Dose-response relationship between smoking and hypertension among middle-aged and elderly people in Ma'anshan City, Anhui Province
-
摘要:
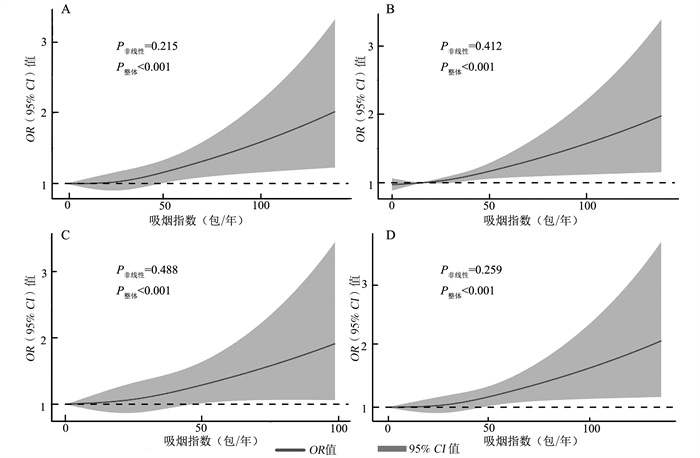
目的 探索安徽省马鞍山市吸烟与中老年(45岁以上)居民高血压的关系,为高血压防制提供针对性的理论依据。 方法 按照多阶段抽样的方法,于2020年8-11月选取了马鞍山市三个地区,共12 132名居民参与问卷调查和体格测量。采用二元logistic回归分析模型分析吸烟与高血压之间是否存在关联,限制性立方样条(restricted cubic spline, RCS)模型和广义线性模型分析二者之间的剂量-反应关系。 结果 本研究共纳入11 457名研究对象,其中高血压患者6 067名,占52.95%。以不吸烟人群作为参照,曾经吸烟人群患高血压风险的OR值在模型一、模型二、模型三中分别为1.37(95% CI: 1.20~1.56)、1.25(95% CI: 1.07~1.46)、1.18(95% CI: 1.00~1.39)。吸烟与高血压的RCS曲线呈现近似“J”型,当吸烟指数>25包/年之后,随着吸烟指数的增加,高血压患病风险呈单调递增的趋势,亚组分析得到一样的结果。均有P非线性>0.05,P整体<0.001,表明吸烟与高血压存在线性剂量-反应关系。广义线性模型的结果显示,吸烟指数每增加1包/年,高血压的患病风险增加1.004倍。 结论 中老年人群中,吸烟与高血压存在剂量-反应关系。 Abstract:Objective To explore the relationship between smoking and hypertension among middle-aged and elderly residents in Ma'anshan city, Anhui Province, and provide theoretical basis of hypertension prevention and treatment. Methods According to the multi-stage sampling method, 12 132 residents were selected from August to November 2020 in three districts of Ma'anshan city, and participated in questionnaire survey and physical measurement. Binary logistic regression was used to analyze the association between smoking and hypertension, and the dose-response relationship for smoking and hypertension was analyzed using the restricted cubic spline (RCS) model and the generalize linear model. Results There were 11 457 subjects in this study, including 6 067 patients with hypertension(52.95%). Taking non-smokers as the reference, the OR value of the risk of hypertension in former smokers was 1.37(95% CI: 1.20-1.56), 1.25(95% CI: 1.07-1.46) and 1.18(95% CI: 1.00-1.39) in Model 1, Model 2 and Model 3, respectively. The RCS curve of smoking and hypertension presents an approximate "J" shape. When the smoking index was greater than 25 pack-years, the risk of hypertension increased monotonically with the increase of smoking index, and the subgroup analysis showed the same results. Pnon-linear was greater than 0.05 and Ptotal was less than 0.001, indicating a linear dose-response relationship between smoking and hypertension. The results of the generalize linear model showed that for every 1-pack-year increased in the smoking index, the risk of hypertension increased 1.004-fold. Conclusion There is a significant dose-response relationship between smoking and hypertension in middle-aged and elderly people. -
Key words:
- Smoking /
- Hypertension /
- Restricted cubic spline model /
- Middle-aged and elderly people
-
图 1 吸烟与高血压的剂量-反应关系
注:A是总人群吸烟与高血压的RCS曲线(调整了性别、年龄、BMI、文化程度、婚姻状况、家庭年收入、高血压家族史、职业、近一年的饮酒频率、是否参加规律性体育锻炼),吸烟指数取3个节点(7.5包/年、27.0包/年、52.0包/年);B是男性人群吸烟与高血压的RCS曲线(调整了年龄、BMI、文化程度、家庭年收入、高血压家族史、职业、近一年的饮酒频率、是否参加规律性体育锻炼),吸烟指数取3个节点(7.7包/年、28.0包/年、54.4包/年);C是中年人群吸烟与高血压的RCS曲线(调整了性别、BMI、职业、高血压家族史、近一年的饮酒频率),吸烟指数取3个节点(7.5包/年、26.0包/年、51.0包/年);D是老年人群吸烟与高血压的RCS曲线(调整了性别、BMI、文化程度、高血压家族史),吸烟指数取3个节点(7.5包/年、30.0包/年、57.8包/年)。
Figure 1. Dose-response relationship between smoking and hypertension
表 1 研究对象根据是否患有高血压的基本人口学特征[n(%)]
Table 1. Basic characteristics of study participants with hypertension [n(%)]
变量 高血压组(n=6 067) 非高血压组(n=5 390) χ2/Z值 P值 变量 高血压组(n=6 067) 非高血压组(n=5 390) χ2/Z值 P值 性别 8.90 0.003 职业 62.32 <0.001 男 2 663(43.89) 2 217(41.13) 职员 568(9.36) 743(13.78) 女 3 404(56.11) 3 173(58.87) 离退休人员 3 443(56.75) 2 792(51.80) 年龄(岁) 160.72 < 0.001 其他 945(15.58) 834(15.47) 0~ < 60 2 107(34.73) 2 499(46.36) 高血压家族史 14.01 < 0.001 ≥60 3 960(65.27) 2 891(53.64) 是 2 519(41.52) 2 053(38.09) BMI(kg/m2) -9.92 a < 0.001 否 3 548(58.48) 3 337(61.91) < 18.5 118(1.94) 111(2.06) 饮酒频率 -2.88 a 0.004 18.5~<24.0 2 782(45.85) 2 909(53.97) 每天 779(12.84) 544(10.09) 24.0~<28.0 2 414(39.79) 1 970(36.55) 3~6 d/周 214(3.53) 191(3.54) ≥28.0 753(12.41) 400(7.42) 1~2 d/周 273(4.50) 238(4.42) 文化程度 -6.14 a < 0.001 1~3 d/月 226(3.73) 256(4.75) 未正式上过学 1 025(16.89) 776(14.40) 少于1 d/月 4 575(75.41) 4 161(77.20) 小学 1 398(23.04) 1 102(20.45) 睡眠时间(h) -0.38 a 0.701 初中 2 021(33.31) 1 861(34.53) < 7 1 088(17.93) 872(16.18) 高中/中专/技校 1 157(19.07) 1 131(20.98) 7~ < 9 3 970(65.44) 3 695(68.55) 大专及以上 466(7.68) 520(9.65) ≥9 1 009(16.63) 823(15.27) 婚姻状况 16.69 < 0.001 参与规律性体育锻炼 6.06 0.014 已婚 5 350(88.18) 4 834(89.68) 是 3 400(56.04) 2 897(53.75) 离异 168(2.77) 175(3.25) 否 2 667(43.96) 2 493(46.25) 丧偶与其他 549(9.05) 381(7.07) 吸烟状况 -3.90 a < 0.001 家庭平均年收入(万元) -2.61 a 0.009 从不吸烟 4 183(68.95) 3 875(71.89) < 1 152(2.51) 120(2.23) 目前吸烟 1 283(21.15) 1 107(20.54) 1~ < 3 797(13.14) 689(12.78) 曾经吸烟 601(9.91) 408(7.57) 3~ < 10 4 198(69.19) 3 652(67.76) 被动吸烟 -0.47 a 0.642 ≥10 920(15.16) 929(17.24) 每天 1 699(28.00) 1 533(28.44) 职业 62.32 < 0.001 4~6 d/周 955(15.74) 842(15.62) 工人 446(7.35) 405(7.51) 1~3 d/周 440(7.25) 393(7.29) 农民 665(10.96) 616(11.43) 没有 2 973(49.00) 2 622(48.65) 注:a为单向有序类型变量,采用Mann-Whitney U检验。 表 2 吸烟与高血压关系的二元logistic回归分析
Table 2. Binary logistic regression analysis on the relationship between smoking and hypertension
吸烟状况 模型一a 模型二b 模型三c OR(95% CI)值 P值 OR(95% CI)值 P值 OR(95% CI)值 P值 从不吸烟 1.00 1.00 1.00 目前吸烟 1.07(0.98~1.18) 0.128 1.10(0.98~1.25) 0.120 1.05(0.93~1.19) 0.446 曾经吸烟 1.37(1.20~1.56) < 0.001 1.25(1.07~1.46) 0.006 1.18(1.00~1.39) 0.044 0包/年 1.00 1.00 1.00 < 15包/年 1.06(0.92~1.23) 0.419 1.09(0.92~1.28) 0.328 1.06(0.89~1.25) 0.513 15包/年~ < 30包/年 1.10(0.97~1.26) 0.136 1.11(0.95~1.30) 0.173 1.06(0.91~1.25) 0.456 ≥30包/年 1.24(1.11~1.38) < 0.001 1.20(1.04~1.37) 0.011 1.13(0.98~1.30) 0.104 注:a模型一为单因素分析; b模型二调整了性别与年龄; c模型三在模型二的基础上调整了BMI、文化程度、职业、婚姻状况、家庭年收入、高血压家族史、近一年的平均饮酒频率、是否参加规律性的体育锻炼。 表 3 吸烟指数对高血压患病影响的广义线性回归分析
Table 3. Generalize linear regression analysis of the influence of smoking index on hypertension
影响因素 β值 sx值 P值 OR(95% CI)值 影响因素 β值 sx值 P值 OR(95% CI)值 吸烟指数 0.004 0.001 0.008 1.00(1.00~1.01) 家庭年收入 0.011 0.032 0.735 1.01(0.95~1.08) 性别 -0.048 0.052 0.350 0.95(0.86~1.05) 职业 0.019 0.014 0.180 1.02(0.99~1.05) 年龄 0.428 0.043 < 0.001 1.53(1.41~1.67) 高血压家族史 0.198 0.040 < 0.001 1.22(1.13~1.32) BMI 0.258 0.028 < 0.001 1.29(1.23~1.37) 近一年的饮酒频率 -0.026 0.013 0.041 0.97(0.95~0.99) 文化程度 -0.056 0.018 0.002 0.95(0.91~0.98) 是否参与规律性的体育锻炼 0.056 0.039 0.146 1.06(0.98~1.14) 婚姻状况 0.060 0.036 0.094 1.06(0.99~1.14) 注:性别、年龄、BMI、文化程度、婚姻状况、家庭年收入、高血压家族史、职业、近一年的饮酒频率、是否参加规律性体育锻炼均为协变量。 -
[1] 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会, 高血压联盟(中国), 中华医学会心血管病学分会, 等. 中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2019, 24(1): 24-56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2019.01.002.Writing Group of 2018 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension, Chinese Hypertension League, Chinese Society of Cardiology, et al. 2018 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension[J]. Chin J Cardiovasc Med, 2019, 24(1): 24-56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2019.01.002. [2] Mills KT, Bundy JD, Kelly TN, et al. Global disparities of hypertension prevalence and control: a systematic analysis of population-based studies from 90 countries[J]. Circulation, 2016, 134(6): 441-450. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018912. [3] Wu J, Pan G, Huang YT, et al. Effects of passive smoking and its duration on the prevalence of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese women[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2020, 12(10): 9440-9446. DOI: 10.18632/aging.103217. [4] 李新华. 2018中国成人烟草调查报告[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2020: 6-24.Li XH. Chinese Adult Tobacco Survey Report 2018[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2020: 6-24. [5] 苏健, 覃玉, 沈冲, 等. 吸烟和戒烟行为与男性2型糖尿病血糖控制关系的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(11): 1454-1459. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.11.003.Su J, Qin Y, Shen C, et al. Association between smoking cesstion and glycemic control in male patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(11): 1454-1459. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.11.003. [6] Hou J, Gu J, Liu X, et al. Long-term exposure to air pollutants enhanced associations of obesity with blood pressure and hypertension[J]. Clin Nutr, 2021, 40(4): 1442-1450. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.02.029. [7] 甘俊英, 魏昊, 邱光文, 等. 马鞍山市2019年主城区公共场所健康危害因素监测结果分析[J]. 安徽预防医学杂志, 2021, 27(5): 355-358. DOI: 10.19837/j.cnki.ahyf.2021.05.006.Gan JY, Wei H, Qiu GW, et al. Analysis on the monitoring results of health hazard factors in public places in the main urban area of Ma'anshan City in 2019[J]. Anhui Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2021, 27(5): 355-358. DOI: 10.19837/j.cnki.ahyf.2021.05.006. [8] Sohn K. Relationship of smoking to hypertension in a developing country[J]. Glob Heart, 2018, 13(4): 285-292. DOI: 10.1016/j.gheart.2018.01.004. [9] Kim SH, Lee JS. The association of smoking and hypertension according to cotinine-verified smoking status in 25, 150 Korean adults[J]. Clin Exp Hypertens, 2019, 41(5): 401-408. DOI: 10.1080/10641963.2018.1489548. [10] 周筠, 郑鸿尘, 薛恩慈, 等. 中老年人群中吸烟与血压关联的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(6): 896-901. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200312-00320.Zhou J, Zhen HC, Xue EC, et al. A prospective cohort study on the association between smoking and blood pressure among middle-aged and elderly people[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2020, 41(6): 896-901. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200312-00320. [11] Dikalov S, Itani H, Richmond B, et al. Tobacco smoking induces cardiovascular mitochondrial oxidative stress, promotes endothelial dysfunction, and enhances hypertension[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2019, 316(3): H639-H646. DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00595.2018. [12] Liu X, Byrd JB. Cigarette smoking and subtypes of uncontrolled blood pressure among diagnosed hypertensive patients: paradoxical associations and implications[J]. Am J Hypertens, 2017, 30(6): 602-609. DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpx014. [13] Li G, Wang H, Wang K, et al. The association between smoking and blood pressure in men: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2017, 17(1): 797. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-017-4802-x. [14] 胡文斌, 张婷, 史建国, 等. 男性吸烟与高血压病的剂量-反应关系[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2014, 42(9): 773-777. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2014.09.013.Hu WB, Zhang T, Shi JG, et al. Association between cigarette smoking and hypertension in men: a dose response relationship analysis[J]. Chin J Cardiol, 2014, 42(9): 773-777. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2014.09.013. -





 下载:
下载: