The influencing factors of vaccination willingness in pneumococcal vaccine in Chinese senior citizen: a Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
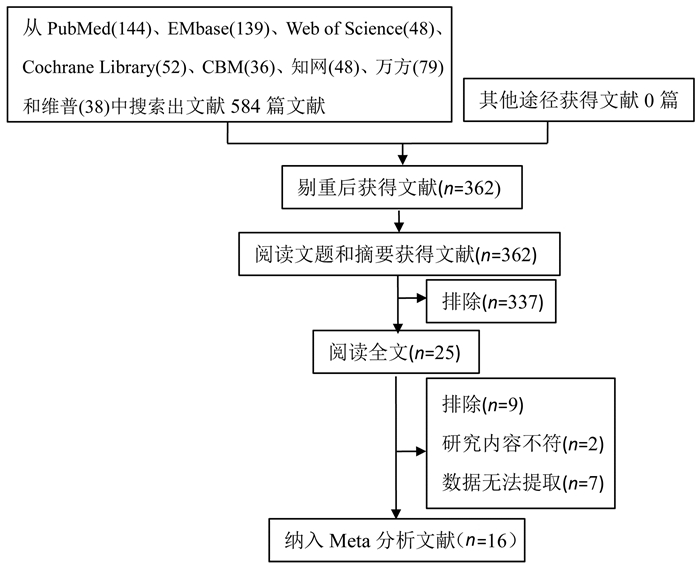
目的 系统评价中国老年人肺炎球菌疫苗(pneumococcal vaccine, PV)接种意愿的影响因素。 方法 首先检索PubMed、Cochrane Library、Web of Science、EMbase、CBM、中国知网、维普网和万方数据知识服务平台中涉及中国老年人PV接种意愿影响因素研究;再由2名研究人员独立筛选文献、质量评价和数据提取,最后进行Meta分析。 结果 最终纳入16篇研究,Meta分析结果显示:家庭收入(OR=1.94, 95% CI: 1.21~3.09, P=0.006)、PV知晓情况(OR=1.93, 95% CI: 1.12~3.33, P=0.019)、肺炎病史(OR=2.09, 95% CI: 1.00~4.36, P=0.050)、医生推荐(OR=2.80, 95% CI: 1.18~6.62, P=0.019)与中国老年人PV接种意愿的关系有统计学意义;而文化程度(OR=1.17, 95% CI: 0.81~1.70, P=0.408)、PV接种史(OR=1.06, 95% CI: 0.14~8.13, P=0.957)、是否患有慢性病(OR=1.22, 95% CI: 0.76~1.97, P=0.409)与中国老年人PV接种意愿的关系无统计学意义。 结论 家庭收入高、知晓PV、有肺炎病史、医生推荐是中国老年人PV接种意愿的促进因素,尚不能证明文化程度、PV接种史、是否患慢性病是中国老年人PV接种意愿的影响因素。 -
关键词:
- 中国老年人 /
- 肺炎球菌疫苗接种意愿 /
- 影响因素 /
- Meta分析
Abstract:Objective To systematically review the influencing factors of the pneumococcal vaccine (PV) vaccination willingness of the elderly in China. Methods PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, EMbase, CBM, CNKI, VIP and WanFang were searched to query the original studies. Two reviewers then screened the studies, extracted the data and assessed the quality. A Meta-analysis was then performed. Results A total of 16 studies eventually fulfilled the eligibility criteria. The pooled findings of this Meta-analysis demonstrated that family income (OR=1.94, 95% CI: 1.21-3.09, P=0.006), situation of PV information (OR=1.93, 95% CI: 1.12-3.33, P=0.019), history of pneumonia (OR=2.09, 95% CI: 1.00-4.36, P=0.050), recommended by doctors (OR=2.80, 95% CI: 1.18-6.62, P=0.019)were statistically significant in relation to influencing factors of the PV vaccination willingness of the elderly in China. There was no statistically significant difference between degree of education (OR=1.17, 95% CI: 0.81-1.70, P=0.408), history of PV vaccination (OR=1.06, 95% CI: 0.14-8.13, P=0.957), and whether to suffer from chronic disease (OR=1.22, 95% CI: 0.76-1.97, P=0.409). Conclusion Family income, situation of PV information, history of pneumonia, and recommended by doctors are promoters of PV vaccination willingness among the elderly in China; It is not proved that education level, history of PV vaccination, and chronic disease were the influencing factors of PV vaccination willingness among Chinese elderly. -
表 1 纳入研究基本特征与质量评价结果
Table 1. Basic characteristics and quality evaluation about the literature
第一作者 发表时间(年) 城市 样本量(例) 年龄(岁) 男/女(例) 影响因素 质量等级 白云晔[7] 2018 北京市 1 007 ≥65 447/560 C、D、F、G 高 卑伟慧[11] 2015 上海市 500 ≥60 226/274 B、E 中 陈小英[9] 2016 西安市 600 ≥60 232/368 A、B 中 李琴[12] 2019 宁波市 568 ≥65 320/248 F、G 高 林声[13] 2015 上海市 3 569 ≥60 1 570/1 999 A、B 高 陆红梅[14] 2016 上海市 1 393 ≥60 633/759 A、B 高 毛俊[15] 2018 平凉市 556 ≥60 304/252 B 高 王婧[16] 2014 上海市 200 ≥60 94/106 A、B 中 周杰[8] 2017 上海市 1 101 ≥60 527/574 B、C、G 高 陈敏[17] 2020 资阳市 1 178 ≥60 533/645 A、B、D 高 季晓颖[18] 2018 上海市 500 ≥60 253/247 C、G 中 尤志军[19] 2015 上海市 3 000 ≥65 1 363/1 637 A、B、E 高 Liu shijun[20] 2015 北京市 2 926 ≥60 1 176/1 750 D、F、G 中 许敏锐[21] 2020 常州市 1 354 — 595/759 A 中 张小娟[22] 2015 上海市 902 ≥60 387/515 B、F 中 杜琼华[23] 2020 巴中市 298 ≥60 185/113 B、E、F 高 注:危险因素:A:文化程度;B:家庭收入;C:PV知晓情况;D:PV接种史;E:肺炎病史;F:是否患有慢性病;G:医生推荐。 表 2 敏感性分析与发表偏倚结果
Table 2. Sensitivity analysis and publication bias results
危险因素 效应模型OR(95% CI)值 稳定性 Egger检验 固定模型 随机模型 t值 P值 家庭收入 1.62(1.32~1.99) 1.94(1.21~3.09) 稳定 0.83 0.450 PV知晓情况 1.96(1.59~2.42) 1.93(1.12~3.33) 稳定 -0.00 0.986 肺炎病史 1.64(1.23~2.19) 2.09(1.00~4.36) 稳定 1.14 0.464 医生推荐 2.34(1.95~2.81) 2.80(1.18~6.62) 稳定 0.51 0.637 -
[1] 王圆媛, 李靖欣, 曹嘉倩, 等. 肺炎球菌结合疫苗免疫学替代终点的研究进展[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2019, 53(8): 851-854. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2019.08.010.Wang YY, Li JX, Cao JQ, et al. Research progress of immunological surrogate endpoint of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine[J]. Chin J Prevent Med, 2019, 53(8): 851-854. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2019.08.010. [2] 姚开虎. 更新疾病负担评估观念重视肺炎链球菌疾病[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2018, 56(8): 561-563. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2018.08.001.Yao KH. Upgrading the concept of burden assessment to pay attention to pneumococcal diseases[J]. Chin J Pediatr, 2018, 56(8): 561-563. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2018.08.001. [3] 郭云, 杜紫燕, 王振, 等. 老年社区获得性肺炎预后评估方法[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2021, 31(1): 63-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202101016.htmGuo Y, Du ZY, Wang Z, et al. Assessment of outcome of community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly[J]. Chin J Nosocomiol, 2021, 31(1): 63-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202101016.htm [4] Chen X. The etiology and clinical study of pneumonia in the elderly[J]. Guide of China Medicine, 2013, 11(23): 171-172. [5] Hu SL, Shi Q, Chen CI, et al. Estimated public health impact of nationwide vaccination of infants with 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in China[J]. Int J of Infect Dis, 2014, 26: 116-122. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.04.012. [6] 杨彦华, 张淑君, 赖智维, 等. 长沙市老年人肺炎疫苗接种率及影响因素研究[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2019, 20(7): 623-626. DOI: 10.16506/j.1009-6639.2019.07.014.Yang YH, Zhang SJ, Lai ZW, et al. The research of vaccine coverage rate and influencing factors of pneumonia among the elderly in Changsha[J]. Chin J Prevent Med, 2019, 20(7): 623-626. DOI: 10.16506/j.1009-6639.2019.07.014. [7] 白云骅, 马伟, 吕敏, 等. 北京市朝阳区65岁以上老年人肺炎球菌疫苗接种意愿及影响因素[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2018, 24(4): 462-466. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201804020.htmBai YY, Ma W, Lyv M, et al. Vaccination willingness and influencing factors of pneumococcal vaccine among elderly over 65 years old in Chaoyang District, Beijing[J]. Chinese J of Vaccines and Immunization, 2018, 24(4): 462-466. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201804020.htm [8] 周杰, 汤喜红, 赵家俊, 等. 2014年上海市金山区60岁以上老年人肺炎疫苗接种意愿及影响因素分析[J]. 实用预防医学, 2017, 24(3): 309-312. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2017.03.014.Zhou J, Tang XH, Zhao JJ, et al. Analysis on the willingness and influencing factors of pneumonia vaccination among the elderly over60 years old in Jinshan District, Shanghai in 2014[J]. Pract Prev Med, 2017, 24(3): 309-312. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2017.03.014. [9] 陈小英, 张义, 李广智, 等. 西安市60岁以上老年人肺炎疫苗接种意愿及其影响因素[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学, 2016, 27(6): 21-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FBYF201606006.htmChen XY, Zhang Y, Li GZ, et al. Vaccination willingness and influencing factors of pneumonia vaccine among the elderly over 60 years old in Xi 'an[J]. J Pub Health Prev Med, 2016, 27(6): 21-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FBYF201606006.htm [10] 曾宪涛, 刘慧, 陈曦, 等. Meta分析系列之四: 观察性研究的质量评价工具[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2012, 4(4): 297-299. DOI: 10.3969/j.1674-4055.2012.04.004.Zeng XT, Liu H, Chen X, et al. Meta-analysis seriesiv: quality assessment tools for observational studies[J]. Chin J Evid Based Cardiovasc Med, 2012, 4(4): 297-299. DOI: 10.3969/j.1674-4055.2012.04.004. [11] 卑伟慧, 胡宏, 高洁, 等. 上海市静安区老年人免费肺炎疫苗接种意愿及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2015, 16(11): 883-887. DOI: 10.16506/j.1009-6639.2015.11.006.Bi WH, Hu H, Gao J, et al. Study on the willingness of the elderly to receive free pneumonia vaccine and its influencing factors in Jing'an District, Shanghai[J] Chin J Prevent Med, 2015, 16(11): 883-887. DOI: 10.16506/j.1009-6639.2015.11.006. [12] 李琴. 海曙区老年人群肺炎疫苗接种意愿及影响因素分析[J]. 中国公共卫生管理, 2019, 35(2): 280-282, 288. DOI: 10.19568/j.cnki.23-1318.2019.02.037.Li Q. Analysis on the willingness and influencing factors of pneumonia vaccination among the elderly in Haishu District[J]. Chin Public Health Manage, 2019, 35(2): 280-282, 288. DOI: 10.19568/j.cnki.23-1318.2019.02.037. [13] 林声, 郭翔, 李加, 等. 上海市老年人肺炎疫苗接种意愿及影响因素分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2015, 19(10): 975-978. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2015.10.002.Lin S, Guo X, Li J, et al. Analysis on the willingness of the elderly to vaccinate against pneumonia and its influencing factors in Shanghai[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2015, 19(10): 975-978. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2015.10.002. [14] 陆红梅, 朱祺, 沈金花, 等. 上海市松江区户籍老年人肺炎疫苗接种态度及其影响因素[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志, 2016, 29(7): 781-784. DOI: 10.13200/j.cnki.cjb.001389.Lu HM, Zhu Q, Shen JH, et al. Attitudes and influencing factors of pneumonia vaccination among the elderly with household registration in Songjiang District, Shanghai[J]. Chin J Biologicals, 2016, 29(7): 781-784. DOI: 10.13200/j.cnki.cjb.001389. [15] 毛俊, 郭李玲. 平凉市崆峒区老年人肺炎疫苗接种意愿及影响因素调查[J]. 慢性病学杂志, 2018, 19(9): 1246-1247, 1250. DOI: 10.16440/j.cnki.1674-8166.2018.09.032.Mao J, Guo LL. Investigation on the willingness of the elderly to vaccinate against pneumonia and its influencing factors in Kongtong District, Pingliang City[J]. Chronic Pathematology J, 2018, 19(9): 1246-1247, 1250. DOI: 10.16440/j.cnki.1674-8166.2018.09.032. [16] 王婧, 牟文, 姜铭波. 上海市黄浦区老年人肺炎疫苗接种意愿及影响因素调查[J]. 健康教育与健康促进, 2014, 9(2): 113-115. DOI: 10.16117/j.cnki.31-1974/r.2014.02.013.Wang J, Mou W, Jiang MB. Investigation on the willingness of the elderly to vaccinate again stpneumonia and its influencing factorsin Huangpu district, Shanghai[J]. Health Education and Health Promotion, 2014, 9(2): 113-115. DOI: 10.16117/j.cnki.31-1974/r.2014.02.013. [17] 陈敏, 马英, 蒋莉. 2018年资阳市雁江区60岁及以上未接种肺炎疫苗老年人接种认知情况[J]. 预防医学情报杂志, 2020, 36(2): 203-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YFYX202002014.htmChen M, Ma Y, Jiang L. The cognition of the elderly aged 60 and over who had not received pneumonia vaccine in Yanjiang District, Ziyang City in 2018[J]. J Prevent Med Inf, 2020, 36(2): 203-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YFYX202002014.htm [18] 季晓颖, 程丽森, 赵开栋. 宝山社区老年人肺炎疫苗接种行为影响因素分析及家庭医生健康干预效果[J]. 社区医学杂志, 2018, 16(9): 9-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SQYX201809004.htmJi XY, Cheng LS, Zhao KD. Influencing factors of pneumonia vaccination behavior among the elderly in Baoshan community and theeffect of family doctor health intervention[J]. J Community Med, 2018, 16(9): 9-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SQYX201809004.htm [19] 尤志军, 林冰, 高中. 上海市青浦区老年人肺炎疫苗接种率及其影响因素分析[J]. 医药与保健, 2015, (3): 89-89.You ZJ, Lin B, Gao Z. Analysis of pneumonia vaccination rate and its influencing factors among the elderly in Qingpu District, Shanghai[J]. Med Health Care, 2015, (3): 89-89. [20] Shijun L, Erping X, Yan L, et al. Factors associated with pneumococcal vaccination among an urban elderly population in China[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2014, 10(10). DOI: 10.4161/21645515.2014.972155. [21] 许敏锐, 周义红, 强德仁, 等. 常州市武进区慢性病患者流感和肺炎疫苗接种意愿及影响因素[J]. 江苏预防医学, 2020, 31(3): 300-302. DOI: 10.13668/j.issn.1006-9070.2020.03.020.Xu MR, Zhou YH, Qiang DR, et al. Influenza and pneumonia vaccination willingness and influencing factors of chronic patients in Wujin District of Changzhou City[J]. Jiangsu J Prevent Med, 2020, 31(3): 300-302. DOI: 10.13668/j.issn.1006-9070.2020.03.020. [22] 张小娟, 黄瑾, 徐敏钢, 等. 上海市闸北区户籍老年人肺炎疾病及疫苗知识、态度、行为调查[J]. 中国初级卫生保健, 2015, 29(1): 80-84. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-568X.2015.01.0029.Zhang XJ, Huang J, Xu MG, et al. Investigation on knowledge, attitude and behavior of pneumonia disease and vaccine among the elderly with household registration in Zhabei District, Shanghai[J]. Chin Primary Health Care, 2015, 29(1): 80-84. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-568X.2015.01.0029. [23] 杜琼华, 杜青, 李芳, 等. 老年住院慢性阻塞性肺疾病病人接种流感疫苗、肺炎疫苗意愿及影响因素分析[J]. 医学动物防制, 2020, 36(10): 937-940. DOI: 10.7629/yxdwfz202011006.Du QH, Du Q, Li F, et al. Influential factors and willingness of elderly in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease to receive influenza vaccine and pneumonia vaccine[J]. J Med Pest Control, 2020, 36(10): 937-940. DOI: 10.7629/yxdwfz202011006. [24] 靳雪征. 健康信念理论的建立和发展[J]. 中国健康教育, 2007, 23(2): 945-946. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9982.2007.12.024.Jin XZ. The establishment and development of health belief theory[J]. Chin J Health Education, 2007, 23(2): 945-946. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9982.2007.12.024. [25] Liao SL, Huang T, Huang YC, et al. Survey of the status of self-paid varicalla vaccination among children one to six years of age in Taiwan[J]. J Microbiol Immunol Infect, 2007, 40(2): 112-115. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/fefb/5e0178e60f38331bbac67f99a3e5dc1f3a29.pdf [26] Manthiram K, Blood EA. Predictors of optional immunization uptake in an urban south Indian population[J]. Vaccine, 2014, 32(27): 3417-3423. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.04.012. [27] Ganczak M, Dmytrzyk-Danilow G, Karakiewicz, et al. Determinants influencing self-paid vaccination coverage in 0-5 years old polish children[J]. Vaccine, 2013, 31(48): 5687-5692. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.09.056. [28] 阮玉华, 郭欣, 傅继华, 等. 利用需求弹性理论探讨肾综合征出血热灭活疫苗接种价格[J]. 中国计划免疫, 2001, (2): 49-51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-916X.2001.02.016.Ruan YH, Guo X, Fu JH, et al. The price of inactivated vaccine for hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) was studied byusing the theory of elasticity of demand[J]. Chin J Vaccine Immunization, 2001, (2): 49-51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-916X.2001.02.016. [29] 仲志磊, 苏婷, 张世宏, 等. 预防接种与血小板减少性紫癜的关联—13例案例分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 25(9): 1014-1019. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.09.005.Zhong ZL, Su T, Zhang SH, et al. Association between vaccination and thrombocytopenic purpura: a case study of 13 cases[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2021, 25(9): 1014-1019. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.09.005. [30] Schneeberg A, Bettinger JA, Mcneil S, et al, Knowledge, attitudes, beliefs and behaviours of older adults about pneumococcal immunization, a public health agency of Canada/Canadian Institutes of health research influenza research network (PCIRN) investigation[J]. BMC Public Health, 2014, 14: 442. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-442. [31] 杨弦弦, 丁贤彬, 毛德强, 等. 重庆市65岁以上老年人流感疫苗知晓率及其影响因素[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学, 2018, 29(4): 94-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FBYF201804026.htmYang XX, Ding XB, Mao DQ, et al. Influenza vaccine awareness rate and influencing factors of the elderly over 65 years old in Chongqing City[J]. J Pub Health Prev Med, 2018, 29(4): 94-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FBYF201804026.htm [32] 苗芳, 戴海辉, 仲文江, 等. 上海市青浦区某镇老年人肺炎疫苗接种意愿及相关因素[J]. 上海预防医学, 2019, 31(10): 842-847. DOI: 10.19428/j.cnki.sjpm.2019.18625.Miao F, Dai HH, Zhong WJ, et al. Vaccination willingness and related factors of pneumonia among the elderly in a town of QingpuDistrict, Shanghai[J]. Shanghai J Prevent Med, 2019, 31(10): 842-847. DOI: 10.19428/j.cnki.sjpm.2019.18625. [33] Pack R, Wang Y, Singh A, et al. Willingness to be vaccinated against shigella and other forms of dysentery: a comparison of three regions in Asia[J]. Vaccine, 2006, 24(4): 485-494. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.07.094. [34] Malosh R, Ohmit SE, Petrie JG, et al. Factors associated with influenza vaccine receipt in community dwelling adults and their children[J]. Vaccine, 2014, 32(16): 1841-1847. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.01.075. [35] Dong H, Kouyate B, Snow R, et al. Gender's effect on willingness-to-pay for community-based insurance in Burkina Faso[J]. HealthPolicy, 2003, 64(2): 153-162. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8510(02)00144-6. [36] Wang LDL, Lam WWT, Wu JT, et al. Chinese immigrant parents' vaccination decision making for children: a qualitative analysis[J]. BMC Public Health, 2014, 14(1): 133. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-133. [37] Darden PM, Jacobson RM. Impact of a physician recommendation[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2014, 10(9): 2632-2635. DOI: 10.4161/hv.29020. -





 下载:
下载: