的关系初探[J].湖北气象, 1998(2): 17-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800216176Zhao JF, Lyu ZK, Zhao YN. Preliminary study on the relationship between influenza and meteorological conditions[J]. Meteorology Journal of Hubei, 1998(2): 17-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800216176 [4] 李文娟.青藏高原(青海省)蚊虫和蚊传虫媒病毒及其与当地疾病关系的研究[D].济南: 山东大学, 2011.LI WJ. Research on the relationship between mosquito and mosquito borne arboviruses and local diseases in Qinghai-tibet plateau(Qinghai province)[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2011. [5] 王潘劳, 刘连新, 张伟勤, 等.青藏高原高海拔高寒地区建筑材料使用寿命研究[J].青海大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 23(1): 11-13.DOI: 10. 3969/j. issn. 1006-8996. 2005. 01. 003.Wang PL, Liu XL, Zhang WQ, et al. Study on the service life of building materials in the cold and high-altitude areas of Qinghai-tibet plateau[J]. J Qinghai Univ(Natural Science Edition), 2005, 23(1): 11-13. DOI: 10. 3969/j. issn. 1006-8996. 2005. 01. 003. [6] 中华人民共和国卫生部.全国流感监测方案(2010年版)[J].国际呼吸杂志, 2011, 31(2): 85-88.DOI: 10. 3760/cma. j. issn. 1673-436X. 2011. 002. 002.Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. national influenza surveillance program(2010 edition)[J]. Int J Respir, 2011, 31(2): 85-88. DOI: 10. 3760/cma. j. issn. 1673-436X. 2011. 002. 002. [7] 仇桑桑.江苏省流感流行现况及抗流感药物研究[D].南京: 南京医科大学, 2015.Qu SS. The situation of influenza epidemic and study on anti-influenza drugs in Jiangsu province[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing medical university, 2015. [8] Kasowski EJ, Garten RJ, Bridges CB. Influenza pandemic epidemiologic and virologic diversity: reminding ourselves of the possibilities[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2011, 52(Suppl 1): S44-S49.DOI: 10. 1093/cid/ciq010. [9] 郭素荣. 1960-2010年青海省气候变化的时空特征分析[D].兰州: 西北师范大学, 2012.Guo SR. Spatial and temporal characteristics of climate change in Qinghai province from 1960 to 2010[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2012. [10] 张世虎, 王一峰, 侯勤正.青海省干旱指数时空变化特征与气候指数的关系[J].草业科学, 2015, 32(12): 1980-1987.DOI: 10. 11829/j. issn. 1001-0629. 2015-0543.Zhang SH, Wang YF, Hou QZ, et al. Spatial and temporal characteristics of aridity index and association with AO and ENSO in Qinghai province[J]. Pratacult Sci, 2015, 32(12): 1980-1987. DOI: 10. 11829/j. issn. 1001-0629. 2015-0543. [11] 杨筱婷, 刘新凤, 何健, 等.甘肃省流感季节性流行特征及病原变迁研究[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(6): 763-766.DOI: 10. 3760/cma. j. issn. 0254-6450. 2017. 06. 015.Yang XT, Liu XF, He J, et al. Study on seasonal characteristics and pathogenic distribution of influenza in Gansu province of China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(6): 763-766. DOI: 10. 3760/cma. j. issn. 0254-6450. 2017. 06. 015. [12] 于德山, 李红育, 张慧, 等.甘肃省2009-2012年流感病毒流行特征分析[J].中国病毒病杂志, 2014(2): 132-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgbdbzz201402009Yu DS, Li HY, zhang H, et al. Surveillance analysis of influenza from 2009 to 2012 in Gansu province of China[J]. Chin J Viral Dis, 2014(2): 132-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgbdbzz201402009 [13] Viboud C, Wladimir JA, Simonsen L, et al. Influenza in tropical regions[J]. PLoS Med, 2006, 3(4): 468-471.DOI: 10. 1371/journal. pmed. 0030089. [14] Arkema JM, Meijer A, Meerhoff TJ, et al. Epidemiological and virological assessment of influenza activity in Europe, during the 2006-2007 winter[J]. Euro Surveill, 2008, 13(34): 18958.DOI: 10. 2807/ese. 13. 34. 18958-en. [15] 罗会明, 余宏杰.流行性感冒的预防与控制[J].华南预防医学, 2002, 28(5): 1-4.DOI: 10. 3969/j. issn. 1671-5039. 2002. 05. 001.Luo HM, Yu HJ. Prevention and control of influenza[J]. South China J Prev Med, 2002, 28(5): 1-4. DOI: 10. 3969/j. issn. 1671-5039. 2002. 05. 001. [16] 李媛.天津市流行性感冒流行特征及与气象因素关系研究[D].天津: 天津医科大学, 2011.Li Y. Research on the epidemic characteristics of influenza and its relationship with meteorological factors in Tianjin[D]. Tianjin Medical University, 2011. [17] 王伟. 2009-2014年山东省流感样病例流行特征及其与气象因素关系研究[D].济南: 山东大学, 2016.Wang W. Epidemiological characteristics of influenza-like cases and their relationship with meteorological factors in Shandong province from 2009 to 2014[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2016. -





 下载:
下载: