Smoking affects the development of rheumatoid arthritis through the IRF4 signaling pathway
-
摘要:
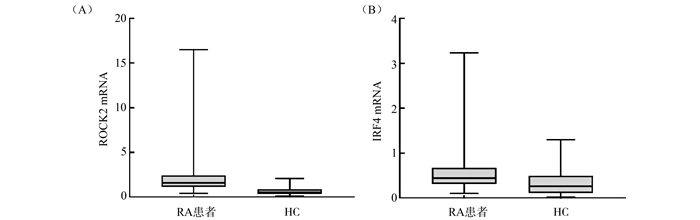
目的 比较吸烟与非吸烟类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis, RA)患者及健康对照(healthy control, HC)外周血单个核细胞(peripheral blood mononuclear cell, PBMC)中干扰素调节因子4(interferon regulatory factor 4, IRF4)、Rho相关蛋白激酶2(Rho-associated protein kinase 2, ROCK2)mRNA的表达水平,探讨吸烟是否通过IRF4信号通路途径影响RA的发病。 方法 实时荧光定量聚合酶反应(real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, RT-qPCR)检测PBMC中芳香烃受体(aryl hydrocarbon receptor, AHR)、细胞色素P4501A1(cytochrome P4501A1, CYP1A1)及ROCK2、IRF4 mRNA的表达水平,分析ROCK2、IRF4 mRNA与AHR、CYP1A1 mRNA的表达水平之间相关性,以及各mRNA表达水平与RA患者红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ESR)、C反应蛋白(C-reactive protein, CRP)、抗环瓜氨酸多肽抗体(anti-cyclic citrulline peptide antibody, A-CCP)、类风湿因子(rheumatoid factor, RF)、RA患者28个关节疾病活动评分(disease activity score in 28 joints, DAS28)等临床指标的相关性。 结果 ROCK2、IRF4 mRNA表达水平在RA病例组中高于HC组,差异均有统计学意义(均有P<0.05);IRF4 mRNA表达水平在RA吸烟组中高于RA非吸烟组,差异有统计学意义(P=0.011);HC吸烟组PBMC中IRF4 mRNA表达水平高于HC非吸烟者,差异有统计学意义(P=0.004)。RA吸烟组中CYP1A1 mRNA与ROCK2及IRF4 mRNA表达水平均呈正相关,同时ROCK2、IRF4 mRNA表达水平与ESR、A-CCP、RF、关节肿胀数(swollen joint count, SJC)均呈正相关。 结论 RA患者PBMC中ROCK2、IRF4 mRNA表达水平增高,提示这两者可能参与RA的发病;吸烟可能通过活化AHR导致IRF4高表达进而参与RA的发病。 Abstract:Objective To compare the expression levels of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) and Rho-associated protein kinase 2 (ROCK2) mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) of smoking and non-smoking rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and healthy control (HC) subjects, and to investigate whether smoking is involved in RA pathogenesis through the IRF4 signaling pathway. Methods Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) method was used to detect the expression levels of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), cytochrome P4501A1 (CYP1A1) and ROCK2, IRF4 mRNA in PBMC, and to analyze the correlation between ROCK2, IRF4 mRNA and AHR, CYP1A1 mRNA expression levels, as well as the correlation between the expression levels of each mRNA and clinical indicators such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), anti-cyclic citrulline peptide antibody (A-CCP), rheumatoid factor (RF) and disease activity score in 28 joints scores in RA patients. Results ROCK2 and IRF4 mRNA expressions were higher in RA group than in HC group, and the differences were statistically significant (all P < 0.05); IRF4 mRNA expression levels was higher in RA smoking group than in RA non-smoking group, and the difference was statistically significant (P=0.011); IRF4 mRNA expression levels in PBMC of healthy smokers was higher than that of healthy non-smokers, and the difference was statistically significant (P=0.004). CYP1A1 mRNA was positively correlated with ROCK2 and IRF4 mRNA expression levels in the RA smoking group, while ROCK2 and IRF4 mRNA expression levels were positively correlated with ESR, A-CCP, RF and swollen joint count. Conclusions ROCK2 and IRF4 mRNA expression levels was increased in PBMC of RA patients, suggesting that both may be involved in the pathogenesis of RA. Smoking may be involved in the pathogenesis of RA by activating AHR leading to high IRF4 expression. -
Key words:
- Rheumatoid arthritis /
- Smoking /
- Interferon regulatory factor 4
-
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primers used in RT-qPCR experiments
项目 引物序列(5’-3’) β-actin F:CCCTGGAGAAGAGCTACGAG R:GGAAGGAAGGCTGGAAGAGT AHR F:CGTCTAAGGTGTCTGCTGGA R:TGGTGGCTGAAGTGGAGTAG CYP1A1 F:TACCTACCCAACCCTTCCCT R:AGTGCTCAATCAGGCTGTCT ROCK2 F:GAACGTCAGGATGCAGATGG R:GCCAAAGAGTCCCGTTCATC IRF4 F:CCACAGAGCCAAGCATAAGG R:CCGGTAGTACAGGCAGATGT 表 2 RA病例组与HC组的一般资料比较
Table 2. Characteristics of RA patients group and HC group
组别 例数
(例)性别
(男/女)年龄
[min~max (x±s), 岁]RA患者 60 13/47 28~80(54.38±11.70) HC 30 10/20 25~72(50.83±12.78) χ2/t值 0.015 1.316 P值 0.902 0.192 表 3 RA吸烟组与非吸烟组的一般资料比较
Table 3. Characteristics of smokers and non-smokers in RA patients
组别 例数
(例)性别
(男/女)年龄
[min~max (x±s), 岁]病程
(年)吸烟量
(支/年)RA吸烟 30 9/21 27~76(53.50±12.21) 20.80±10.40 325.20±232.90 RA非吸烟 30 4/26 28~80(55.17±11.54) 18.70±9.20 χ2/t/Z值 2.455 0.544 0.686 1.121 P值 0.117 0.588 0.735 0.162 表 4 RA吸烟组AHR、CYP1A1、ROCK2、IRF4表达量之间相关性
Table 4. Comparison between AHR/CYP1A1/ROCK2/IRF4 mRNA of RA smokers
项目 AHR CYP1A1 ROCK2 IRF4 r值 P值 r值 P值 r值 P值 r值 P值 AHR 0.258 0.128 0.233 0.215 0.211 0.264 CYP1A1 0.793 <0.001 0.792 <0.001 ROCK2 0.752 <0.001 IRF4 表 5 RA吸烟者ROCK2、IRF4 mRNA表达水平与临床指标间相关性
Table 5. Comparison between ROCK2/IRF4 mRNA and clinical characteristics of RA smokers
临床指标 IRF4 ROCK2 r值 P值 r值 P值 ESR -0.597 0.001 -0.525 0.003 CRP -0.245 0.193 -0.191 0.312 A-CCP 0.441 0.015 0.392 0.023 RF 0.373 0.042 0.659 <0.001 DAS28 0.298 0.121 0.272 0.146 TJC 0.001 0.606 0.003 0.989 SJC 0.571 0.001 0.451 0.012 吸烟量 -0.228 0.226 -0.222 0.239 -
[1] Sparks JA, Karlson EW. The roles of cigarette smoking and the lung in the transitions between phases of preclinical rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Curr Rheumatol Rep, 2016, 18(3): 15. DOI: 10.1007/s11926-016-0563-2. [2] Heluany CS, Kupa L, Viana MN, et al. In vivo exposure to hydroquinone during the early phase of collagen-induced arthritis aggravates the disease[J]. Toxicology, 2018, 408: 22-30. DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2018.06.010 [3] 程琳, 钱龙, 谭悦, 等. 芳香烃受体在类风湿关节炎患者外周血CD4+ CD25+ T细胞的表达及意义[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2016, 20(4): 379-382. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.04.014.Cheng L, Qian L, Tan Y, et al. Expression and significance of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in peripheral blood CD4+ CD25+ T of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2016, 20(4): 379-382. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.04.014. [4] Biswas PS, Gupta S, Chang E, et al. Phosphorylation of IRF4 by ROCK2 regulates IL-17 and IL-21 production and the development of autoimmunity in mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2010, 120(9): 3280-3295. DOI: 10.1172/jci42856. [5] Tousa S, Semitekolou M, Morianos I, et al. Activin-A co-opts IRF4 and AhR signaling to induce human regulatory T cells that restrain asthmatic responses[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2017, 114(14): e2891-e2900. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1616942114. [6] Nguyen NT, Nakahama T, Kishimoto T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and experimental autoimmune arthritis[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2013, 35(6): 637-644. DOI: 10.1007/s00281-013-0392-6. [7] Toh ML, Miossec P. The role of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis: new subsets and new targets[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2007, 19(3): 284-288. DOI: 10.1097/bor.0b013e32805e87e0. [8] Alunno A, Carubbi F, Giacomelli R, et al. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: new players and therapeutic targets[J]. BMC Rheumatol, 2017, 1: 3. DOI: 10.1186/s41927-017-0001-8. [9] Veldhoen M, Hirota K, Christensen J, et al. Natural agonists for aryl hydrocarbon receptor in culture medium are essential for optimal differentiation of Th17 T cells[J]. J Exp Med, 2009, 206(1): 43-49. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20081438. [10] Yamamoto M, Kato T, Hotta C, et al. Shared and distinct functions of the transcription factors IRF4 and IRF8 in myeloid cell development[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(10): e25812. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025812. [11] Esser C, Rannug A. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in barrier organ physiology, immunology, and toxicology[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2015, 67(2): 259-279. DOI: 10.1124/pr.114.009001. [12] Nguyen NT, Nakahama T, Nguyen CH, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonism and its role in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. J Exp Pharmacol, 2015, 7: 29-35. DOI: 10.2147/jep.s63549. [13] 程琳, 钱龙, 李向培, 等. 吸烟对类风湿关节炎外周血芳香烃受体的影响[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2016, 51(7): 1006-1010. DOI: 10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2016.07.019.Cheng L, Qian L, Li XP, et al. Effects of smoking on peripheral blood aryl hydrocarbon receptor of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Anhui, 2016, 51(7): 1006-1010. DOI: 10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2016.07.019. [14] Lahoti TS, John K, Hughes JM, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonism mitigates cytokine-mediated inflammatory signalling in primary human fibroblast-like synoviocytes[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013, 72(10): 1708-1716. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202639. [15] Hu T, Pan Z, Yu Q, et al. Benzo(a)pyrene induces interleukin (IL)-6 production and reduces lipid synthesis in human SZ95 sebocytes via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathway[J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, 2016, 43: 54-60. DOI: 10.1016/j.etap.2016.02.011. [16] Talbot J, Peres RS, Pinto LG, et al. Smoking-induced aggravation of experimental arthritis is dependent of aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation in Th17 cells[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2018, 20(1): 119. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-018-1609-9. [17] Chen Q, Yang W, Gupta S, et al. IRF-4-binding protein inhibits interleukin-17 and interleukin-21 production by controlling the activity of IRF-4 transcription factor[J]. Immunity, 2008, 29(6): 899-911. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.10.011. [18] Rozo C, Chinenov Y, Maharaj RK, et al. Targeting the RhoA-ROCK pathway to reverse T-cell dysfunction in SLE[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76(4): 740-747. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209850. [19] Rodríguez-Carrio J, López P, Alperi-López M, et al. IRF4 and IRGs delineate clinically relevant gene expression signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 3085. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03085. [20] Weng CH, Gupta S, Geraghty P, et al. Cigarette smoke inhibits ROCK2 activation in T cells and modulates IL-22 production[J]. Mol Immunol, 2016, 71: 115-122. DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2016.01.013. -





 下载:
下载: