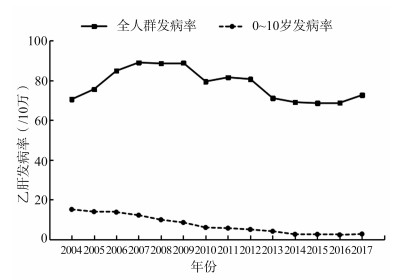
Incidence trend of hepatitis B among people aged 0-10 years in China from 2004 to 2017
-
摘要:
目的 分析2004-2017年全国0~10岁人群乙型肝炎(简称乙肝)发病趋势。 方法 2004-2017年0~10岁人群乙肝发病数据来自国家公共卫生科学数据中心。应用Joinpoint回归分析模型分析发病趋势变化,计算年均变化百分比和年度变化百分比。构建年龄-时期-队列模型,分析年龄、时期和出生队列对乙肝发病趋势变化的影响。 结果 2004-2017年全国0~10岁人群新发乙肝病例共17 007万例,发病率为7.74/10万。Joinpoint回归分析模型结果显示,2004-2017年0~10岁人群的乙肝发病率总体呈下降趋势(AAPC=-12.060 45,P<0.001),2015-2017年(APC=2.28,P=0.907 7)呈无规律变化。出生队列分析发现出生年代越晚的人群,乙肝发病率越低。同时,年龄-时期-队列模型结果表明,0~10岁人群乙肝发病率变化受到年龄、时期和队列因素的影响(均有P<0.001)。 结论 2004-2017年全国0~10岁人群的乙肝发病率总体不断降低,2015-2017年间下降趋势有所放缓。建议进一步加强对乙肝的防制措施,不断降低乙肝发病风险。 -
关键词:
- 乙型肝炎 /
- 发病率 /
- 趋势分析 /
- 年龄-时期-队列模型
Abstract:Objective To analyze the incidence trend of hepatitis B among people aged 0-10 years old in China from 2004 to 2017. Methods The data of hepatitis B incidence among people aged 0-10 years old from 2004 to 2017 was used from the National Public Health Science Data Center. The incidence trend was analyzed by Joinpoint regression, and the average percent change and the annual percent change were calculated. At the same time, the age-period-cohort model was constructed to analyze the impalt of age, period and birth cohort on the trend of hepatitis B. Results From 2004 to 2017, there were 170 700 new cases of hepatitis B among the 0-10 years old in China, and the incidence rate was 7.74/100 000. Besides, the results of Joinpoint regression showed that the incidence rate of hepatitis B among people aged 0-10 years old presented a general downward trend from 2004 to 2017 (AAPC=-12.060 45, P < 0.001), and there was an irregular change from 2015 to 2017 (APC=2.28, P=0.9077). Birth cohort analysis showed that the incidence rate of hepatitis B was lower in the later generation. Meanwhile, the results of the age-period-cohort model showed that the incidence rate of hepatitis B among the 0-10 years old population was significantly influenced by age, period and cohort (all P < 0.001). Conclusions From 2004 to 2017, the incidence of hepatitis B among people aged 0-10 years old in China has decreased continuously, and the downward trend has slowed down. It is suggested to strengthen the prevention and control of hepatitis B in order to reduce the risk of hepatitis B. -
Key words:
- Hepatitis B /
- Incidence rate /
- Trend analysis /
- Age-period-cohort model
-
表 1 2004-2017年全国0~10岁人群乙肝发病率APC模型检验(Wald检验)
Table 1. The APC model test of the incidence rate of hepatitis B among the whole population and 0-10 years old in China, 2004-2017 (Wald Tests)
零假设 χ2值 df值 P值 全局变化(Net Drift)= 0 1788.787 9 1 <0.001 总年龄偏差(All Age Deviations)= 0 352.830 9 8 <0.001 总时期偏差(All Period Deviations)= 0 225.003 4 12 <0.001 总队列偏差(All Cohort Deviations)= 0 660.709 6 21 <0.001 全时期RR(All Period RR)= 1 1910.706 5 13 <0.001 全队列RR(All Cohort RR)= 1 2418.131 0 22 <0.001 所有局部变化(All Local Drifts)=全局变化(Net Drift) 561.820 3 10 <0.001 -
[1] Mitchell T, Armstrong GL, Hu DJ, et al. The increasing burden of imported chronic hepatitis B--United States, 1974-2008[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(12). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027717 [2] Han L, Zhang HW, Xie JX, et al. A meta-analysis of lamivudine for interruption of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus[J]. World J Gastroentero, 2011, 17(38): 4321-4333. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i38.4321 [3] Schweitzer A, Horn J, Mikolajczyk RT, et al. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386(10003): 1546-55. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)61412-X [4] 贾继东, 庄辉. 携手推动中国慢性乙型肝炎治疗的可及性[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(4): 613-614. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2016.04.001Jia JD, Zhuang H. Working together to promote the accessibility of chronic hepatitis B treatment in China[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(4): 613-614. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2016.04.001 [5] 曾妮, 叶兴, 黄河浪. 乙肝免疫球蛋白联合乙肝疫苗阻断乙型肝炎母婴传播的系统评价[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2017, 21(1): 48-51, 60. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.01.011Zeng Ni, Ye xing, Huang HL, A systemic review on the effect of hepatitis B immunoglobulin with hepatitis B vaccines on preventio[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2017, 21(1): 48-51, 60. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.01.011. [6] NATIONAL CANCER INSTITUTE. Joinpoint Trend Analysis Software, Version 4.4[EB/OL]. (2017-01-04)[2018-03-05].[EB/OL]. https://surveillance.cancer.gov/joinpoint/. [7] Kim HJ, Fay MP, Feuer EJ, et al. Permutation tests for joinpoint regression with applications to cancer rates[J]. Stat Med, 2000, 19(3): 335-351. DOI:10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(20000215)19:3<335::aid-sim336>3.0.co;2-z [8] Iqbal SA, Winston CA, Bardenheier BH, et al. Age-period-cohort analyses of tuberculosis incidence rates by nativity, United States, 1996-2016[J]. 2018, 108(S4): S315-S320. DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2018.304687 [9] Li Z, Wang P, Gao G, et al. Age-period-cohort analysis of infectious disease mortality in urban-rural China, 1990-2010[J]. Int Jor Equity Health, 2016, 15(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12939-016-0343-7 [10] 王辛未, 孙群露, 饶展宏, 等. 2005-2016年深圳市宝安区丙型肝炎报告发病率的年龄-时期-队列分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2018, 24(3): 268-271. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2018.03.15Wang XW, Sun QL, Rao ZH, et al. An age-period-cohort analysis of hepatitis C reported incidence in Bao'an District, Shenzhen (2005-2016)[J]. Chin J AIDS STD, 2018, 24(3): 268-271. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2018.03.15 [11] Rosenberg PS, Check DP, Anderson WF. A web tool for age-period-cohort analysis of cancer incidence and mortality rates[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2014, 23(11): 2296-2302. DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0300. [12] Qu C, Chen T, Fan C, et al. Efficacy of neonatal HBV vaccination on liver cancer and other liver diseases over 30-year follow-up of the Qidong hepatitis B intervention study: a cluster randomized controlled trial[J]. PLoS Med, 2014, 11(12): e1001774. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001774 [13] 李栋梁, 汤仁树, 刘振武, 等. 乙肝免疫球蛋白在乙肝感染孕妇产前阻断中的作用[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2016, 20(9): 885-887, 892. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.09.006.Li DL, Tang RS, Liu ZW, et al. Effects of the hepatitis B immune globulin on the antenatal interruption of pregnant women infected[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2016, 20(9): 885-887, 892. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.09.006. [14] 刘小锦, 李文龙, 彭友悦, 等. 四川省绵阳市1~12岁儿童乙肝表面抗原和乙肝表面抗体的分布现况[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2018, 49(2): 304-308. DOI: 10.13464/j.scuxbyxb.2018.02.031Liu XJ, Li WL, Peng YY, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigens and hepatitis B surface antibodies in 1-12 Years-old children in Mianyang, Sichuan[J]. J Sichuan Univ (Med Sci Edi), 2018, 49(2): 304-308. DOI: 10.13464/j.scuxbyxb.2018.02.031 [15] 郭艺玮, 王宗武, 吴疆, 等. 北京市1992—2013年乙肝疫苗计划免疫对慢性乙型肝炎成本效果评价[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2020, 36(10): 1467-1470. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws1123505Guo YW, Wang ZW, Wu J, et al. Cost-effectiveness of hepatitis B vaccine immunization program for chronic hepatitis B in Beijing from 1992 to 2013[J]. Chin J Public Health, 2020, 36(10): 1467-1470. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws1123505 [16] 徐英, 张培, 刘建华, 等. 农村乙型肝炎家庭中学龄前儿童乙型肝炎病毒血清学感染模式研究[J]. 中国病毒病杂志, 2019, 9(1): 12-17. DOI: 10.16505/j.2095-0136.2019.0006Xu Y, Zhang P, Liu JH, et al. Serologic patterns of hepatitis B virus infections among rural preschool children after implementing the hepatitis B mother-to-child transmission program in Yichang city, Hubei Province of China[J]. Chin J Viral Dis, 2019, 9(1): 12-17. DOI: 10.16505/j.2095-0136.2019.0006 [17] 闫永平, 张维璐, 苏海霞, 等. 我国乙型病毒性肝炎防治研究新进展和面临的挑战[J]. 中国热带医学, 2019, 19(10): 916-921. DOI: 10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2019.10.03Yan YP, Zhang WL, Su HX, et al. Research progress and challenges for hepatitis B prevention and treatment in China[J]. Chin Trop Med, 2019, 19(10): 916-921. DOI: 10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2019.10.03 [18] 张顺祥, 孙盼盼, 夏云. 我国2006-2030年乙肝免疫预防经济学效果的评价和预测[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(7): 741-746. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.07.020.Zhang SX, Sun PP, Xia Y. Evaluation and forecast for economic outcomes of hepatitis B immunoprophylaxis strategies in China from 2006 to 2030[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(7): 741-746. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.07.020. [19] 刘兰, 汪俊华, 黄文湧, 等. 贵州省少数民族地区乙肝防治知识、态度、行为现况调查[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2015, 19(11): 1092-1095, 1100. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2015.11.004.Liu L, Wang JH, Huang WY, et al. A cross-sectional investigation of hepatitis B prevention knowledge, attitude and practice in minority areas of Guizhou Province[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2015, 19(11): 1092-1095, 1100. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2015.11.004. [20] 刘彩, 李莹, 王晓方, 等. 天津郊县居民风险态度对乙型肝炎疫苗接种行为的影响研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(1): 45-49. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.01.010.Liu C, Li Y, Wang XF, et al. Study on the influence of risk attitude to hepatitis B vaccination behavior of residents in suburban areas[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(1): 45-49. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.01.010. [21] 刘和平. 125名新生儿接种乙肝疫苗及低/无应答者再免疫效果分析[J]. 实用预防医学, 2016, 23(3): 350-352. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2016.03.030.Liu HP. Analysis on the effect of reimmunization of 125 newborns with low/none response to hepatitis B[J]. Pract Prevent Med, 2016, 23(3): 350-352. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2016.03.030. -





 下载:
下载: