Integrative bioinformatic and functional analyses of genes related to non-small cell lung cancer in female
-
摘要:
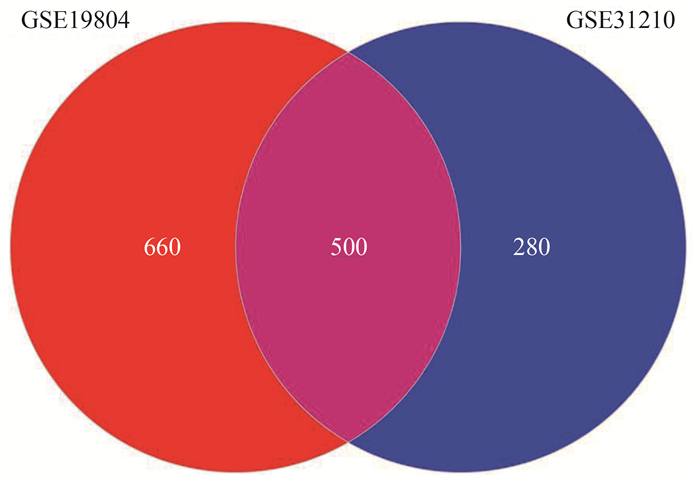
目的 通过对女性非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)相关基因的生物信息学分析和功能预测,探讨女性NSCLC的发病机制和预后生物标志物。 方法 从基因表达综合数据库(Gene Expression Omnibus, GEO)下载女性NSCLC患者的数据,使用limma包鉴定差异表达基因(differentially expressed genes, DEGs)。对DEGs进行基因本体(Gene Ontology, GO)和Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes(KEGG)分析和构建蛋白质相互作用(protein-protein interaction, PPI) 网络分析。利用igraph包筛选关键DEG,利用Oncomine数据库及NSCLC细胞系验证关键DEGs的表达情况,并采用Log-rank检验分析关键DEGs的表达水平与女性NSCLC患者预后的关联。 结果 共筛选出500个DEGs,GO富集分析表明,DEGs主要参与细胞增殖、细胞迁移和细胞外结构组成(均有P < 0.05)。KEGG富集分析表明,这些途径主要与细胞外基质(extracellular matrix, ECM)受体相互作用、蛋白质消化吸收和白细胞跨内皮迁移信号有关。通过PPI网络分析得到3个关键DEGs:白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6, IL-6)、表皮细胞生长因子(epidermal growth factor, EGF)和基质金属蛋白酶-9(matrix metalloprotein-9, MMP-9)。Oncomine数据库分析和NSCLC细胞系结果显示NSCLC组织和细胞系中IL-6的表达较低,而EGF和MMP-9的表达较高。Log-rank检验表明IL-6(χ2= 6.90,P=0.009)和EGF(χ2= 7.73,P=0.005)表达与女性NSCLC患者预后有关。 结论 在女性NSCLC患者中,IL-6和EGF可能是NSCLC发病与预后机制中的重要基因,是治疗的潜在靶点。 Abstract:Objective To explore the pathogenesis and prognostic biomarkers of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in female patients by bioinformatic analysis and functional prediction of potential NSCLC-associated genes. Methods Gene expression profile data for female patients with NSCLC were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified using limma package. Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and protein-protein interaction (PPI) analyses were performed for DEGs. The igraph package was used to screen the key DEGs from PPI. The expression pattern of key DEGs were confirmed in Oncomine database and NSCLC cell lines. The Log-rank test was used to assess the association between key DEGs and overall survival. Results A total of 500 DEGs were identified, and GO analysis showed that these genes were mainly involved in cell proliferation, cell migration, and extracellular structure organization (P < 0.05). The KEGG analysis indicated that these genes were primarily related to ECM-receptor interactions, protein digestion and absorption, and leukocyte transendothelial migration signalling. Three key DEGs [interleukin-6 (IL-6), epidermal growth factor (EGF), matrix metalloprotein-9 (MMP-9)] were screened from the PPI network. The expression of IL-6 was downregulated in NSCLC tissues and cell lines, while EGF and MMP-9 expressions were upregulated. The log-rank test found that IL-6 and EGF were associated with overall survival of female patients with NSCLC. Conclusions In female patients, IL-6 (χ2 =6.90, P=0.009) and EGF (χ2 =7.73, P=0.005) may be key genes for pathogenesis and prognosis of NSCLC, and represent novel therapeutic targets. -
表 1 各基因引物
Table 1. Primers for each gene
基因引物 引物序列 IL-6上游引物 GAGATACCACTCCCAACAGACC IL-6下游引物 AAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTCATACA EGF上游引物 TCTGAACCCGGACGGATTG EGF下游引物 GACATCGCTCGCGAACGTAG MMP-9上游引物 GAGATACCACTCCCAACAGACC MMP-9下游引物 CCGAGTTGGAACCACGACGC GAPDH上游引物 GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT GAPDH下游引物 GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG -
[1] Levy DT, Meza R, Zhang YA, et al. Gauging the effect of U.S. tobacco control policies from 1965 through 2014 using SimSmoke[J]. Am J Prev Med, 2016, 50(4): 535-542. DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2015.10.001. [2] Sauer AG, Siegel RL, Jemal A, et al. Updated review of prevalence of major risk factors and use of screening tests for cancer in the United States[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2017, 26(8): 1192-1208. DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0219. [3] Vavalà T, Levra MG, Novello S. Lung cancer in never smokers: a different disease[J]. Curr Respir Care Rep, 2014, 3(1): 26-34. DOI: 10.1038/nrc2190. [4] Kim JH, Park K, Yim SH, et al. Genome-wide association study of lung cancer in Korean non-smoking women[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2013, 28(6): 840-847. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.6.840. [5] Huber RM. Is lung cancer in never-smokers a different disease?-Back to the figures[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2007, 2(9): 787-788. DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318153f3c5. [6] Lu TP, Tsai MH, Lee JM, et al. Identification of a novel biomarker, SEMA5A, for non-small cell lung carcinoma in nonsmoking women[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2010, 19(10): 2590-2597. DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0332. [7] Yamauchi M, Yamaguchi R, Nakata A, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase defines critical prognostic genes of stage Ⅰ lung adenocarcinoma[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(9): e43923. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043923. [8] Stiles BM, Rahouma M, Hussein MK, et al. Never smokers with resected lung cancer: different demographics, similar survival[J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2018, 53(4): 842-848. DOI: 10.1093/ejcts/ezx390. [9] Choi JR, Park SY, Noh OK, et al. Gene mutation discovery research of non-smoking lung cancer patients due to indoor radon exposure[J]. Ann Occup Environ Med, 2016, 28(1): 13. DOI: 10.1186/s40557-016-0095-2. [10] Zhao JG, Wang JF, Feng JF, et al. HHIP overexpression inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(11): e0225755. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225755. [11] Tsukamoto H, Fujieda K, Senju S, et al. Immune-suppressive effects of interleukin-6 on T-cell-mediated anti-tumour immunity[J]. Cancer Sci, 2018, 109(3): 523-530. DOI: 10.1111/cas.13433. [12] Flint TR, Janowitz T, Connell CM, et al. Tumor-induced IL-6 reprograms host metabolism to suppress antitumour immunity[J]. Cell Metab, 2016, 24(5): 672-684. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.10.010. [13] Jiang W, Tian W, Ijaz M, et al. Inhibition of EGF induced migration and invasion by sulfated polysaccharide of sepiella maindroni ink via the suppression of EGFR/Akt/p38/MAPK/MMP-2 signaling pathway in KB cells[J]. Biomed Pharmaeother, 2017(11): 95-102. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.050. [14] Kim J, Kong JN, Chang H, et al. EGF induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through phospho-Smad2/3-Snail signalling pathway in breast cancer cells[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(51): 85021-85032. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13116. [15] Ni Y, Ye X, Wan C, et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation(MWA)increased the serum levels of VEGF and MMP-9 in stage Ⅰ non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2017, 33(4): 435-439. DOI: 10.1080/02656736.2017.1284350. -





 下载:
下载: