The complete gene sequence characteristic analysis of coxsackievirus A6 strains isolated from China
-
摘要:
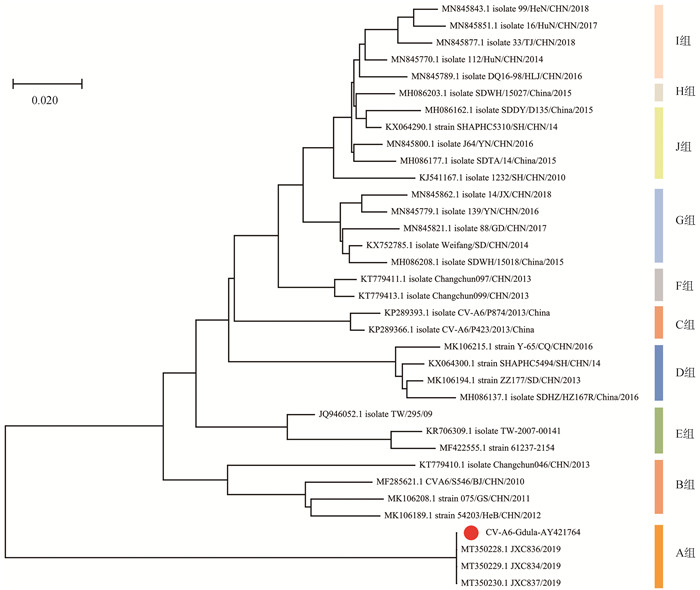
目的 分析中国2007-2019年柯萨奇病毒A组6型(coxsackievirus A6,CVA6)毒株遗传进化规律,以期为疾病预防及疫苗研发提供理论依据。 方法 收集中国截至2021年3月1日Genbank数据库中454株CVA6毒株全基因序列,分析毒株分离年份、地区信息,构建系统发育树揭示进化规律并进行基因重组分析。 结果 地区信息显示,毒株主要分布于中国沿海及南方地区,时间信息表明,自2013年起,CVA6毒株报告数量逐渐增加。系统进化结果表明,454株CVA6毒株分10个分支,A分支中3株分离自江西省的毒株与CVA6原型毒株Gdula(AY421764)亲缘关系极为接近,核酸序列相似度近乎100%,J分支是中国流行最广泛的毒株群,包含了中国较多省份如山东省、广东省等。基因重组分析显示,基因重组现象较为普遍,大部分CVA6代表毒株在P2区和P3区与其他肠道病毒A组毒株之间存在基因重组现象。 结论 2007-2019年CVA6毒株在中国广泛传播,毒株间基因重组现象普遍存在。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the genetic evolutionary characteristic of coxsackievirus A6 (CVA6) strains reported from 2007 to 2019 of China to provide theoretical basis for disease prevention and development of vaccines. Methods The whole information of gene sequences of 454 Chiness CVA6 strains reported up to March 1, 2021 were collected from Genbank, and the isolation year and region of the strains were analyzed. Phylogenetic tree was constructed to reveal the evolutionary character of the strains and gene recombination analysis was conducted. Results The information of isolated region showed that the CVA6 strains were mainly originated from coastal areas and south of China. The number of reported CVA6 strains had a significant increase since 2013. The phylogenetic tree revealed that 454 CVA6 strains were mainly clustered into 10 branches. Three strains in Group A isolated from Jiangxi Province was most closely related to the CVA6 prototype strain Gdula (AY421764), with nearly 100% similarity of nucleic acid sequence. Group J isolated from many provinces in China, such as Shandong Province and Guangdong Province, was the most widespread group of strains. Recombination analysis showed that gene recombination of most strains was common. Most representative strains of CVA6 were recombined with some other Enterovirus A strains in P2 and P3 regions. Conclusion From 2007 to 2019, the CVA6 strains have been spreading widely in China, and the phenomenon of gene recombination among CVA6 strains is widespread. -
Key words:
- Hand foot and mouth disease /
- CVA6 /
- Phyletic evolution /
- Gene recombination
-
表 1 常见HEV-A毒株原型株汇总表
Table 1. Summary of common strains of HEV-A
血清型 原型毒株名称 GenBank序列号 年份 国家 CV-A2 Fleetwood AY421760 1947 美国 CV-A3 Olson AY421761 1948 美国 CV-A4 High Point AY421762 1948 美国 CV-A5 Swartz AY421763 1950 美国 CV-A6 Gdula AY421764 1949 美国 CV-A7 Parker AY421765 1949 美国 CV-A8 Donovan AY421766 1949 美国 CV-A10 Kowalik AY421767 1950 美国 CV-A12 Texas-12 AY421768 1948 美国 CV-A14 G-14 AY421769 1950 南非共和国 CV-A16 G-10 U05876 1951 南非共和国 EV-A71 BrCr U22521 1970 美国 EV-A76 FRA91-10369 AY697458 1991 法国 EV-A89 BAN00-10359 AY697459 2000 孟加拉国 EV-A90 BAN99-10399 AY697460 1999 孟加拉国 EV-A91 BAN00-10406 AY697461 2000 孟加拉国 EV-A92 USA/GA99-RJg-7 EF667344 1999 美国 表 2 毒株地区信息
Table 2. The regional information of collected CVA6 strains
地区 数量(株) 地区 数量(株) 山东 93 黑龙江 7 北京 73 吉林 7 上海 44 河南 7 浙江 37 天津 6 广东 35 青海 5 云南 32 香港 5 甘肃 14 未知 5 江苏 14 宁夏 4 重庆 13 新疆 2 江西 13 海南 2 台湾 13 四川 1 河北 12 辽宁 1 湖南 8 安徽 1 表 3 毒株时间信息
Table 3. The time information of collected CVA6 strains
年份(年) 数量(株) 年份(年) 数量(株) 2007 1 2014 46 2008 5 2015 130 2009 3 2016 49 2010 8 2017 49 2011 23 2018 43 2012 8 2019 4 2013 85 表 4 用于基因重组分析的代表株序列信息
Table 4. The information of strains for genetic recombination analysis
分组 年份(年) 地区 可能发生重组区域 GenBank序列号 A组 2019 江西 P3 MT350228 B组 2010 北京 P1、P3 MF285621 C组 2013 浙江 P2、P3 KP289393 D组 2013 山东 P3 MK106194 E组 2007 台湾 P3 KR706309 F组 2013 吉林 P2、P3 KT779411 G组 2014 山东 P2、P3 KX752785 H组 2015 山东 P2、P3 MH086203 I组 2014 湖南 P1、P2、P3 MN845770 J组 2010 上海 P2、P3 KJ541167 -
[1] Yu F, Zhu R, Jia L, et al. Sub-genotype change and recombination of coxsackievirus A6s may be the cause of it being the predominant pathogen for HFMD in children in Beijing, as revealed by analysis of complete genome sequences[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2020, 99: 156-162. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.010. [2] Lu QB, Zhang XA, Wo Y, et al. Circulation of Coxsackievirus A10 and A6 in hand-foot-mouth disease in China, 2009-2011[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(12): e52073. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052073. [3] Osterback R, Vuorinen T, Linna M, et al. Coxsackievirus A6 and hand, foot, and mouth disease, Finland[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2009, 15(9): 1485-1488. DOI: 10.3201/eid1509.090438. [4] Wu Y, Yeo A, Phoon MC, et al. The largest outbreak of hand; foot and mouth disease in Singapore in 2008: the role of enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A strains[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2010, 14(12): e1076-1081. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2010.07.006. [5] Fujimoto T, Iizuka S, Enomoto M, et al. Hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6, Japan, 2011[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2012, 18(2): 337-339. DOI: 10.3201/eid1802.111147. [6] Montes M, Artieda J, Pineiro LD, et al. Hand, foot, and mouth disease outbreak and coxsackievirus A6, northern Spain, 2011[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2013, 19(4): 676-678. DOI: 10.3201/eid1904.121589. [7] Puenpa J, Chieochansin T, Linsuwanon P, et al. Hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6, Thailand, 2012[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2013, 19(4): 641-643. DOI: 10.3201/eid1904.121666. [8] Feng X, Guan W, Guo Y, et al. A novel recombinant lineage's contribution to the outbreak of coxsackievirus A6-associated hand, foot and mouth disease in Shanghai, China, 2012-2013[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 11700. DOI: 10.1038/srep11700. [9] Han JF, Xu S, Zhang Y, et al. Hand, foot, and mouth disease outbreak caused by coxsackievirus A6, China, 2013[J]. J Infect, 2014, 69(3): 303-305. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.03.015. [10] Lu J, Zeng H, Zheng H, et al. Hand, foot and mouth disease in Guangdong, China, in 2013: new trends in the continuing epidemic[J]. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2014, 20(7): 442-445. DOI: 10.1111/1469-0691.12468. [11] Hongyan G, Chengjie M, Qiaozhi Y, et al. Hand, foot and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6, Beijing, 2013[J]. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 2014, 33(12): 1302-1303. DOI: 10.1097/inf.0000000000000467. [12] Aswathyraj S, Arunkumar G, Alidjinou EK, et al. Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD): emerging epidemiology and the need for a vaccine strategy[J]. Med Microbiol Immunol, 2016, 205(5): 397-407. DOI: 10.1007/s00430-016-0465-y. [13] 罗亮, 王雪红, 姚相杰, 等. 2019年深圳市坪山区手足口病病原谱及柯萨奇病毒A6型基因特征分析[J]. 中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2020, 43(4): 264-268. DOI: 10.16408/j.1004-9770.2020.04.013.Luo L, Wang XH, Yao XJ, et al. Analysis of the pathogen spectrum of hand, foot and mouth disease and the genetic characteristics of coxsackievirus A6 in Pingshan District, Shenzhen, 2019[J]. Chinese Frontier Health Quarantine, 2020, 43(4): 264-268. DOI: 10.16408/j.1004-9770.2020.04.013. [14] 王宇, 任刚, 苏飞, 等. 2015-2016年贵州省柯萨奇病毒A6型分离株的基因特征分析[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2018, 13(2): 177-180. DOI: 10.13350/j.cjpb.180216.Wang Y, Ren G, Su F, et al. Genetic characteristics of coxsackievirus A6 strains isolated in Guizhou Province from 2015-2016[J]. Journal of Pathogen Biology, 2018, 13(2): 177-180. DOI: 10.13350/j.cjpb.180216. [15] 董兆鹏, 孙箐爽, 臧昊, 等. 金山区柯萨奇病毒A组6型基因特征分析[J]. 预防医学, 2019, 31(11): 1136-1139. DOI: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2019.11.014.Dong ZP, Sun JS, Zang H, et al. Genetic characteristics of coxsackievirus A6 strains isolated in JinShan district[J]. Prev Med, 2019, 31(11): 1136-1139. DOI: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2019.11.014. [16] 张平, 张静. 我国2014-2015年其他感染性腹泻监测现状分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(4): 424-430. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.04.003.Zhang P, Zhang J. Surveillance on other infectious diarrheal diseases in China from 2014 to 2015[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(4): 424-430. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.04.003. [17] Mao Y, Zhang N, Zhu B, et al. A descriptive analysis of the Spatio-temporal distribution of intestinal infectious diseases in China[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2019, 19(1): 766. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-4400-x. [18] 陈鹏. 肠道病毒A组山东株的基因重组、进化起源及其时空动态传播研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018.Chen P. Recombination, Evolutionary origin and spatiotemporal dynamic transmission of enterovirus a species in Shandong Province[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2018. [19] He S, Chen M, Wu W, et al. An emerging and expanding clade accounts for the persistent outbreak of Coxsackievirus A6-associated hand, foot, and mouth disease in China since 2013[J]. Virology, 2018, 518: 328-334. DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.03.012. [20] Du Z, Zhao Y, Luo Y, et al. Ongoing change of severe hand, foot, and mouth disease pathogens in Yunnan, China, 2012 to 2016[J]. J Med Virol, 2019, 91(5): 881-885. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.25393. [21] Bian L, Wang Y, Yao X, et al. Coxsackievirus A6: a new emerging pathogen causing hand, foot and mouth disease outbreaks worldwide[J]. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther, 2015, 13(9): 1061-1071. DOI: 10.1586/14787210.2015.1058156. [22] 张颖, 甄若楠, 谢华萍, 等. 2010-2015年广州地区手足口病Cox A6, Cox A4和Cox A10的病原监测和流行分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2016, 31(10): 817. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2016.10.006.Zhang Y, Zhen RN, Xie HP, et al. Surveillance for hand foot and mouth disease pathogens Cox A6, Cox A4 and Cox A10 in Guangzhou[J]. Disease Surveillence, 2016, 31(10): 817. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2016.10.006. [23] Zhao TS, Du J, Sun DP, et al. A review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology and clinical presentation of coxsackievirus A6 causing hand-foot-mouth disease in China and global implications[J]. Rev Med Virol, 2020, 30(2): e2087. DOI: 10.1002/rmv.2087. [24] 吕秀芝, 张楠楠. 手足口病柯萨奇病毒A6型病原学及流行病学研究进展[J]. 社区医学杂志, 2018, 16(22): 1685-1688. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SQYX201822019.htmLyu XZ, Zhang NN. Study progress in etiology and epidemiology of coxsackievirus A6-related hand foot and mouth disease[J]. J Community Med, 2018, 16(22): 1685-1688. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SQYX201822019.htm [25] 曾汉日, 陆靖, 郑焕英, 等. 中国广东省18株柯萨奇病毒A6型分离株全基因组特征分析[J]. 病毒学报, 2016, 32(5): 566-573. DOI: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.003022.Zeng HR, Lu J, Zheng HY, et al. Genome-wide characterization of 18 Corsacki virus type A6 isolates in Guangdong Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2016, 32(5): 566-573. DOI: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.003022. [26] 苏志磊. 2016-2018年青岛地区手足口病柯萨奇病毒CA6基因特征分析[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2020.Su ZL. Phylogenetic analysis of coxsackievirus A6 in hand, foot and mouth disease in Qingdao in 2016-2018[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2020. [27] 何鑫, 杨婷, 谢忠平. 柯萨奇病毒A6所致手足口病研究现况[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(3): 312-316. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.03.022.He X, Yang T, Xie ZP. Advances in research on hand, foot and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(3): 312-316. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.03.022. -





 下载:
下载: