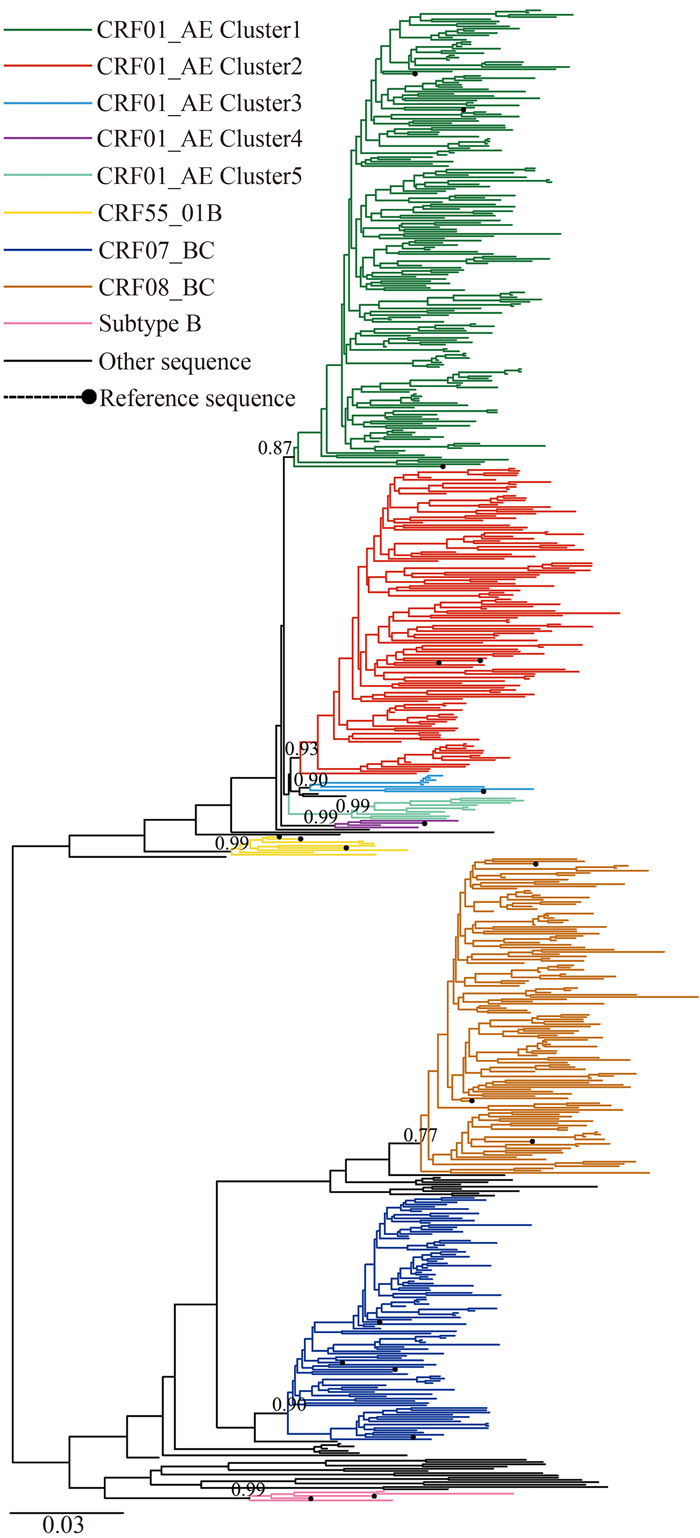
广西壮族自治区2020年新报告≥50岁男性HIV感染者的HIV-1基因亚型分布及其与首次CD4+T淋巴细胞的关联
doi: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2022.12.005
Distribution of HIV-1 genotypes and its association with first CD4+T lymphocytes among HIV-infected men aged 50 and over newly reported in Guangxi in 2020
-
摘要:
目的 分析2020年广西壮族自治区(简称广西)新报告50岁及以上男性(简称中老年男性)HIV感染者的HIV-1基因亚型构成特点及不同基因亚型与首次CD4+T淋巴细胞(简称CD4)计数的关联。 方法 以市为抽样单位,采用分层随机抽样法选取广西2020年新报告中老年男性HIV感染者为研究对象,对其血浆进行病毒RNA提取、逆转录扩增、测序、HIV-1基因亚型和亚簇判定,使用多因素模型评价CD4计数可能存在统计学关联的影响因素。 结果 共纳入分析606例HIV感染者,主要流行毒株有CRF01_AE、CRF07_BC及CRF08_BC三种,其构成比分别为57.6%(349/606)、17.2%(104/606)及22.1%(134/606),其首次CD4中位数分别为145(51, 271) 个/μL、212(110, 330) 个/μL及178(100, 307)个/μL。CRF01_AE感染者首次CD4值低于CRF07_BC感染者(Z=-3.363, P=0.002),也低于CRF08_BC感染者(Z=-2.983, P=0.009)。二元logistic回归分析模型分析显示,CRF01_AE为广西中老年人群CD4≤200个/μL的独立危险因素(aOR=1.453, 95% CI: 1.047~2.017)。 结论 CRF01_AE、CRF07_BC和CRF08_BC为广西2020年新报告中老年男性HIV感染者主要毒株,其构成以CRF01_AE为主,CRF01_AE为CD4≤200个/μL的独立危险因素,提示感染CRF01_AE毒株中老年男性的疾病进展较快,对广西艾滋病流行危害较大。 -
关键词:
- 艾滋病病毒 /
- 中老年男性 /
- 基因亚型 /
- CD4+T淋巴细胞计数
Abstract:Objective To analyze the compositional characteristics of HIV-1 genotype among HIV-infected men aged 50 and over (referred to as middle-aged and elderly men) newly reported in Guangxi in 2020, and to analyze the association between different genotypes and the CD4+ T lymphocyte(referred to as CD4) count at HIV diagnosis. Methods The stratified random sampling method was used to select middle-aged and elderly male HIV-infected patients in 2020 newly reported in 14 cities in Guangxi as the research subjects, and the plasma of infected patients was subjected to viral RNA extraction, reverse transcription amplification, sequencing, HIV-1 genotype and sub-cluster determination. A multivariate model was used to evaluate possible statistically associated influencing factors of CD4 counts. Results A total of 606 HIV-infected patients were included and analyzed, and the main circulating strains were CRF01_AE, CRF07_BC and CRF08_BC, and their proportions were 57.6%(349/606), 17.2%(104/606) and 22.1%(134/606) respectively, and the medians of their first CD4 at diagnosis were 145(51, 271), 212(110, 330) and 178(100, 307) cells/μL, respectively. The first CD4 count at diagnosis of CRF01_AE infected patients was lower than that of CRF07_BC infected patients(Z=-3.363, P=0.002), and lower than that of CRF08_BC infected patients(Z=-2.983, P=0.009). Binary logistic regression model showed that CRF01_AE was an independent risk factor for CD4 ≤200 cells/μL among newly reported middle-aged and elderly men with HIV infection in Guangxi(aOR=1.453, 95% CI: 1.047-2.017). Conclusions CRF01_AE, CRF07_BC and CRF08_BC are the three main circulating strains of HIV infection among middle-aged and elderly males newly reported in Guangxi in 2020, and major in CRF01_AE. CRF01_AE is an independent risk factor for CD4 ≤200 cells/μL, suggesting that the disease progresses rapidly in middle-aged and elderly men with CRF01_AE strain, which is more harmful to the HIV/AIDS epidemic in Guangxi. -
Key words:
- HIV /
- Middle-aged and elderly men /
- Genetic subtypes /
- CD4+T cell counts
-
表 1 广西2020年新报告606例中老年男性HIV感染者的基本情况及亚型分布特征[n(%)]
Table 1. The basic characteristics and subtypes distribution of 606 middle-aged and elderly males HIV cases newly reported in 2020 in Guangxi [n(%)]
变量 合计(N=606) 基因亚型 χ2值 P值 CRF01_AE (n=349) 其他亚型(n=257) 年龄(岁) 2.534 0.282 50~<60 228(37.6) 122(35.0) 106(41.2) 60~<70 238(39.3) 142(40.7) 96(37.4) ≥70 140(23.1) 85(24.3) 55(21.4) 职业 2.301 0.129 农民 522(86.1) 307(88.0) 215(83.7) 非农民 84(13.9) 42(12.0) 42(16.3) 婚姻状况 0.044 0.834 已婚有配偶 359(59.3) 208(59.6) 151(58.7) 其他 247(40.7) 141(40.4) 106(41.3) 民族 0.009 0.925 汉族 350(57.8) 201(57.6) 149(58.0) 其他 256(42.2) 148(42.4) 108(42.0) 文化程度 0.646 0.422 文盲及小学 379(62.5) 223(63.9) 156(60.7) 初中及以上 227(37.5) 126(36.1) 101(39.3) 感染途径 1.000 a 异性传播 602(99.3) 347(99.4) 255(99.2) 同性传播 4(0.7) 2(0.6) 2(0.8) 首次CD4(个/μL) 4.895 0.027 ≤200 352(58.1) 216(61.9) 136(52.9) >200 254(41.9) 133(38.1) 121(47.1) 注:其他亚型,包括CRF07_BC、CRF08_BC、CRF55_01B、CRF85_BC、B、C和URFs;括号内为构成比,省略“%”,括号外为绝对数; a表示使用Fisher精确概率法计算所得P值。 表 2 广西新报告中老年男性HIV感染者的CD4≤200的二元logistic回归分析模型
Table 2. Binary logistic regression analysis for CD4 ≤200 among middle-aged and elderly male HIV cases newly reported in Guangxi
变量 β值 sx值 Wald值 aOR(95% CI)值 P值 HIV-1亚组 CRF01_AE 0.374 0.167 4.988 1.453(1.047~2.017) 0.026 其他亚型 1.000 年龄组(岁) 50~<60 -0.222 0.218 1.042 0.801(0.523~1.227) 0.307 60~<70 -0.290 0.216 1.798 0.748(0.490~1.143) 0.180 ≥70 1.000 常量 -0.291 0.183 2.534 0.111 -
[1] 刘玄华, 朱秋映, 苏锦明, 等. 广西壮族自治区2008-2015年艾滋病病毒感染者基线CD4+T淋巴细胞计数水平对抗病毒治疗脱失的影响[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(9): 1216-1221. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.09.014.Liu XH, Zhu QY, Su JM, et al. Effect of baseline CD4(+) T cell count on drop-out of antiretroviral therapy in HIV infected persons in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 2008-2015[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2018, 39(9): 1216-1221. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.09.014. [2] 韩晶, 汤后林, 毛宇嵘. 2012-2016年新报告HIV感染者首次CD4+T淋巴细胞检测情况分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2018, 24(5): 461-465. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2018.05.09.Han J, Tang HL, Mao YR. First CD4+ T cell test of newly reported HIV/AIDS cases between 2012 and 2016[J]. China J AIDS STD, 2018, 24(5): 461-465. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2018.05.09. [3] Li Y, Han Y, Xie J, et al. CRF01_AE subtype is associated with X4 tropism and fast HIV progression in Chinese patients infected through sexual transmission[J]. AIDS, 2014, 28(4): 521-530. DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000125. [4] Chu M, Zhang W, Zhang X, et al. HIV-1 CRF01_AE strain is associated with faster HIV/AIDS progression in Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 1570. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01858-2. [5] 朱秋映, 陈欢欢, 吴兴华, 等. 广西中老年男性人群艾滋病流行现状及相关影响因素分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2017, 23(11): 1006-1009. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2017.11.09.Zhu QY, Chen HH, Wu XH, et al. HIV/AIDS epidemic and related influencing factors of HIV infection among the middle-aged and elderly male population[J]. China J AIDS STD, 2017, 23(11): 1006-1009. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2017.11.09. [6] 孟琴, 沈智勇, 刘玄华, 等. 广西2008-2016年≥50岁HIV/AIDS病人的特征分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2018, 24(4): 341-344. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2018.04.07.Meng Q, Shen ZY, Liu XH, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and trends of people aged above 50 living with HIV/AIDS in Guangxi from 2008 to 2016[J]. China J AIDS STD, 2018, 24(4): 341-344. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2018.04.07. [7] 葛宪民, 杨文敏, 朱秋映, 等. 广西壮族自治区2010-2017年艾滋病流行病学特征分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2019, 40(3): 315-321. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.03.011.Ge XM, Yang WM, Zhu QY, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of HIV/AIDS in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 2010-2017[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2019, 40(3): 315-321. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.03.011. [8] 曹志强, 王卫军, 林兆森, 等. 广西钦州市2016―2018年新报告HIV感染者不同基因型首次CD4+T细胞计数分析[J]. 中国热带医学, 2020, 20(5): 397-401. DOI: 10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2020.05.01.Cao ZQ, Wang WJ, Lin ZS, et al. HIV genetic subtypes and comparison of first CD4+T cell counts in newly reported HIV infections in Qinzhou, Guangxi, 2016-2018[J]. China Tropical Medicine, 2020, 20(5): 397-401. DOI: 10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2020.05.01. [9] Feng Y, He X, Hsi JH, et al. The rapidly expanding CRF01_AE epidemic in China is driven by multiple lineages of HIV-1 viruses introduced in the 1990s[J]. AIDS, 2013, 27(11): 1793-1802. DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328360db2d. [10] 吴尊友. 中国特色的艾滋病防治策略[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(8): 885-889. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.08.001.Wu ZY. HIV/AIDS prevention strategy with Chinese characteristics[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(8): 885-889. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.08.001. [11] Yu XF, Chen J, Shao Y, et al. Emerging HIV infections with distinct subtypes of HIV-1 infection among injection drug users from geographically separate locations in Guangxi Province, China[J]. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr, 1999, 22(2): 180-188. DOI: 10.1097/00126334-199910010-00011. [12] Piyasirisilp S, McCutchan FE, Carr JK, et al. A Recent Outbreak of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection in Southern China Was Initiated by Two Highly Homogeneous, Geographically Separated Strains, Circulating Recombinant Form AE and a Novel BC Recombinant[J]. J Virol, 2000, 74(23): 11286-11295. DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.23.11286-11295.2000. [13] 李剑军, 方宁烨, 张鸿满, 等. 广西HIV-1分子流行病学20年[J]. 应用预防医学, 2017, 23(2): 173-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYX201702027.htmLi JJ, Fang NY, Zhang HM, et al. Molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 in Guangxi for 20 years[J]. Applied Prev Med, 2017, 23(2): 173-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYX201702027.htm [14] Zhang J, Shen ZY, Li Z, et al. Genetic Characteristics of CRF01_AE among newly diagnosed HIV-1-infected 16- to 25-year olds in 3 geographic regions of Guangxi, China[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2015, 94(21): e894. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000894. [15] 周信娟, 沈智勇, 孟琴, 等. 广西医疗机构2010-2014年HIV抗体检测及病例发现情况[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2016, 22(4): 244-247. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2016.04.07.Zhou XJ, Shen ZY, Meng Q, et al. HIV antibody tests and case detection by medical institutions from 2010 to 2014 in Guangxi[J]. China J AIDS STD, 2016, 22(4): 244-247. DOI: 10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2016.04.07. [16] Li Y, Han Y, Xie J, et al. CRF01_AE subtype is associated with X4 tropism and fast HIV progression in Chinese patients infected through sexual transmission[J]. AIDS, 2014, 28(4): 521-530. DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000125. [17] 许洪波, 杨文敏, 沈智勇, 等. 广西接受抗病毒治疗的老年HIV/AIDS患者死亡和脱失情况及其影响因素分析[J]. 应用预防医学, 2019, 25(3): 173-176, 180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYX201903001.htmXu HB, Yang WM, Shen ZY, et al. Mortality and drop-out of elderly HIV/AIDS patients receiving antiretroviral therapy in Guangxi and its influencing factors[J]. Applied Prev Med, 2019, 25(3): 173-176, 180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYX201903001.htm -





 下载:
下载: