Role of RIPK1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and analysis of its geneticsusceptibility
-
摘要:
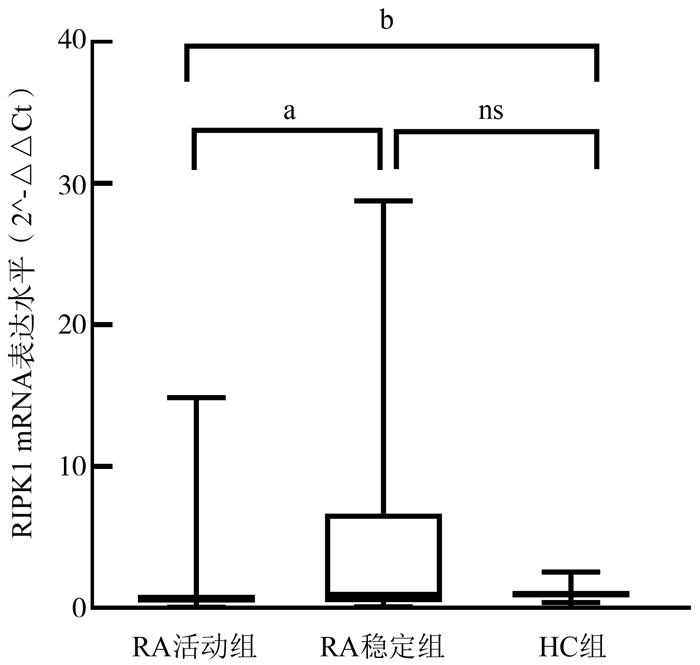
目的 分析受体相互作用蛋白激酶1(receptor interacting serine/threonine protein kinase 1, RIPK1)在类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis, RA)发病中的作用及其基因多态性与RA遗传易感性的关联。 方法 采用实时定量PCR(quantitative real-time PCR, qRT-PCR)方法检测RA和健康对照者的外周血单个核细胞(peripheral blood mononuclear cell, PBMC)中RIPK1的mRNA水平,分析其在RA发病中的作用。在RIPK1调控区和蛋白修饰功能区中筛选单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP)位点,筛选了rs111393904、rs115041708、rs1158343326、rs116040763、rs116603010、rs116696494、rs1186968649、rs1189800403、rs1193251671、rs1255389565、rs138277932、rs17548629、rs200610530、rs547953577、rs557588787、rs561972571、rs760405932、rs77736895和rs934053809共19个位点,采用iMLDR技术进行基因分型,分析RIPK1基因多态性与RA遗传易感性的关联。 结果 比较88例RA患者和85例健康对照者RIPK1 mRNA表达水平,结果显示RA组低于健康对照组(Z=3.152, P < 0.000 1);进一步比较RA活动组(50例)、RA稳定组(38例)和健康对照组三组间差异,结果显示RA活动组RIPK1 mRNA表达水平低于稳定组(Z=2.987, P=0.008 4)和健康对照组(Z=4.247, P < 0.000 1),RA稳定组与健康对照组间差异无统计学意义(Z=0.584, P>0.999 0)。对103例RA患者和90例健康对照者的SNP位点进行基因分型,结果显示RA患者上述SNP位点基因型和等位基因频率与健康对照组的差异均无统计学意义(均有P>0.05)。 结论 RIPK1对RA病情活动可能有保护作用,但其基因多态性与RA遗传易感性可能无关联。 -
关键词:
- 类风湿关节炎 /
- 受体相互作用蛋白激酶1 /
- 单核苷酸多态性
Abstract:Objective To analyze the role of receptor interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and exploring the association between gene polymorphism and genetic susceptibility to RA. Methods The mRNA level of RIPK1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of RA and healthy controls was detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), and its role in the pathogenesis of RA was analyzed. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites were screened in RIPK1 regulatory region and protein modification functional region, which include rs111393904, rs115041708, rs1158343326, rs116040763, rs11660010, rs116696494, rs1186968649, rs1189800403, rs1193251671, rs1255389565, rs138277932, rs17548629, rs200610530, rs547953577, rs557588787, rs561972571, rs760405932, rs77736895 and rs934053809. The association between RIPK1 gene polymorphism and RA susceptibility was analyzed by iMLDR. Results A total of 88 RA patients and 85 healthy controls were selected, and the expression level of RIPK1 gene in the samples was analyzed. It was found that the expression level of RIPK1 gene in the RA group was lower than that in the healthy control group (Z=3.152, P < 0.000 1). According to the active degree, RA patients were divided into RA active group (50 cases) and RA stable group (38 cases). It was found that the expression level of RIPK1 gene in the RA active group was lower than that in the RA stable group (Z=2.987, P=0.008 4) and healthy control group (Z=4.247, P < 0.000 1). There was no significant difference exist between the RA disease stable group and the healthy control group (Z=0.584, P>0.999 0). A total of 103 RA patients and 90 healthy controls were selected to extract DNA from the PBMC of each group. The genotyping results showed that the difference in genotype and allele frequency of the above SNP loci in RIPK1 gene in RA patients was not statistically significance compared with the healthy controls (all P>0.05). Conclusion RIPK1 may have a protective effect on RA disease activity, but its genetic polymorphism may not be associated with RA genetic susceptibility. -
表 1 RIPK1翻译后修饰位点对应的SNP位点
Table 1. SNP sites corresponding to post-translation modification sites of RIPK1
氨基酸位点 功能 SNP S14[10] 激酶活化标志 rs561972571 S15[10] 激酶活化标志 rs1186968649 K45[2] 突变失去激酶活性 rs111393904 S166[10] 激酶活化标志 rs138277932 T189[2] 抑制激酶激活 rs547953577,rs1193251671 S330[10] 磷酸化 rs1255389565 S333[5] 磷酸化,抑制激酶激活 rs557588787 S335[5] 磷酸化,抑制激酶激活 rs1158343326 K377[5] 激活TAK1,存活,抑制坏死 rs760405932 D138[10] 突变抑制激酶活性,挽救TBK1缺失的致死 rs1189800403,rs934053809 表 2 RIPK1关键SNP位点相关信息
Table 2. RIPK1 key SNP sites related information
SNP 染色质 染色质位点 功能变化 等位基因 rs17548629 6 3114457 - C/T rs116040763 6 3113491 p.Thr645Met C/T rs1193251671 6 3083425 p.Thr189Ile C/T rs200610530 6 3105730 p.Glu341Ser G/A rs116603010 6 3081259 p.Ile123Thr T/C rs1158343326 6 3090980 - A/G rs77736895 6 3113880 - C/T rs111393904 6 3077192 p.Lys45Asn A/C rs760405932 6 3105839 p.Lys377Thr A/C rs934053809 6 3081305 p.Asp138Glu C/G rs1186968649 6 3077102 p.Ser15Arg T/G rs138277932 6 3083357 p.Ser166Arg C/G rs116696494 6 3106044 p.His445Gln T/A rs115041708 6 3083400 p.Gly181Ser G/A/T rs1255389565 6 3104532 p.Ser330Ter C/A/T rs1189800403 6 3081303 p.Asp138Tyr G/T rs547953577 6 3083424 p.Thr189Pro A/C rs561972571 6 3077097 p.Ser14Ala T/G rs557588787 6 3090974 - C/T 表 3 RA和HC间RIPK1不同SNP位点基因型及等位基因频率分布的差异
Table 3. Allele and genotype frequencies of SNPs in the RIPK1 gene in RA patients
SNP 遗传模型 RA HC χ2值 OR(95% CI)值 P值 rs17548629 C vs. T 159/47 134/46 0.394 1.161(0.728~1.853) 0.530 CC vs. TT 62/6 50/6 0.126 1.240(0.377~4.081) 0.723 CT vs. TT 35/6 34/6 0.002 1.029(0.302~3.508) 0.963 CC+CT vs. TT 97/6 84/6 0.058 1.155(0.359~3.716) 0.809 CC vs. CT+TT 62/41 50/40 0.424 1.210(0.682~2.146) 0.515 rs77736895 C vs. T 198/8 168/12 1.515 1.768(0.706~4.427) 0.218 CC vs. TT 10/0 79/1 0.126 1.013(0.988~1.038) 0.722 CT vs. TT 8/0 10/1 0.768 1.100(0.913~1.326) 0.381 CC+CT vs. TT 103/0 89/1 1.150 1.011(0.989~1.034) 0.283 CC vs. CT+TT 95/8 79/11 1.074 1.653(0.634~4.311) 0.300 rs116696494 A vs. T 2/204 1/179 0.215 1.755(0.158~19.516) 0.643 AA vs. TT 0/101 0/89 AT vs. TT 2/101 1/89 0.217 1.762(0.157~19.766) 0.642 AA+AT vs. TT 1/101 1/89 0.008 0.881(0.054~14.295) 0.929 AA vs. AT+TT 0/103 0/90 -
[1] Paleolog E. The therapeutic potential of TNF-α blockade in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2003, 12(7): 1087-1095. DOI: 10.1517/13543784.12.7.1087. [2] Petrie EJ, Czabotar PE, Murphy JM. The structural basis of necroptotic cell death signaling[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2019, 44(1): 53-63. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2018.11.002. [3] Dondelinger Y, Delanghe T, Priem D, et al. Serine 25 phosphorylation inhibits RIPK1 kinase-dependent cell death in models of infection and inflammation[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 1729. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09690-0. [4] Dondelinger Y, Darding M, Bertrand MJ, et al. Poly-ubiquitination in TNFR1-mediated necroptosis[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2016, 73(11-12): 2165-2176. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-016-2191-4. [5] Yuan J, Amin P, Ofengeim D. Necroptosis and RIPK1-mediated neuroinflammation in CNS diseases[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2019, 20(1): 19-33. DOI: 10.1038/s41583-018-0093-1. [6] Huang Y, Chen K, Yu H, et al. Up-regulated microRNA-411 or declined RIPK1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis mice via decreased NF-κB pathway[J]. Cell Cycle, 2020, 19(6): 666-683. DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1717033. [7] Jhun J, Lee SH, Kim SY, et al. RIPK1 inhibition attenuates experimental autoimmune arthritis via suppression of osteoclastogenesis[J]. J Transl Med, 2019, 17(1): 84. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-019-1809-3. [8] Weisel K, Berger S, Thorn K, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled experimental medicine study of RIPK1 inhibitor GSK2982772 in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2021, 23(1): 85. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-021-02468-0. [9] Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 62(9): 2569-2581. DOI: 10.1002/art.27584. [10] Lafont E, Draber P, Rieser E, et al. TBK1 and IKKε prevent TNF-induced cell death by RIPK1 phosphorylation[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2018, 20(12): 1389-1399. DOI: 10.1038/s41556-018-0229-6. [11] Lin L, Wang Y, Liu L, et al. Clinical phenotype of a Chinese patient with RIPK1 deficiency due to novel mutation[J]. Genes Dis, 2020, 7(1): 122-127. DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.10.008. [12] Cuchet-Lourenco D, Eletto D, Wu C, et al. Biallelic RIPK1 mutations in humans cause severe immunodeficiency, arthritis, and intestinal inflammation[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6404): 810-813. DOI: 10.1126/science.aar2641. -





 下载:
下载: