Temporal-spatial distribution characteristics and its influencing factors of tuberculosis epidemic in the Chinese mainland from 2014 to 2018
-
摘要:
目的 分析2014-2018年中国大陆31个省份结核病发病率受每千人床位数、人均国内生产总值(gross domestic product, GDP)、人口密度与全年日照时数等因素影响的时空变化特征,为今后结核病的防治提供理论依据。 方法 通过空间自相关分析,探究各年份中国大陆结核病发病的时空集聚性;建立时空加权Logistic回归分析模型,揭示结核病发病的时空非平稳性,同时与经典Logistic回归分析模型拟合结果相比较。 结果 2014-2018年中国大陆结核病发病率全局空间Moran's I指数分别为0.43、0.44、0.47、0.49、0.37,呈现一定的时空相关性;时空加权Logistic回归分析模型系数函数取值在(-1,1)区间波动,能很好反映结核病发病的时空异质性,各系数函数可信区间均不含0,通过时空非平稳性检验。多项拟合优度检验结果均优于经典Logistic回归分析模型。 结论 中国大陆31个省份结核病发病率与四个宏观因素密切相关,各地区需因时因地制宜制定区域防控策略。 -
关键词:
- 结核病 /
- 时空自相关 /
- 时空加权Logistic回归分析模型 /
- 时空非平稳性
Abstract:Objective The number of beds per thousand, gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, population density and annual sunshine hours were investigated to analyze the spatio-temporal characteristics of tuberculosis incidence of 31 provinces in the Chinese mainland from 2014 to 2018, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and control of the spread of tuberculosis in the future. Methods The spatial autocorrelation analysis was performed to explore the spatio-temporal agglomeration of the incidence of tuberculosis in the Chinese mainland in each year. A geographically and temporally weighted Logistic regression analysis model was established to reveal the spatio-temporal non-stationarity of tuberculosis incidence, and to compare the fitting results with the classic Logistic regression analysis model. Results The global spatial Moran's I index of tuberculosis incidence in the Chinese mainland from 2014 to 2018 were 0.43, 0.44, 0.47, 0.49, 0.37, showing a certain spatiotemporal correlation. The coefficient function of the geographically and temporally weighted Logistic regression analysis model fluctuated in the interval (-1, 1), and could reflect the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of tuberculosis well. The confidence interval of each coefficient function did not contain 0, which had spatio-temporal non-stationarity. The results of the goodness of fit test were better than the classic Logistic regression analysis model. Conclusions The incidence of tuberculosis in 31 provinces in the Chinese mainland was closely related to four macro factors, and appropriate strategies should be formulated for tuberculosis prevention and control according to the difference of regional social macro factors. -
表 1 2014-2018年中国大陆结核病发病率时空相关性分析结果
Table 1. The spatio-temporal correlation of tuberculosis incidence in the Chinese mainland from 2014 to 2018
年份(年) 全局Moran's I指数 P值 2014 0.43 0.001 2015 0.44 0.001 2016 0.47 0.001 2017 0.49 0.001 2018 0.37 0.002 表 2 2014-2018年中国大陆结核病发病率宏观指标分布表(/10万)
Table 2. Distribution of macro-indicators of tuberculosis incidence in the Chinese mainland from 2014 to 2018 (/100 000)
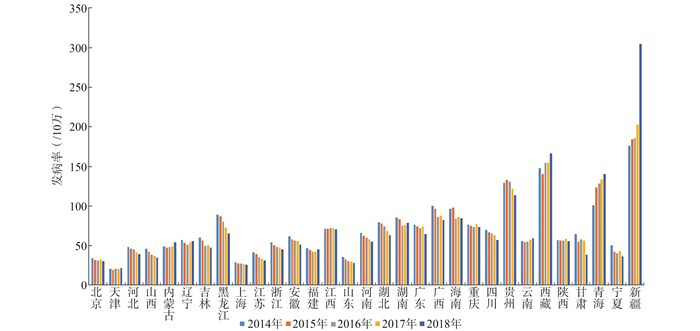
年份(年) 最小值 P25 P50 P75 最大值 四分位间距 中国大陆发病率 2014 21.27 48.15 61.84 85.88 176.00 37.73 65.63 2015 19.52 44.82 56.66 83.00 184.53 38.18 63.42 2016 21.14 42.74 56.77 75.50 185.66 32.76 61.00 2017 20.91 42.79 57.53 76.07 202.59 33.28 60.53 2018 21.39 38.71 55.81 73.37 304.94 34.66 59.27 表 3 GTWLR模型与LR模型系数函数估计值范围
Table 3. Range of coefficient function estimates of GTWLR and LR
系数 宏观因素 最小值 P25 P50 P75 最大值 LR模型系数值 β1 每千人床位数 -0.507 -0.102 0.122 0.220 0.744 0.08 β2 人均GDP -0.883 -0.127 -0.081 -0.002 0.447 -0.10 β3 人口密度 -1.297 -0.047 -0.007 0.043 1.120 -0.01 β4 全年日照时数 -1.225 -0.482 -0.310 -0.057 1.009 -0.06 表 4 时空非平稳性检验
Table 4. Spatio-temporal non-stationary test
系数 β1 β2 β3 β4 GTWLR (0.070,0.140) (-0.120,-0.050) (-0.150,-0.010) (-0.360,-0.230) LR (0.010,0.160) (-0.140,-0.070) (-0.020,0.001) (-0.170,0.050) 表 5 拟合优度检验
Table 5. Goodness of fit test
回归模型 AICc R2值 RSS GTWLR 584.71 0.97 103.18 LR 855.35 0.45 2 120.57 表 6 时空加权Logistic回归分析模型系数函数分布
Table 6. Distribution of coefficient function of geographically and temporally weighted Logistic regression analysis model
β变化区间 区间内地区分布 β1 (-0.35, 0.00) 吉林、黑龙江、广西、陕西、甘肃、青海 (0.00, 0.23) 内蒙古、辽宁、江苏、浙江、安徽、福建、江西、湖北、湖南、广东、海南、贵州、云南、西藏、宁夏、新疆 (0.23, 0.60) 北京、天津、河北、山西、山东、河南、重庆、四川、上海 β2 (-0.63, -0.32) 重庆、四川、云南、贵州 (-0.32, 0.00) 北京、天津、河北、山西、辽宁、吉林、黑龙江、上海、江苏、浙江、安徽、福建、江西、山东、河南、湖北、湖南、广东、广西、海南 (0.00, 0.36) 内蒙古、西藏、陕西、甘肃、青海、宁夏、新疆 β3 (-1.18, -0.66) 西藏、甘肃、青海、宁夏 (-0.66, 0.00) 北京、山西、内蒙古、辽宁、吉林、黑龙江、上海、江苏、浙江、安徽、福建、江西、湖北、新疆 (0.00, 0.58) 天津、河北、山东、河南、湖南、广东、广西、海南、重庆、四川、贵州、云南、陕西 β4 (-0.97, -0.64) 甘肃、青海、宁夏 (-0.64, 0.00) 北京、天津、河北、山西、内蒙古、辽宁、吉林、黑龙江、上海、江苏、浙江、安徽、福建、山东、河南、湖北、湖南、广西、重庆、四川、贵州、云南、西藏、陕西 (0.00, 0.97) 江西、广东、海南、新疆 -
[1] World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2018[R]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2018. [2] 路丽苹, 洪建军, 高谦, 等. 上海松江2006-2011年新登记肺结核时空分布规律及影响因素[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2014, 18(8): 709-714. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201408005Lu LP, Hong JJ, Gao Q, et al. Spatio-temporal patterns and risk factors of tuberculosis clustering between 2006 and 2011 in Songjiang District, Shanghai[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2014, 18(8): 709-714 http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201408005 [3] Wang T, Xue FZ, Chen YJ, et al. The spatial epidemiology of tuberculosis in Linyi City, China, 2005-2010[J]. BMC Public Health, 2012, 12: 885. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-885. [4] Sun WY, Gong JH, Zhou JP, et al. A spatial social and environmental study of tuberculosis in China using statistical and GIS technology[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2015, 12(2): 1425-1448. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph120201425. [5] 饶华祥, 徐莉立, 蔡芝锋, 等. 空间截面回归模型在肺结核病社会影响因素生态学分析中的应用[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2018, 35(5): 646-649, 654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201805002.htmRao HX, Xu LL, Cai ZF, et al. The application of space cross-section regression model in the ecological analysis of tuberculosis related social factors[J]. Chin J Health Statistics, 2018, 35(5): 646-649, 654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201805002.htm [6] 王微, 靳圆圆, 王泽, 等. 新疆地区结核病空间分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2016, 33(4): 672-674. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201604033.htmWang W, Jin YY, Wang Z, et al. Study on the spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of tuberculosis in Xinjiang[J]. Chin J Health Statistics, 2016, 33(4): 672-674. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201604033.htm [7] 阿提开木·吾布力. 新疆活动性结核病的空间分布特征、季节性以及影响因素的生态学研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2016.Atikaimu W. Spatial distribution, seasonality and influencing factors of active tuberculosis in Xinjiang, an ecological study[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Medical University, 2016. [8] 王庆喜, 蒋烨, 陈卓咏. 区域经济研究实用方法: 基于ArcGIS、GeoDa和R的运用[M]. 北京: 经济科学出版社, 2014.Wang QX, Jiang Y, Chen ZY. Practical methods of regional economic research: based on the application of ArcGIS, GeoDa and R[M]. Beijing: Economic Science Press, 2014. [9] 梅长林, 王宁. 近代回归分析方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.Mei CL, Wang N. Modern regression analysis method[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. [10] Huang B, Wu B, Barry M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices[J]. Int J Geogr Inf Sci, 2010, 24(3): 383-401. DOI: 10.1080/13658810802672469. [11] 王静, 胡镜涛. 对临床试验中显著性检验、区间检验及置信区间检验之间的关系一致性的认识[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2011, 16(3): 281-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLZL201103012.htmWang J, Hu JT. Understanding of the consistency of the relationship among the significance test, interval test and confidence interval test in clinical trials[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2011, 16(3): 281-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLZL201103012.htm [12] 孙舒曼, 李智明, 张辉国, 等. 2011-2016年中国艾滋病疫情时空特征分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(12): 1207-1210, 1215. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.002.Sun SM, Li ZM, Zhang HG, et al. Temporal-spatial characteristic analysis of AIDS/HIV epidemic during 2011-2016 in China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(12): 1207-1210, 1215. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.002. [13] 王永. 肺结核发病的时空聚集性研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2008.Wang Y. Spatio-temporal cluster research of tuberculosis incidence[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2008. [14] 国务院办公厅. 国务院办公厅关于印发"十三五"全国结核病防治规划的通知[J]. 中华人民共和国国务院公报, 2017(7): 32-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYB201707007.htmGeneral Office of the State Council. Notice of the General Office of the State Council on printing and distributing the Thirteenth Five-Year Plan national tuberculosis prevention and control plan[J]. The State Council Bulletin of the People's Republic of China, 2017(7): 32-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYB201707007.htm [15] 严非. 中国结核病控制现状、问题与对策-社会评价案例研究[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2007.Yan F. Current situation and strategy for tuberculosis control in China-social assessment study in four provinces[D]. Shanghai: Fudan University, 2007. [16] 汪业胜, 王建美, 王伟炳. 2004-2016年我国结核病流行的时空特征分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(4): 526-531. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20190614-00441.Wang YS, Wang JM, Wang WB. Temporal-spatial distribution of tuberculosis in China, 2004-2016[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2020, 41(4): 526-531. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20190614-00441. [17] 胡文穗, 刘伟, 侯建荣, 等. 2010-2019年广州市肺结核流行特征及时空聚集性[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2020, 24(9): 1037-1041. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.09.009.Hu WS, Liu W, Hou JR, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and temporal-spatial clustering analysis of tuberculosis in Guangzhou from 2010 to 2019[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2020, 24(9): 1037-1041. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.09.009. -





 下载:
下载: