Analysis on the factors influencing adolescents smoking behavior in Jiangsu Province using a structural equation model
-
摘要:
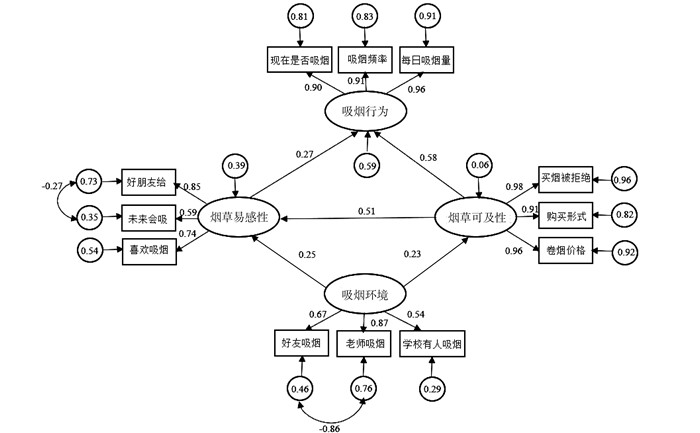
目的 探究江苏省青少年吸烟行为的现况与影响因素,结合结构方程模型(structural equation model, SEM),为控烟干预提供依据。 方法 运用多阶段整群抽样(probability proportionate to size sampling, PPS)方法,向青少年发放调查问卷,分析方法采用结构方程模型。 结果 本次研究累计调查青少年6 104人,江苏省初中生青少年吸烟率为2.65%。logistic回归分析模型分析显示,男性(OR=1.623)、好友中有人吸烟(OR=7.827)、好友给烟可能会使用(OR=7.219)、喜欢吸烟(OR=3.120)、认为自己未来会吸烟(OR=2.854)、老师吸烟(OR=2.068)、室内二手烟暴露(OR=2.196)、认为戒烟很难(OR=2.010)、二手烟危害认知欠缺(OR=1.738)是青少年吸烟的危险因素, 差异均有统计学意义(均有P < 0.05)。在SEM中,烟草易感性对吸烟行为体现为直接作用,效果为0.270,吸烟环境对吸烟行为的间接作用为0.236,烟草可及性对吸烟行为的总作用为0.719,其中直接作用为0.580,间接作用为0.139,模型适配度良好。 结论 青少年吸烟行为的主要影响因素包括烟草易感性、烟草可及性与吸烟环境,将个体与环境等多方面有机结合进行干预可有效降低青少年吸烟率。 Abstract:Objective To identify the factors influencing adolescent smoking behavior in Jiangsu Province by a Structural Equation Model (SEM) model, providing a reference for tobacco control initiatives.. Methods Probability Proportionate to Size Sampling (PPS) was used to distribute questionnaires to adolescents, and the SEM model was conducted for data analysis. Results A total of 6 104 students were surveyed, revealing a 2.65% smoking rate among junior high school students in Jiangsu Province. Logistic analysis showed that the risk factors for student smoking as males (OR=1.623), having friends who smoke (OR=7.827), use cigarettes given by friends (OR=7.219), enjoying smoking (OR=3.120), potential predisposition to smoking (OR=2.854), having teachers who smoke (OR=2.068), exposure to indoor secondhand smoke (OR=2.196), the belief that quitting smoking is difficult (OR=2.010), and a lack of awareness about the harms of secondhand smoke (OR=1.738) (all P<0.05). The results of the SEM demonstrated a direct effect of tobacco susceptibility on smoking behavior (0.270), an indirect effect of smoking environment (0.236). And a total effect of tobacco access (0.719), with a direct effect of 0.580 and an indirect effect of 0.139. The model exhibited a good fit. Conclusions Tobacco susceptibility, access to tobacco, and the smoking environment are the primary factors influencing adolescent smoking behavior. Interventions addressing both individual and environmental aspects can effectively reduce youth smoking rates. -
Key words:
- Smoking behavior /
- Adolescents /
- Influence factors /
- Structural equation model
-
表 1 江苏省初中生吸烟现况单因素分析[n(%)]
Table 1. Univariate analysis on the smoking status of junior high school students in Jiangsu Province [n(%)]
变量 调查人数 吸烟人数 χ2值 P值 性别 25.172 <0.001 男 3 379(55.36) 121(3.58) 女 2 725(44.64) 41(1.50) 年级 50.636 <0.001 初一 2 031(33.27) 18(0.88) 初二 2 065(33.83) 54(2.62) 初三 2 006(32.86) 90(4.49) 每周零花钱(元) 73.204 <0.001 ≤20 4 261(69.92) 64(1.50) 21~50 1 120(18.38) 60(5.36) >50 713(11.70) 38(5.33) 家里是否看到有人吸烟 68.605 <0.001 是 2 033(33.32) 103(5.06) 否 4 069(66.68) 59(1.45) 在室外是否看到有人吸烟 60.378 <0.001 是 2 947(48.30) 127(4.31) 否 3 155(51.70) 35(1.11) 是否在电视中看到吸烟镜头 41.434 <0.001 是 3 074(50.36) 122(3.97) 否 3 030(49.64) 40(1.32) 是否见过控烟信息 7.972 0.005 是 3 812(62.45) 84(2.20) 否 2 292(37.55) 78(3.40) 是否在课堂学习过烟草知识 12.347 <0.001 是 2 632(43.12) 48(1.82) 否 3 472(56.88) 114(3.28) 父母吸烟状况 22.813 <0.001 至少有1人吸烟 3 201(52.44) 107(3.34) 都不吸烟 2 903(47.56) 55(1.89) 好友吸烟状况 537.061 <0.001 身边有朋友吸烟 1 240(20.31) 150(12.10) 身边朋友都不吸烟 4 864(79.69) 12(0.25) 是否见过老师在校内吸烟 134.845 <0.001 是 2 309(37.83) 132(5.72) 否 3 795(62.17) 30(0.79) 吸烟对年轻人魅力的影响 72.605 <0.001 更有吸引力 470(7.70) 41(8.72) 减少吸引力或没有区别 5 634(92.30) 121(2.15) 社交时吸烟感受 158.748 <0.001 更舒服 195(3.19) 33(16.92) 更不舒服或没差别 5 909(96.81) 129(2.18) 好友给烟是否会使用 1 395.411 <0.001 有可能会 440(7.21) 133(30.23) 肯定不会 5 664(92.79) 29(0.51) 认为自己未来是否会吸烟 1 175.089 <0.001 有可能会 454(7.44) 125(27.53) 肯定不会 5 650(92.56) 37(0.65) 喜欢吸烟 922.015 <0.001 同意 199(3.26) 73(36.68) 反对 5 905(96.74) 89(1.51) 表 2 江苏省初中生吸烟现况影响因素非条件logistic回归分析模型
Table 2. Unconditional logistic regression analysis model of influencing factors on the smoking status of junior high school students in Jiangsu Province
变量 β值 sx Wald值 OR值(95% CI) P值 男性 0.484 0.233 4.329 1.623(1.028~2.560) 0.037 好友中有人吸烟 2.058 0.339 36.918 7.827(4.030~15.200) <0.001 好友给烟可能会使用 1.977 0.302 42.779 7.219(3.992~13.053) <0.001 喜欢吸烟 1.138 0.246 21.417 3.120(1.927~5.052) <0.001 认为自己未来会吸烟 1.049 0.288 13.238 2.854(1.622~5.022) <0.001 老师吸烟 0.726 0.247 8.647 2.068(1.274~3.355) 0.003 室内二手烟暴露 0.787 0.254 9.606 2.196(1.335~3.611) 0.002 认为戒烟很难 0.698 0.214 10.608 2.010(1.321~3.060) 0.001 二手烟危害认知欠缺 0.553 0.215 6.622 1.738(1.141~2.648) 0.010 常量 -7.755 0.410 357.826 <0.001 <0.001 表 3 SEM拟合指标
Table 3. SEM fit metrics
拟合指数 RMSEA GFI NFI CFI IFI RMR 模型指标 0.068 0.964 0.976 0.977 0.977 0.007 参考标准 <0.08 >0.90 >0.90 >0.90 >0.90 <0.05 注:近似误差均方差(root mean square error of approximation,RMSEA);拟合优度指数(goodness of fit index,GFI);赋范拟合指数(normed fit index,NFI);比较拟合指数(comparative fit index,CFI);增值拟合指数(incremental fit index,IFI);均方根残差(root mean square residual,RMR)。 表 4 吸烟行为影响因素的直接与间接作用
Table 4. Direct and indirect effects of influencing factors on the smoking behavior
影响因素 直接作用 间接作用 总体作用 吸烟环境→吸烟行为 <0.001 0.236 0.236 烟草可及性→吸烟行为 0.580 0.139 0.719 烟草易感性→吸烟行为 0.270 <0.001 0.270 吸烟环境→烟草可及性 0.235 <0.001 0.235 吸烟环境→烟草易感性 0.250 0.120 0.371 烟草可及性→烟草易感性 0.513 <0.001 0.513 -
[1] 《中国吸烟危害健康报告2020》编写组. 《中国吸烟危害健康报告2020》概要[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2021, 36(10): 937-952. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.10.001.The Writing Committee of 2020 Report on Health Hazards of Smoking in China. 2020 Report on Health Hazards of Smoking in China: an Updated Summary [J]. Chin Circul J, 2021, 36(10): 937-952. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.10.001. [2] Makadia LD, Roper PJ, Andrews JO, et al. Tobacco use and smoke exposure in children: new trends, harm, and strategies to improve health outcomes [J]. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep, 2017, 17(8): 55. DOI: 10.1007/s11882-017-0723-0. [3] Īçmeli ÖS, Türker H, Gündoģuş B, et al. Behaviours and opinions of adolescent students on smoking [J]. Tuber Toraks, 2016, 64(3): 217-222. DOI: 10.5578/tt.20925. [4] Park SE, Lee KS, Yun SN, et al. Structural model of factors influencing smoking behavior among Korean-Chinese adolescent boys [J]. Appl Nurs Res, 2014, 27(3): 192-197. DOI: 10.1016/j.apnr.2014.01.002. [5] El-toukhy S, Sabado M, Choi K. Trends in susceptibility to smoking by race and ethnicity [J]. Pediatrics, 2016, 138(5): e20161254. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-1254. [6] 崔岚, 覃玉, 苏健, 等. 江苏省青少年烟草广告暴露情况与吸烟易感性分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2018, 39(1): 42-44, 49. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2018.01.013.Cui L, Qin Y, Su J, et al. Exposure to tobacco advertising and smoking susceptibility among teenagers of Jiangsu Province in 2013 [J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2018, 39(1): 42-44, 49. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2018.01.013. [7] Bold KW, Buta E, Simon P, et al. Using latent class analysis to examine susceptibility to various tobacco products among adolescents [J]. Nicotine Tob Res, 2020, 22(11): 2059-2065. DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntz216. [8] Heris CL, Chamberlain C, Gubhaju L, et al. Factors influencing smoking among indigenous adolescents aged 10-24 years living in Australia, New Zealand, Canada, and the United States: a systematic review [J]. Nicotine Tob Res, 2020, 22(11): 1946-1956. DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntz219. [9] Wang TW, Gentzke AS, Creamer MR, et al. Tobacco product use and associated factors among middle and high school students-United States, 2019 [J]. MMWR Surveill Summ, 2019, 68(12): 1-22. DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6812a1. [10] Paynter J, Edwards R. The impact of tobacco promotion at the point of sale: a systematic review [J]. Nicotine Tob Res, 2009, 11(1): 25-35. DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntn002. [11] Kuipers MA, Best C, Wilson M, et al. Adolescents' perceptions of tobacco accessibility and smoking norms and attitudes in response to the tobacco point-of-sale display ban in Scotland: results from the DISPLAY study [J]. Tobacco Control, 2020, 29(3): 348-356. DOI: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054702. [12] Kong G, Morean ME, Cavallo DA, et al. Sources of electronic cigarette acquisition among adolescents in Connecticut [J]. Tob Regul Sci, 2017, 3(1): 10-16. DOI: 10.18001/TRS.3.1.2. [13] Cooper M, Creamer MR, Lyu C, et al. Social norms, perceptions and dual/poly tobacco use among texas youth [J]. Am J Health Behav, 2016, 40(6): 761-770. DOI: 10.5993/AJHB.40.6.8. [14] Leshargie CT, Alebel A, Kibret GD, et al. The impact of peer pressure on cigarette smoking among high school and university students in Ethiopia: a systemic review and meta-analysis [J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(10): e0222572. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222572. -





 下载:
下载: