Analysis of spatial clustering and influencing factors of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Nanning based on Nuclear Density and Geodetector
-
摘要:
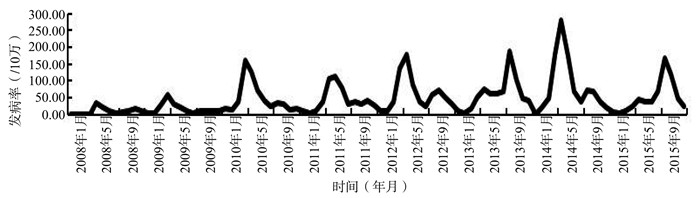
目的 分析2008-2015年南宁市手足口病(hand, foot and mouth disease, HFMD)空间聚集及影响因素,为南宁市防控HFMD提供参考。 方法 收集南宁市2008-2015年HFMD疫情数据,通过核密度方法分析空间聚集,通过地理探测器分析气象因素与社会经济因素对发病的影响。 结果 2008-2015年南宁市累计报告HFMD 326 785例,年均发病率为505.24/10万,发病高峰主要集中在4-7月。核密度分析显示HFMD存在明显的空间聚集,其中8年均出现聚集的地区是兴宁区、青秀区、江南区、良庆区和西乡塘区五个区的交界处及马山县的部分地区;地理探测器分析发现气象因素的影响大于社会经济因素的影响,且因素间的交互作用大于它们的单独作用。气温和相对湿度的单独作用及交互作用均是最强的,交互作用最大q值可达0.71(P<0.001)。 结论 2008-2015年南宁市HFMD受气象因素影响较大,社会经济因素的影响可能存在双向作用,中心城区和部分基层地区是防控的关注点。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the spatial clustering and influencing factors of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) in Nanning during the period from 2008 to 2015, so as to provide reference for HFMD prevention and control in Nanning. Methods The information about HFMD in Nanning from 2008 to 2015 was collected, spatial clustering was analyzed by nuclear density, and the effects of meteorological factors and socioeconomic factors on HFMD incidence was analyzed by Geodetector. Results A total of 326 785 HFMD cases were reported from 2008 to 2015 in Nanning. The average annual incidence was 505.24/100 000 with the peak incidence concentrating from April to July. The nuclear density analysis showed that there was obvious spatial clustering of HFMD. The areas of clustering in all eight years were the junction of five districts: Xingning District, Qingxiu District, Jiangnan District, Liangqing District and Xixiangtang District, and the parts of Mashan County. The Geodetector analysis revealed that meteorological factors had stronger impact on HFMD than socioeconomic factors, and the interactive effects between factors were stronger than their individual effects. Both the individual and interactive effects of temperature and relative humidity were the strongest, with interactions up to a maximum q value of 0.71 (P < 0.001). Conclusions The meteorological factors could have stronger effects on the HFMD incidence in Nanning from 2008 to 2015, the effects of socioeconomic factors may be bi-directional, urban areas and some grassroots areas should be concerned for prevention and control. -
表 1 2008-2015年南宁市报告HFMD发病率统计(/10万)
Table 1. Annual incidence rates of reported HFMD in Nanning from 2008 to 2015(/100 000)
区/县 2008年 2009年 2010年 2011年 2012年 2013年 2014年 2015年 兴宁区 249.76 372.64 1 024.90 691.59 860.25 1 074.06 1 531.26 1 007.03 青秀区 242.47 262.31 692.86 529.64 744.40 813.93 1 143.24 710.57 江南区 138.35 322.00 738.26 709.42 964.61 983.64 1 149.65 815.03 西乡塘区 279.38 349.13 908.90 307.25 668.57 867.15 1 049.33 1 118.39 良庆区 87.91 196.56 603.93 552.60 981.91 979.86 1 263.65 709.43 邕宁区 20.30 67.69 185.70 623.90 630.09 690.50 1 030.33 360.70 武鸣县 94.19 188.04 598.71 399.27 770.18 552.70 983.34 606.64 隆安县 77.77 246.46 264.76 567.88 1 166.42 1 415.60 1 705.12 824.41 马山县 205.34 194.65 596.50 802.42 1 122.61 776.63 1 233.23 622.51 上林县 109.74 149.76 938.05 372.22 569.09 645.36 1 393.39 498.97 宾阳县 50.95 106.25 532.02 512.82 786.41 472.48 949.50 377.91 横县 58.02 174.45 296.90 659.89 282.86 320.09 370.06 202.71 合计 130.32 214.71 603.69 539.01 744.32 744.81 1 050.39 603.91 表 2 2008-2015年各影响因素的独立作用(q值)
Table 2. Individual effects of each impact factor from 2008 to 2015 (q value)
年 RHU TEM POP GDP PRE 2008 0.18 0.14 0.14 0.18 0.15 2009 0.09 0.15 0.15 0.20 0.04 2010 0.12 0.21 0.25 0.17 0.08 2011 0.34 0.36 0.12 0.10 0.07 2012 0.36 0.33 0.11 0.14 0.07 2013 0.03 0.15 0.17 0.10 0.13 2014 0.38 0.26 0.18 0.17 0.09 2015 0.17 0.24 0.16 0.16 0.05 表 3 2008-2015年各影响因素间的交互作用(q值)
Table 3. Interactive effects among impact factors from 2008 to 2015 (q value)
年 TEM RHU PRE GDP & POP TEM & RHU TEM & GDP TEM & POP TEM & PRE RHU & POP RHU & GDP RHU & PRE PRE & POP PRE & GDP 2008 0.43 0.42 0.36 0.39 0.43 0.45 0.38 0.28 0.26 0.28 2009 0.50 0.56 0.49 0.37 0.38 0.41 0.17 0.28 0.27 0.24 2010 0.32 0.28 0.34 0.34 0.33 0.25 0.25 0.34 0.26 0.26 2011 0.62 0.52 0.52 0.46 0.53 0.50 0.47 0.20 0.16 0.13 2012 0.71 0.67 0.60 0.49 0.63 0.60 0.50 0.28 0.26 0.17 2013 0.24 0.28 0.37 0.32 0.28 0.17 0.24 0.26 0.17 0.19 2014 0.63 0.49 0.49 0.41 0.60 0.59 0.59 0.34 0.30 0.20 2015 0.58 0.53 0.50 0.47 0.42 0.43 0.37 0.28 0.24 0.19 -
[1] Hu Y, Xu L, Pan H, et al. Transmission center and driving factors of hand, foot, and mouth disease in China: a combined analysis[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2020, 14(3): e0008070. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008070. [2] Baek S, Park S, Park HK, et al. The epidemiological characteristics and spatio-temporal analysis of childhood hand, foot and mouth disease in Korea, 2011-2017[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(1): e0227803. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227803. [3] Liu H, Song G, He N, et al. Spatial-temporal variation and risk factor analysis of hand, foot, and mouth disease in children under 5 years old in Guangxi, China[J]. BMC Public Health, 2019, 19(1): 1491. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-019-7619-y. [4] 刘言玉, 刘志东, 劳家辉, 等.南宁市2008-2011年气象因素对手足口病的影响及其交互作用[J].山东大学学报(医学版), 2018, (8): 95-100. DOI: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2018.165.Liu YY, Liu ZD, Lao JH, et al. Effect of meteorological factors and their interaction on hand-foot-mouth disease in Nanning City, China during 2008 to 2011[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Health Sciences), 2018, (8): 95-100. DOI: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2018.165. [5] Xu C, Zhang X, Wang L, et al. Effects of temperature fluctuations on spatial-temporal transmission of hand, foot, and mouth disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 2541. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-59265-z. [6] Xu Z, Hu W, Jiao K, et al. The effect of temperature on childhood hand, foot and mouth disease in Guangdong Province, China, 2010-2013: a multicity study[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2019, 19(1): 969. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-4594-y. [7] 阳益萍, 陈敏玫, 居昱, 等. 2008-2014年广西手足口病流行病学及病原分布特征[J].应用预防医学, 2015, (6): 365-368, 372. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GXYX201506001.htmYang YP, Chen MM, Ju M, et al. Epidemiology and pathogen distribution of hand-foot-mouth disease in Guangxi, 2008-2014[J]. Applied Prev Med, 2015, (06): 365-368, 372. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GXYX201506001.htm [8] 南宁市统计局.南宁统计年鉴[M].南宁:中国统计出版社, 2019.Nanning Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Nanning Statistical Yearbook[M]. Nanning: China Statistics Press, 2019. [9] 施迅, 王法辉.地理信息技术在公共卫生与健康领域的应用[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2016: 33-56.Shi X, Wang FH. Applications of geospatial information technologies in public health[M]. Beijing: High Education Press, 2016: 33-56. [10] 王劲峰, 廖一兰, 刘鑫.空间数据分析教程(第二版)[M].北京:科学出版社, 2019: 107-119.Wang JF, Liao YL, Liu X. Spatial data analysis course(second edition)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 107-119. [11] 王劲峰, 徐成东.地理探测器:原理与展望[J].地理学报, 2017, (1): 116-134.DOI: 10.11821/dlxb201701010.Wang JF, Xu CD. Geodetector: Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, (1): 116-134. DOI: 10.11821/dlxb201701010. [12] Xu CD. Spatio-Temporal Pattern and Risk Factor Analysis of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease Associated with Under-Five Morbidity in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region of China[J]. Int J Env Res Pub He, 2017, 14(4):416. DOI:ARTN.416 10.3390/ijerph14040416. [13] 蒋丽娜, 谭毅, 王晶, 等. 2008-2015年广西手足口病流行病学特征及时空聚集性分析[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2017, 21(4): 340-344. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.04.005.Jiang LN, Tan Y, Wang J, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and temporal-spatial clustering of hand, foot and mouth disease in Guangxi from 2008 to 2015[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2017, 21(4): 340-344. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.04.005. [14] 李梅, 邱宝强, 颜云盈. 2013-2015年南宁市手足口病流行病学及临床特征分析[J].广西医学, 2017, (1): 132-134. DOI:10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304. 2017.01.43.Li M, Qiu BQ, Yan YY. Analysis on epidemiological and clinical characteristics of hand, foot and mouth disease in Nanning, 2013-2015[J]. Guangxi Med J, 2017, (1): 132-134. DOI:10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304. 2017.01.43. [15] 李东明, 林明, 李颖丰, 等. 2012-2016年南宁市重症手足口病流行病学分析[J].中华全科医学, 2018, (9): 1554-1557. DOI: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000423.Li DM, Lin M, Li YF, et al. Epidemiological analysis of severe hand-foot-mouth disease in Nanning from 2012 to 2016[J]. Chinese Journal of General Practice, 2018, (9): 1554-1557. DOI: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000423. [16] He X, Dong S, Li L, et al. Using a Bayesian spatiotemporal model to identify the influencing factors and high-risk areas of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) in Shenzhen[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2020, 14(3): e0008085. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.000808.5 [17] 陈婷, 汤洪洋, 黄成伟, 等.南宁市幼教人员手足口病核心知识知晓现状和健康教育需求调查[J].健康教育与健康促进, 2020, 15(3): 280-283. DOI: 10.16117/j.cnki.31-1974/r.202003019.Chen T, Yang HY, Huang CW, et al. A Survey on the current situation of the knowledge of HFMD and the needs of health education among preschool education staff in Nanning[J]. Health Education and Health Prornotion, 2020, 15(3): 280-283. DOI: 10.16117/j.cnki.31-1974/r.202003019. [18] 阳益萍, 谭毅, 莫建军, 等.手足口病高发地区儿童家长防治知识知信行调查[J].应用预防医学, 2017, (1): 18-22. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxyfyx201701004Yang YP, Tan Y, Mo JJ, et al. Investigation on knowledge-attitude-practice of hand-foot-mouth disease among parents of children in high prevalence areas[J]. Applied Prev Med, 2017, (1): 18-22. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxyfyx201701004 -





 下载:
下载: