Application of SARIMA-GRNN combined model in forecasting the monthly incidence of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever
-
摘要:
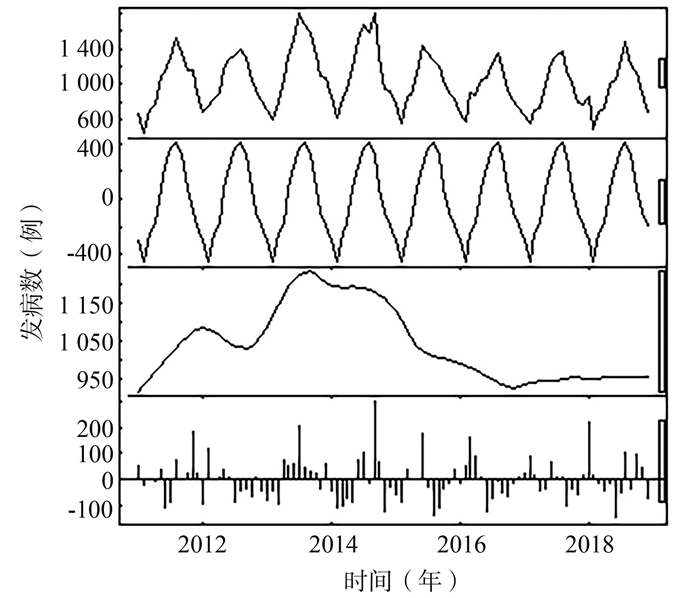
目的 建立季节性差分自回归移动平均(seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average, SARIMA)-广义回归神经网络(generalized regression neural network, GRNN)组合模型,为伤寒与副伤寒发病数的预测提供方法学上的新思路。 方法 利用2011年1月-2019年12月中国伤寒与副伤寒逐月发病数资料,分别构建SARIMA模型和SARIMA-GRNN组合模型,比较两种模型的拟合和预测效果。 结果 最优的SARIMA模型为SARIMA (2, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12,SARIMA-GRNN组合模型的最优光滑因子(spread)为0.21。评价SARIMA-GRNN组合模型拟合效果的参数均方根误差(root mean squared error, RMSE)、平均绝对误差(mean absolute error, MAE)和平均绝对百分比误差(mean absolute percentage error, MAPE)为90.08、71.44和7.07%,分别小于SARIMA模型的99.44、79.15和7.86%;评价预测效果的RMSE、MAE和MAPE为100.86、75.94和9.57%,均小于SARIMA模型的125.44、97.33和10.89%。 结论 SARIMA-GRNN组合模型比传统SARIMA模型更能拟合中国伤寒与副伤寒逐月的发病数,而且预测精度更高,可应用于伤寒与副伤寒逐月发病数的预测。 -
关键词:
- 伤寒与副伤寒 /
- 季节性差分自回归移动平均模型 /
- 广义回归神经网络 /
- 组合模型
Abstract:Objective This study aimed to establish a seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average (SARIMA)-general regression neural network (GRNN) combined model, so as to provide new methodological ideas for forecasting the incidence of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever. Methods Using data of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever from January 2011 to December 2019, the SARIMA model and the SARIMA-GRNN combined model were constructed respectively, and the fitting and forecasting effects of the two models were compared. Results The optimal SARIMA model was SARIMA (2, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12 and the optimal smoothing factor of SARIMA-GRNN combined model was 0.21. The root mean squared error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of the SARIMA-GRNN combined model fitting effect were 90.08, 71.44, and 7.07%, which were smaller than the SARIMA model's 99.44, 79.15, and 7.86% respectively. The RMSE, MAE, and MAPE of the forecasting effect were 100.86, 75.94, 9.57%, which were all smaller than 125.44, 97.33, 10.89% of the SARIMA model. Conclusions The SARIMA-GRNN combined model has a better fitting effect and higher forecasting effect than the traditional SARIMA model to forecast the monthly incidence of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever in China. It can be used to predict the monthly incidence of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever. -
Key words:
- Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever /
- SARIMA Model /
- GRNN /
- Combined Model
-
表 1 SARIMA (2, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12模型参数显著性检验
Table 1. Significance test of the SARIMA (2, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12 model parameters
模型 参数 标准差 t值 P值 ar1 -1.069 5 0.167 7 -6.377 4 < 0.001 ar2 -0.465 0 0.102 8 4.523 3 < 0.001 ma1 0.838 5 0.206 4 4.062 5 < 0.001 sma1 -0.999 9 0.331 8 -3.013 6 < 0.001 表 2 两种模型2019年逐月发病数的预测值及相对误差
Table 2. Forecast value and relative error of monthly incidence of two models in 2019
时间 实际值 SARIMA模型 SARIMA-GRNN模型 预测值 相对误差(%) 预测值 相对误差(%) 2019年1月 702 653.19 6.95 681.62 2.90 2019年2月 502 502.73 0.15 626.55 24.81 2019年3月 591 631.55 6.86 669.97 13.36 2019年4月 1 000 754.62 24.54 779.69 22.03 2019年5月 950 1 146.91 20.73 1 067.44 12.36 2019年6月 1 000 1 078.38 7.84 1 015.80 1.58 2019年7月 1 102 1 336.12 21.25 1 274.82 15.68 2019年8月 1 040 1 127.72 8.43 1 050.82 1.04 2019年9月 881 967.54 9.82 937.11 6.37 2019年10月 806 816.81 1.34 836.96 3.84 2019年11月 642 569.49 11.29 648.61 1.03 2019年12月 571 505.46 11.48 627.53 9.90 注: 相对误差=(预测值-实际值)/实际值×100%。 表 3 SARIMA模型与SARIMA-GRNN模型拟合和预测效果的比较
Table 3. Comparison of fitting and forecasting effects between SARIMA model and SARIMA-GRNN model
模型 拟合效果(2012-2018年) 预测效果(2019年) RMSE MAE MAPE(%) RMSE MAE MAPE(%) SARIMA 99.44 79.15 7.86 125.44 97.33 10.89 SARIMA-GRNN 90.08 71.44 7.07 100.86 75.94 9.57 -
[1] 张莹, 张静. 伤寒、副伤寒疾病负担研究现状[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2011, 15(5): 437-440. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201105024Zhang Y, Zhang J. The current research status of typhoid and paratyphoid disease burden[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2011, 15(5): 437-440. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201105024 [2] Fattah J, Ezzine L, Aman Z, et al. Forecasting of demand using ARIMA model[J]. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 2018, 10: 1-9. DOI: 10.1177/1847979018808673. [3] 卞子龙, 汤佳琪, 倪春辉, 等. 应用ARIMA-GRNN组合模型分析江苏尘肺病发病情况[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2019, 36(8): 755-760. DOI: 10.13213/j.cnki.jeom.2019.19046.Bian ZL, Tang JQ, Ni CH, et al. Application of ARIMA-GRNN combined model to analyze the incidence of pneumoconiosis in Jiangsu[J]. Journal of Environmental and Occupational Medicine, 2019, 36(8): 755-760. DOI: 10.13213/j.cnki.jeom.2019.19046. [4] 叶晓军, 沈毅, 任茹香, 等. 基于GRNN的组合预测模型在传染病发病率预测中的应用[J]. 浙江预防医学, 2012, 24(1): 8-13. DOI:10.19485/j.cnki.issn1007-0931.2012.0 1.003.Ye XJ, Shen Y, Ren RX, et al. Application of combined forecasting model based on GRNN in forecasting the incidence of infectious diseases[J]. Zhejiang Preventive Medicine, 2012, 24(1): 8-13. DOI: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn1007-0931.2012.01.003. [5] 彭志行, 鲍昌俊, 赵杨, 等. 乘积季节模型在伤寒副伤寒发病预测中的应用探析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2007, 11(6): 560-563. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ200706009Peng ZX, Bao CJ, Zhao Y, et al. Application of product seasonal model in predicting the incidence of typhoid and paratyphoid[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2007, 11(6): 560-563. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ200706009 [6] 周敏, 李世玲. 广义回归神经网络在非线性系统建模中的应用[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2007, 15(9): 1189-1191. DOI: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2007.09.032.Zhou M, Li SL. Application of generalized regression neural network in modeling of nonlinear system[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2007, 15(9): 1189-1191. DOI: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2007.09.032. [7] Wei W, Jiang J, Gao L, et al. A new hybrid model using an autoregressive integrated moving average and a generalized regression neural network for the incidence of tuberculosis in Heng county, China[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2017, 97(3): 799-805. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156768. [8] 王雅文, 沈忠周, 严宝湖, 等. ARIMA模型和ARIMA-GRNN模型在AIDS发病预测中的应用[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(12): 1287-1290. DOI:10.1646 2/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.020.Wang YW, Shen ZZ, Yan BH, et al. Application of ARIMA model and ARIMA-GRNN model in predicting the incidence of AIDS[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(12): 1287-1290. DOI:10.1646 2/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.020. [9] 王鲁茜, 阚飙. 伤寒、副伤寒的全球流行概况及其预防控制[J]. 疾病监测, 2007, 22(7): 492-494. doi: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2007.07.022Wang LX, Kan B. The global epidemic situation of typhoid and paratyphoid fever and its prevention and control[J]. Disease Surveillance, 2007, 22(7): 492-494. doi: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2007.07.022 [10] 刘凤凤, 赵善露, 陈琦, 等. 2015年中国伤寒、副伤寒流行病学特征和空间聚类分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(6): 754-758. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254 -6450.2017.06.013.Liu FF, Zhao SL, Chen Q, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and spatial cluster analysis of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever nationwide in 2015[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(6): 754-758. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254 -6450.2017.06.013. [11] 黎景雪, 王培承, 邱瑞香, 等. 灰色模型在我国伤寒副伤寒发病率预测中的应用[J]. 数理医药学杂志, 2010, 23(5): 506-508. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.20 10.05.002.Li JX, Wang PC, Qiu RX, et al. Application of grey model in predicting the incidence of typhoid and paratyphoid in my country[J]. Journal of Mathematical Medicine, 2010, 23(5): 506-508. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.20 10.05.002. [12] 彭志行, 鲍昌俊, 赵杨, 等. 加权马尔可夫链在伤寒副伤寒发病情况预测分析中的应用[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2008, 25(3): 226-229. DOI:CNKI:SUN:ZGWT.0.2008-03-002.Peng ZX, Bao CJ, Zhao Y, et al. Application of Weighted Markov Chain in Prediction and Analysis of Typhoid and Paratyphoid[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Statistics, 2008, 25(3): 226-229. DOI:CNKI:SUN:ZGWT.0.2008-03-002. [13] Wang Y, Shen Z, Jiang Y. Comparison of autoregressive integrated moving average model and generalised regression neural network model for prediction of haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China: a time-series study[J]. BMJ open, 2019, 9(6): e025773. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025773. -





 下载:
下载: