Analysis of diabetes prevalence and related factors among older adults in rural Yunnan Province: a structure equation modelling approach
-
摘要:
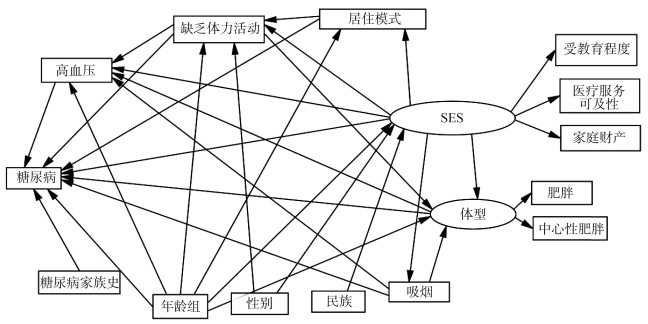
目的 采用结构方程模型(structural equation model, SEM)分析云南省农村老年人糖尿病患病的现状及其影响因素。 方法 在云南农村地区抽取4 833名≥60岁的老年人,采用多阶段分层随机抽样的方法进行问卷调查和体格检查,糖尿病老年人患病的影响因素采用SEM进行分析。 结果 云南农村老年人糖尿病患病率为10.2%,其中男性为203人,占9.2%,女性为291人,占11.0%。SEM的分析结果显示,体型(包括肥胖和中心性肥胖)和缺乏体力活动对糖尿病患病起到直接和间接作用,其路径系数分别为0.134和0.041;高血压和糖尿病家族史对糖尿病患病起到直接作用,其路径系数分别为0.054和0.097;性别、吸烟、居住模式和社会经济地位(socioeconomic status, SES)对糖尿病患病起到间接作用,其路径系数分别为0.045、0.005、-0.007和-0.049。 结论 体型、缺乏体力活动、高血压、糖尿病家族史和吸烟是糖尿病患病的主要影响因素。加强糖尿病的健康教育对SES低的老年人的糖尿病的预防与控制有效。 Abstract:Objective This study aims to analyze the prevalence of diabetes and its associated influencing factors among older adults in rural Yunnan Province. Methods A stratified randomized method was used to select 4 833 older adults aged ≥60 years in rural Yunnan Province. Each participant underwent a questionnaire survey and health examination. The associated influencing factors were analyzed using structural equation modelling (SEM). Results The prevalence of diabetes among older adults in rural Yunnan Province was 10.2%. The results of SEM indicated that body fat distribution (obesity and central obesity) and physical inactivity had both direct and indirect effect on diabetes, with the path coefficients of 0.134 and 0.041, respectively. Hypertension and family history of diabetes had direct effect on diabetes, with path coefficient of 0.054 and 0.097, respectively. Gender, smoking, residential pattern and socioeconomic status (SES) had only indirect effect on diabetes, with path coefficients of 0.045, 0.005, -0.007 and -0.049, respectively. Conclusions The main factors influencing diabetes prevalence include body fat distribution, physical inactivity, hypertension, family history of diabetes, and smoking. Promoting healthy lifestyle education among older adults with low SEP is beneficial for diabetes prevention and control. -
Key words:
- Rural area /
- Diabetes /
- Older adults /
- Structural equation model
-
表 1 不同特征人群的糖尿病患病情况
Table 1. The prevalence of diabetes in different characteristic populations
特征 [n(%)] 95% CI $\chi$2值 P值 特征 [n(%)] 95% CI $\chi$2值 P值 性别 4.269 0.039 医疗服务可及性 9.125 0.003 男 203(9.2) 7.9~10.5 好 362(9.5) 8.6~10.5 女 291(11.0) 9.8~12.3 差 132(12.7) 10.7~14.9 年龄组(岁) 2.096 0.553 吸烟 5.874 0.015 60~ < 65 129(9.7) 8.2~11.4 是 410(10.8) 9.8~11.8 65~ < 70 137(10.7) 9.0~12.4 否 84(8.2) 6.5~9.9 70~ < 75 116(11.1) 9.0~13.0 缺乏体力活动 10.023 0.002 ≥75 112(9.5) 7.8~11.2 是 286(11.6) 10.3~13.0 民族 0.682 0.409 否 208(8.8) 7.6~9.9 汉族 418(10.4) 9.4~11.4 肥胖 30.982 <0.001 少数民族 76(9.4) 7.5~11.5 是 62(19.3) 15.0~23.6 居住模式 0.029 0.865 否 432(9.6) 8.7~10.4 和配偶居住 346(10.3) 9.2~11.3 中心性肥胖 47.229 <0.001 未和配偶居住 148(10.1) 8.6~11.6 是 333(13.1) 11.7~14.2 受教育程度 0.417 0.518 否 161(7.1) 6.0~8.1 文盲 295(10.0) 8.9~11.0 糖尿病家族史 60.860 <0.001 小学及以上 199(10.6) 9.2~11.9 是 66(24.1) 9.5~29.8 家庭财产 3.603 0.058 否 428(9.4) 8.6~10.2 好 371(8.9) 7.4~10.4 高血压 41.576 <0.001 差 123(10.7) 9.7~11.8 是 318(13.0) 11.7~14.4 否 176(7.4) 6.4~8.5 合计 494(10.2) 表 2 基础模型和修正模型
Table 2. Basic model and modified model
模型 $\chi$2/υ RMSEA GFI CFI TLI RMR P值 基础模型 16.148 0.056 0.976 0.845 0.723 0.011 < 0.001 模型A 14.123 0.052 0.976 0.844 0.760 0.011 < 0.001 模型B 9.337 0.042 0.984 0.905 0.858 0.011 < 0.001 模型C 8.180 0.039 0.987 0.908 0.869 0.006 < 0.001 模型D 4.662 0.028 0.993 0.957 0.933 0.004 < 0.001 -
[1] Ogurtsova K, Da RF J, Huang Y, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040 [J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2017, 128: 40-50. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024. [2] Yang L, Shao J, Bian Y, et al. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus among inland residents in China (2000-2014): a meta-analysis [J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2016, 7(6): 845-852. DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12514. [3] 苏蓉. 云南省四个独有少数民族糖尿病患病、管理和控制现状及社会经济影响研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2017.Su R. The prevalence, managment and control of diabetes and relationships with socioeconomic status among four unique ethnic minorities in Yunnan Province [D]. Kunming: Kunming medical University, 2017. [4] 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会. 中国高血压防治指南(2016年修订版) [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016: 770-771.China hypertension guidelines revision committee. China hypertension guidelines (revised in 2016) [M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2016: 770-771. [5] World Health Organization. The asia-pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment [M]. Sydney: Health Communications, 2000: 20-21. [6] Wang Z, Li X, Chen M. Socioeconomic factors and inequality in the prevalence and treatment of diabetes among middle-aged and elderly adults in China [J]. J Diabetes Res, 2018, 2018: 1-12. DOI: 10.1155/2018/1471808. [7] Salas A, Acosta D, Ferri CP, et al. The prevalence, correlates, detection and control of diabetes among older people in low and middle income countries. A 10/66 dementia research group population-based survey [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(2): e149616. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149616. [8] Tripathy JP, Thakur JS, Jeet G, et al. Structural equation modeling to identify the risk factors of diabetes in the adult population of North India [J]. Trop Med Health, 2018, 46(1). DOI: 10.1186/s41182-018-0104-y. [9] Gatimu SM, Milimo BW, Sebastian MS. Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among older adults in Ghana [J]. BMC Public Health, 2016, 16(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-3845-8. [10] Ustulin M, Rhee SY, Chon S, et al. Importance of family history of diabetes in computing a diabetes risk score in Korean prediabetic population [J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 15958. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34411-w. [11] Sliwińska-Mossoń M, Milnerowicz H. The impact of smoking on the development of diabetes and its complications [J]. Diab Vasc Dis Res, 2017, 14(4): 265-276. DOI: 10.1177/1479164117701876. -





 下载:
下载: