Epidemiological characteristics and temporal-spatial clustering analysis of tuberculosis in Guangzhou from 2010 to 2019
-
摘要:
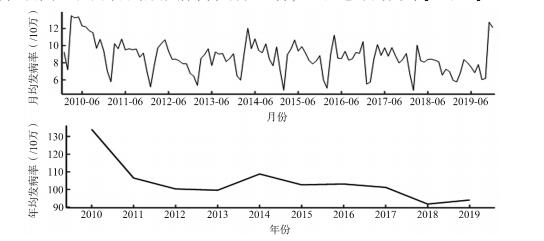
目的 分析2010-2019年广州市肺结核流行特征及时空聚集性,为制定精准防控措施提供参考依据。 方法 收集2010-2019广州市肺结核发病数据,并以街镇为尺度分析肺结核发病的空间聚集性,同时采用时空扫描统计分析时空聚集性。 结果 2010-2019年广州市共报告肺结核136 341例,年均发病率为103.48/10万,总体呈下降趋势(χ2=712.46,P < 0.001)。3~5月为发病高峰,69.59%的肺结核报告病例为男性。肺结核报告发病率全局空间自相关Moran's I介于0.088 3~0.286 0之间(均有P < 0.05),高-高聚集区主要集中在广州市南部南沙区和西北部花都区部分街镇。时空扫描统计结果探测到2个高报告发病率聚集区和1个低报告发病率聚集区,最大可能的高报告发病率聚集区覆盖花都区的赤坭镇、炭步镇等5个街镇,低发病率主要聚集在越秀区、海珠区等中心城区。 结论 2010-2019年广州市肺结核报告率总体呈下降趋势,存在时空聚集性,花都区和南沙区部分街镇应作为防控重点。 Abstract:Objective To study the epidemiological characteristics and temporal-spatial clustering of tuberculosis in Guangzhou from 2010 to 2019, and to provide evidence for developing precise prevention and control measures. Methods The data of tuberculosis incidence was collected and described in Guangzhou from 2010 to 2019. Spatial and spatiotemporal clustering of tuberculosis incidence was analyzed in the township level. Results A total of 136 341 tuberculosis cases were reported in Guangzhou from 2010 to 2019. The average annual incidence was 103.48/100 000. The overall incidence of tuberculosis showed a downward trend form 2010 to 2019 (χ2=712.46, P < 0.001). The peak time of incidence was from March to May, and 69.59% of the reported cases were male. The annual global Moran's I of reported tuberculosis incidence ranged from 0.088 3 to 0.286 0 (all P < 0.05). The high-high area was mainly concentrated in some towns including Nansha and Huadu District located in south and northwest of Guangzhou. Two high-reported and one low-reported incidence clusters were identified by spatiotemporal scanning statistic. 5 towns including Chini and Tanbu in Huadu District was the cluster area of most highest incidence. The lowest incidence cluster areas were mainly concentrated in central urban areas such as Yuexiu and Haizhu District. Conclusion The tuberculosis incidence showed a trend of generally decreasing in Guangzhou from 2010 to 2019, and there was spatiotemporal aggregation. Some streets/towns of Huadu and Nansha District should be the keypoints of prevention and control. -
表 1 2010—2019年广州市肺结核发病情况全局空间自相关分析
Table 1. Global spatial autocorrelation analysis of pulmonary tuberculosis incidence in Guangzhou from 2010 to 2019
年份 Moran’s I值 x±s Z值 P值 2010 0.182 1 -0.004 5±0.048 2 3.873 1 < 0.001 2011 0.088 3 -0.008 5±0.048 5 1.998 0 0.029 2012 0.156 6 -0.003 7±0.048 9 3.276 9 0.003 2013 0.186 1 -0.004 3±0.047 2 4.034 4 < 0.001 2014 0.188 5 -0.007 3±0.048 3 4.053 2 < 0.001 2015 0.249 7 -0.005 4±0.044 9 5.686 5 < 0.001 2016 0.286 0 -0.005 5±0.046 7 6.242 7 < 0.001 2017 0.272 6 -0.005 2±0.047 0 5.909 3 < 0.001 2018 0.268 6 -0.005 3±0.046 8 5.857 5 < 0.001 2019 0.153 2 -0.004 5±0.046 4 3.396 7 0.004 表 2 2010—2019年广州市各街镇肺结核发病情况时空扫描分析结果
Table 2. Spatial and temporal scanning analysis of tuberculosis incidence in every town in Guangzhou from 2010 to 2019
聚集区 扫描半径(km) 实际发病数 期望发病数 RR值 LLR值 P值 一级聚集区 16.21 6 532 3 636.77 1.84 962.33 < 0.001 二级聚集区1 5.43 1 560 514.84 3.05 688.33 < 0.001 二级聚集区2 11.05 18 494 23 431.00 0.76 669.35 < 0.001 -
[1] World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2019[EB/OL]. (2019-10-17)[2019-12-23]. https: //www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. [2] Yang S, Gao Y, Luo W, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of tuberculosis during urbanization in the new urban area of Nanchang City, China, 2010-2018[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2019, 16(22):4395. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16224395. [3] Chen J, Qiu Y, Yang R, et al. The characteristics of spatial-temporal distribution and cluster of tuberculosis in Yunnan Province, China, 2005-2018[J]. BMC Public Health, 2019, 19(1):1715. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-019-7993-5. [4] 林玫, 崔哲哲, 林定文, 等.广西壮族自治区2010-2015年传染性肺结核时空特征分析[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(9):1206-1211. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.09.013.Lin M, Cui ZZ, Lin DW, et al. Visual-spatial and temporal characteristics related to infectious tuberculosis epidemics in Guangxi zhuang autonomous region, 2012-2015[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(9):1206-1211. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.09.013. [5] Pfeiffer D, Robinson T, Stevenson M, et al. Spatial analysis in epidemiology[M]. New York:Oxford University Press, 2004. [6] 肖革新.空间统计实战[M].北京:科学出版社. 2018.Xiao GX. Space statistics[M]. Beijing: Science Press. 2018. [7] 毛强. 2004-2015年全国肺结核流行趋势时空特征及预测研究[D].兰州: 兰州大学, 2018.Mao Q. Study on spatial-temporal characteristic and prediction for tuberculosis trends in China during 2004-2015[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2018. [8] 孙闪华, 高志东, 赵飞, 等.北京市2005-2015年肺结核发病时空特征分析[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(6):816-820.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.06.023.Sun SS, Gao ZD, Zhao F, et al.Spatial-temporal analysis on pulmonary tuberculosis in Beijing during 2005-2015[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2018, 39(6):816-820. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.06.023. [9] 谢赐福, 许林勇, 王孝君, 等.长沙市2013-2016年肺结核流行特征及时空聚集性分析[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2018, 43(8):898-903. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2018.08.013.Xie CF, Xu LY Wang XJ, et al.Epidemiological characteristics and spatial-temporal clustering analysis on pulmonary tuberculosis in Changsha from 2013 to 2016[J]. Cent South Univ(Med Sci), 2018, 43(8):898-903. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2018.08.013. [10] 阙萍, 许小兰, 文小焱, 等.重庆市2011至2014年肺结核发病率与人均GDP水平的时空分析[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2017, 42(10):1328-1331. DOI: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.001391Que P, Xu XL, Wen XY, et al.A spatio-temporal analysis of tuberculosis incidence and regional per capita GDP in Chongqing, 2011-2014[J]. J Chongqing Med Univ, 2017, 42(10):1328-1331. doi: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.001391 [11] Li XX, Wang LX, Zhang J, et al. Exploration of ecological factors related to the spatial heterogeneity of tuberculosis prevalence in P.R. China[J]. Glob Health Action, 2014, 7:23620. DOI: 10.3402/gha.v7.23620 [12] Li T, He XX, Chang ZR, et al. Impact of new migrant populations on the spatial distribution of tuberculosis in Beijing[J]. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis, 2011, 15(2):163-168. http://labs.europepmc.org/abstract/MED/21219675 [13] Willis MD, Winston CA, Heilig CM, et al. Seasonality of tuberculosis in the United States, 1993-2008[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2012, 54(11):1553-1560. DOI: 10.1093/cid/cis235. [14] Moosazadeh M, Khanjani N, Bahrampour A. Seasonality and temporal variations of tuberculosis in the north of iran[J]. Tanaffos, 2013, 12(4):35-41. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20143122599.html [15] 李永文, 程俊, 王浩, 等.山东省2015年肺结核发病时空特征分析[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2016, 37(9):1257-1261. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450. 2016.09.015.Li YW, Cheng J, Wang H, et al. Spatial-temporal analysis of pulmonary tuberculosis in Shandong Province, 2015[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2016, 37(9):1257-1261. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.09.015. [16] 路丽苹, 洪建军, 高谦, 等.上海松江2006-2011年新登记肺结核时空分布规律及影响因素[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2014, 18(8):709-714. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jbkzzz201408005Lu LP, Hong JJ, Gao Q, et al. Spatio-temporal patterns and risk factors of tuberculosis clustering between 2006 and 2011 in Songjiang District, Shanghai[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2014, 18(8):709-714. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jbkzzz201408005 [17] 杨天池, 陈琴, 陈同, 等.宁波市利福平耐药肺结核患者家庭灾难性医疗支出及其影响因素分析[J].中国防痨杂志, 2019, 41(11):1191-1196. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgflzz201911009Yang TC, Chen Q, Chen T, et al. Analysis of catastrophic medical expenditure and its influencing factors in families of drug resistant tuberculosis patients in Ningbo[J]. Chin J Antitubercul, 2019, 41(11):1191-1196. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgflzz201911009 [18] 高健, 杜静.基于空间流行病学的肺结核发病的时空特征研究[J].现代预防医学, 2018, 45(15):2694-2696. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xdyfyx201815002Gao J, Du J. Temporal and spatial characteristics of pulmonary tuberculosis based on spatial epidemiology[J]. Modern Prevent Med, 2018, 45(15):2694-2696. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xdyfyx201815002 [19] Zhang CY, Zhao F, Xia YY, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of active pulmonary tuberculosis among elderly people in China:a population based cross-sectional study[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2019, 8(1):7. DOI: 10.1186/s40249-019-0515-y. [20] Lin HH, Ezzati M, Murray M. Tobacco smoke, indoor air pollution and tuberculosis:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS Med, 2007, 4(1):e20. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040020 [21] 陈伟, 王雪静, 王黎霞, 等.全国五省结核病与性别关系的研究[J].中国防痨杂志, 2010, 32(9):534-539. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgflzz201009015Chen W, Wang XJ, Wang LX, et al. TB and Gender in five provinces of China Chinese[J]. Chin J Antitubercul, 2010, 32(9):534-539. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgflzz201009015 -





 下载:
下载: