Correlation between depressive symptoms and health promotion behavior in the elderly—based on structural equation model
-
摘要:
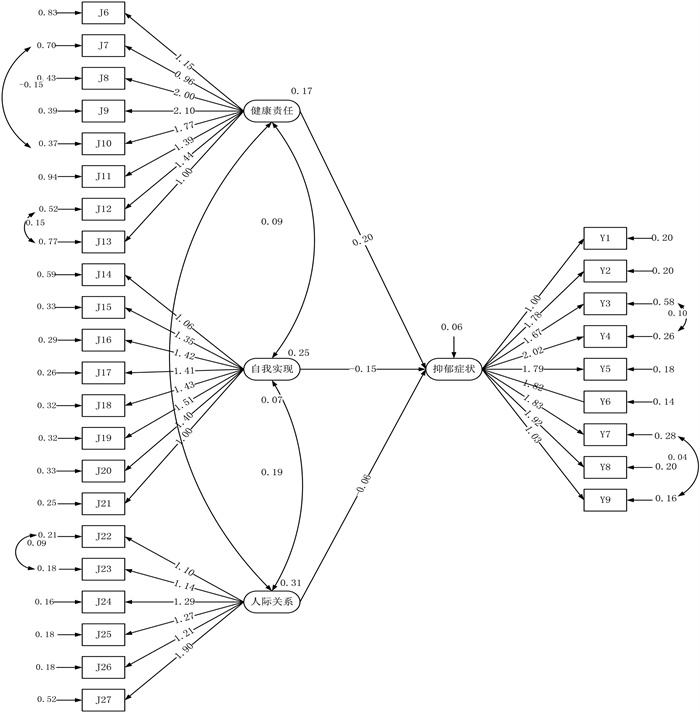
目的 探讨老年人抑郁症状与健康促进行为的相关关系, 为完善老年人心理干预措施提供参考。 方法 采用随机整群抽样的方法, 于2021年5月6日-7月31日对宁夏回族自治区1 949名老年人展开调查, 应用抑郁症筛查量表-9(Patient Health Questionnare-9, PHQ-9)和健康促进生活方式自评量表(Health Promoting Lifestyle Profile, HPLP-C)进行测评, 利用X2检验、二元logistic回归分析模型探讨抑郁症状的影响因素并建立抑郁症状与健康促进行为的结构方程模型。 结果 共有1 937人有效完成问卷, 其中760人有抑郁症状。二元logistic回归分析模型显示: 年龄越大、女性、健康行为等级为不健康的老年人更容易出现抑郁症状(均有P<0.05)。结构方程模型中健康责任(β=0.20)与抑郁症状呈正相关, 自我实现(β=-0.15)、人际关系(β=-0.06)与抑郁症状呈负相关。 结论 老年人抑郁症状与健康促进行为存在相关关系, 可以通过改善老年人的健康行为方式来预防抑郁症状的发生。 Abstract:Objective To explore the relationship between depressive symptoms and health promotion behaviors in the elderly, and to provide a reference for improving psychological intervention measures for the elderly. Methods A random cluster sampling method was used to survey 1 949 elderly people in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region from May 6-July 31, 2021.The Depression Screening Scale (patient health questionnaire, PHQ-9) and the Health Promotion Lifestyle Self-rating Scale (health-promoting lifestyle profile, HPLP-C) were used for evaluation, and the chi-square test and binary logistic regression model were used to explore the influencing factors of depressive symptoms and establish a structural equation model of depressive symptoms and health promotion behaviors. Results A total of 1 937 people completed the questionnaire, and 760(39.2%) people were found to have depressive symptoms.Binary logistic regression showed that older, female, and unhealthy seniors were more likely to have depressive symptoms (all P<0.05).In the structural equation model, there was a positive correlation between health responsibility (β=0.20) and depressive symptoms, while self-actualization (β=-0.15) and interpersonal relationships (β=-0.06) were negatively correlated with depressive symptoms. Conclusions There is a correlation between depressive symptoms and health promotion behaviors in the elderly, and the occurrence of depressive symptoms can be prevented by improving the healthy behaviors of the elderly. -
Key words:
- The elderly /
- Depressive symptoms /
- Health-promotion behavior
-
表 1 不同特征社区老年人抑郁症状分布情况[n(%)]
Table 1. Distribution of depressive symptoms among the elderly in different characteristics of the community [n(%)]
变量 总人数 发生抑郁症状 X2值 P值 年龄(岁) a 16.362 < 0.001 65~<75 1 305 (67.4) 477 (36.6) 75~<85 575 (29.7) 249 (43.3) ≥85 57 (2.9) 34 (59.6) 性别 18.041 < 0.001 男 919 (47.4) 315 (34.3) 女 1 018 (52.6) 445 (43.7) 户籍 < 0.001 0.999 城镇 892 (46.1) 350 (39.2) 农村 1 045 (53.9) 410 (39.2) 文化程度a 4.871 0.027 文盲 914 (47.2) 376 (41.1) 小学 499 (25.8) 203 (40.7) 初中 341 (17.6) 115 (33.7) 高中及以上 183 (9.4) 66 (36.1) 婚姻状况 4.711 0.095 未婚 17 (0.9) 7 (41.2) 已婚 1 507 (77.8) 572 (38.0) 离异/丧偶 413 (21.3) 181 (43.8) 经济状况(元/月) a 4.676 0.031 <2 000 1 190 (61.4) 484 (40.7) 2 000~5 000 684 (35.3) 260 (38.0) >5 000 63 (3.3) 16 (25.4) 居住方式 2.227 0.328 独居 293 (15.1) 126 (43.0) 与伴侣同住 1 300 (67.1) 498 (38.3) 与子女或其他家人同住 344 (17.8) 136 (39.5) 健康行为等级 9.904 0.002 不健康 618 (31.9) 274 (44.3) 健康 1319 (68.1) 486 (36.8) 注:a等级变量,采用趋势X2检验。 表 2 抑郁症状与健康行为关联的多因素非条件logistic回归分析模型分析
Table 2. Multivariate unconditional logistic regression analysis of the association between depressive symptoms and health behavior
变量 β值 X2值 P值 OR(95% CI)值 年龄(岁) 65~<75 1.000 75~<85 0.302 7.897 0.005 1.353(1.096~1.670) ≥85 1.053 13.624 < 0.001 2.867(1.639~5.015) 性别 男 1.000 女 0.372 12.653 < 0.001 1.451(1.182~1.781) 经济状况(元/月) <2 000 1.000 2 000~5 000 -0.149 1.376 0.241 0.862(0.672~1.105) >5000 -0.653 3.855 0.050 0.520(0.271~0.999) 文化程度 文盲 1.000 小学 0.099 0.678 0.410 1.104(0.872~1.399) 初中 -0.085 0.307 0.579 0.919(0.680~1.240) 高中及以上 0.088 0.194 0.659 1.092(0.739~1.614) 健康行为等级 不健康 1.000 健康 -0.281 6.862 0.009 0.755(0.612~0.932) 表 3 抑郁症状与健康行为及其各维度的单因素非条件logistic回归分析模型分析
Table 3. Univariate unconditional logistic regression analysis of depressive symptoms and health behaviors and their dimensions
变量 β值 X2值 P值 OR(95% CI)值 健康行为 -0.008 13.277 0.001 0.992(0.988~0.996) 营养 -0.048 9.268 0.002 0.953(0.924~0.983) 健康责任 0.032 15.161 0.001 1.032(1.016~1.049) 自我实现 -0.065 59.728 0.001 0.937(0.922~0.953) 人际关系 -0.078 44.277 0.001 0.925(0.904~0.947) 体力活动 -0.010 0.500 0.479 0.991(0.965~1.017) 压力管理 -0.021 7.588 0.006 0.979(0.964~0.994) -
[1] Sun X, Zhou M, Huang L et al. Depressive costs: medical expenditures on depression and depressive symptoms among rural elderly in China[J]. Public Health, 2020, 181: 141-150. DOI: 10.1016/j.puhe.2019.12.011. [2] Hua Yan, Wang Bo, Wallen Gwenyth R, et al. Health-promoting lifestyles and depression in urban elderly Chinese[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0117998. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117998. [3] 朱巍嵘. 抑郁症的形成、危害及应对[J]. 政工学刊, 2021, (3): 70-71. DOI: 10.16296/j.cnki.zgxk1979.2021.03.037.Zhu WR. The formation, harm and response of depression[J]. Political Science and Engineering Journal, 2021, (3): 70-71. DOI: 10.16296/j.cnki.zgxk1979.2021.03.037. [4] Hsieh Chee-Ruey, Qin XZ. Depression hurts, depression costs: the medical spending attributable to depression and depressive symptoms in China[J]. Health Econ, 2018, 27(3): 525-544. DOI: 10.1002/hec.3604. [5] 吴华, 刘婷婷. 中国人口老龄化问题的辩证思考[J]. 改革与开放, 2011, (18): 145-146. DOI: 10.16653/j.cnki.32-1034/f.2011.18.085.Wu H, Liu TT. Dialectical thinking on the aging of Chinese population[J]. Reform & Openning, 2011, (18): 145-146. DOI: 10.16653/j.cnki.32-1034/f.2011.18.085. [6] 中华人民共和国统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021: 33.Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: Chin Statistics Press, 2021: 33. [7] 杨小娇, 汪凤兰, 张小丽, 等. 居家不出和抑郁对老年人健康促进行为的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2018, 38(17): 4270-4272. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.17.065.Yang XJ, Wang FL, Zhang XL, et al. The effect of staying at home and depression on the health promotion behavior of the elderly[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2018, 38(17): 4270-4272. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.17.065. [8] Kang SW, Yoo JS. Health-promoting lifestyle and depression in metabolic syndrome patients in Korea[J]. Int J Nurs Pract, 2012, 18(3): 268-274. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-172X.2012.02036.x. [9] 邬时民. 谁来关怀老人心理[J]. 中国社会工作, 2020, (20): 40-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSGZ202020025.htmWu SM. Who cares for the psychology of the elderly[J]. Chin Soc Work, 2020, (20): 40-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSGZ202020025.htm [10] 刘梦, 姜明静, 倪方端, 等. 甘肃省某高校大学生抑郁情绪调查研究[J]. 华南预防医学, 2019, 45(1): 69-72. DOI: 10.13217/j.scjpm.2019.0069.Liu M, Jiang MJ, Ni FD, et al. Investigation and research on depression mood of college students in Gansu Province[J]. South China J Prev Med, 2019, 45(1): 69-72. DOI: 10.13217/j.scjpm.2019.0069. [11] 徐勇, 吴海苏, 徐一峰. 病人健康问卷抑郁量表(PHQ-9)在社区老年人群中的应用——信度与效度分析[J]. 上海精神医学, 2007, 19(5): 257-259, 276. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0829.2007.05.001.Xu Y, Wu HS, Xu YF. Application of patient health questionnaire depression scale (PHQ-9) in community elderly population: reliability and validity analysis[J]. Shanghai Arch Psy, 2007, 19(5): 257-259, 276. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0829.2007.05.001. [12] 胡星辰, 张迎黎, 梁炜, 等. 病人健康问卷抑郁量表(PHQ-9)在青少年中应用的信效度检验[J]. 四川精神卫生, 2014, 27(4): 357-360. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3256.2014.04.021.Hu XC, Zhang YL, Liang W. The reliability and validity test of the patient health questionnaire depression scale (PHQ-9) in adolescents[J]. Sichuan Psy Health, 2014, 27(4): 357-360. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3256.2014.04.021. [13] 杨振, 张会君. 老年健康促进量表的跨文化调适及信效度检验[J]. 护理学杂志, 2021, 36(19): 91-94. DOI: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2021.19.091.Yang Z, Zhang HJ. Cross-cultural adjustment and reliability test of geriatric health promotion scale[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2021, 36(19): 91-94. DOI: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2021.19.091. [14] 龚智力. 抑郁症的危害及防治[J]. 中国社区医师, 2008, 10(9): 35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSQ200809042.htmGong ZL. The harm and prevention of depression[J]. Chin Community Doctor, 2008, 10(9): 35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSQ200809042.htm [15] 林娜, 王晓蕾, 彭彩丽, 等. 浙江省城乡老年人的社会资本与心理健康的研究[J]. 心理月刊, 2021, 16(9): 220-221. DOI: 10.19738/j.cnki.psy.2021.09.106.Lin N, Wang XL, Peng CL, et al. A study on social capital and mental health of the elderly in urban and rural areas of Zhejiang Province[J]. Psy Monthly, 2021, 16(9): 220-221. DOI: 10.19738/j.cnki.psy.2021.09.106. [16] 吴燕, 徐勇. 苏州市城区老年人日常生活能力调查[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2014, 34(3): 745-746. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2014.03.083.Wu Y, Xu Y. A survey of the daily living ability of the elderly in Suzhou[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2014, 34(3): 745-746. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2014.03.083. [17] 王丽, 张晓. 我国农村老年人抑郁症状性别差异及影响因素研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(11): 1148-1151. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.11.013.Wang L, Zhang X. A study on the gender differences and influencing factors of depressive symptoms in rural elderly people in China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(11): 1148-1151. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.11.013. [18] 李德明, 陈天勇, 吴振云. 中国女性老年人的主观幸福感及其影响因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2007, 27(8): 778-780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLXZ200708034.htmLi DM, Chen TY, Wu ZY. Subjective well-being of female elderly people in China and its influencing factors[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2007(8): 778-780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLXZ200708034.htm [19] 程彦如, 路雪芹, 陈传波, 等. 农村失能老年人焦虑及抑郁情绪与健康行为的相关性[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2017, 37(23): 5967-5969. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2017.23.102.Cheng YR, Lu XQ, Chen CB. Correlation between anxiety and depression and healthy behavior in rural disabled elderly[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2017, 37(23): 5967-5969. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2017.23.102. [20] Robinson-Smith G, Pizzi ER. Maximizing stroke recovery using patient self-care self-efficacy[J]. Rehabil Nurs, 2003, 28(2): 48-51. DOI: 10.1002/j.2048-7940.2003.tb02028.x. [21] 毛晓群, 尤黎明, 古素娥, 等. 老年人自我效能和健康行为的相关性研究[J]. 护理研究, 2007, 21(16): 1437-1439. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6493.2007.16.012.Mao XQ, You LM, Gu SE, et al. A study on the correlation between self-efficacy and health behavior in the elderly[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2007, 21(16): 1437-1439. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6493.2007.16.012. [22] Barger SD, Messerli-Bürgy N, Barth J. Relationship correlates of major depressive disorder and depressive symptoms in Switzerland: nationally representative cross sectional study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2014, 14: 273. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-273. [23] 喻晓娇, 董亚菲, 田甜, 等. 泸州市老年人认知功能与社会支持和抑郁的相关性[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2020, 24(5): 607-609, 613. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.05.021.Yu XJ, Dong YF, Tian T, et al. While Luzhou cognitive function in the elderly and the correlation between social support and depression[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2020, 24 (5): 607-609, 613. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.05.021. [24] Chang CF, Lin MH, Wang J, et al. The relationship between geriatric depression and health-promoting behaviors among community-dwelling seniors[J]. J Nurs Res, 2013, 21(2): 75-82. DOI: 10.1097/jnr.0b013e3182921fc9. [25] 杨庆菊, 王璞琳, 刘冬华, 等. 电子健康素养视角下公众信息行为与恐慌探析[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2022, 14(5): 180-183. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2022.05.048.Yang QJ, Wang PL, Liu DH, et al. Public information behavior and panic from the perspective of electronic health literacy[J]. Chin Continuing Med Edu, 2022, 14(5): 180-183. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2022.05.048. [26] 杨清红. 老年人健康保障的群体差异及政策启示——基于中国老年健康影响因素跟踪调查和30位老人的深度访谈[J]. 社会保障研究, 2020, (5): 70-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHBY202005007.htmYang QH. Group differences and policy implications of health security for the elderly: based on a follow-up survey of influencing factors of elderly health in China and an in-depth interview with 30 elderly people[J]. Soc Sec Stud, 2020, (5): 70-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHBY202005007.htm -





 下载:
下载: