Correlation analysis of risk factors related to brucellosis infection based on Apriori algorithm
-
摘要:
目的 分析布鲁菌病(布病)感染相关危险因素间的关联作用,为制定布病防控措施提供依据。 方法 基于全国传染病疫情信息网络直报系统中济宁市2014-2017年数据,识别布病感染高发地区;在高发地区中采用多阶段整群抽样的方法,依靠问卷和血样检测共调查2 892人。通过二分类logistic回归分析模型分析布病的危险因素;运用Apriori算法挖掘相关危险因素的关联规则。 结果 有279人感染布病,感染率为9.65%;logistic回归分析模型显示养殖人员(OR=2.406, 95% CI: 1.726~3.353)、接触羊(OR=3.323, 95% CI: 2.448~4.511)、收购皮毛(OR=21.141, 95% CI: 14.154~31.577)是布病感染的危险因素,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.001);Apriori算法共挖掘出以感染布病为后项的强关联规则203条,最大提升比为10.37,最小为6.22,不同的危险因素组合对布病感染的可能性在关联强度等方面存在差异。 结论 布病感染率较高,应重点关注畜牧养殖、羔羊接触及皮毛收购等重点人群;多种危险因素存在紧密关联性,应注意同时具备强关联规则危险因素的人群,开展针对性措施以降低感染风险,筑牢布病防控屏障。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to analyze the risk factors associated with brucellosis infection and their interrelations, with a view to formulating preventative and control measures. Methods Based on the data of Jining from 2014 to 2017 from the National Infectious Disease Epidemic Information Network Direct Reporting System, the areas with high incidence of brucellosis were identified; In these areas, we carried out multistage cluster sampling, enlisting 2 892 participants for questionnaires and blood samples survey. Binary logistic regression was used to analyze the risk factors of brucellosis. Apriori algorithm was used to mine association rules of related risk factors. Results A total of 279 people were found to be infected with brucellosis, representing an infection rate of 9.65%. Logistic regression showed that being a breeders (OR=2.406, 95% CI: 1.726-3.353), contact with sheep (OR=3.323, 95% CI: 2.448-4.511) and fur purchaing (OR=21.141, 95% CI: 14.154-31.577) were significant risk factors for brucellosis infection (all P < 0.001).The Apriori algorithm mined 203 strong association rules with linking risk factors to brucellosis infection, with lift ratios ranging from 6.22 to 10.37. The strength of correlations varied among different risk factor combinations. Conclusions The infection rate of brucellosis is relatively high, necessitating greater focus on key groups such as those in the breeding industry, individuals in contact with sheep, and those involved in fur purchasing. Given the close interrelation of numerous risk factors, special attention should be given to individuals associated with high-risk factors determined by the strong association rules. Tailored measures are required to lower infection risks, creating a robust defense against brucellosis. -
Key words:
- Brucellosis /
- Risk factors /
- Health education /
- Association rules
-
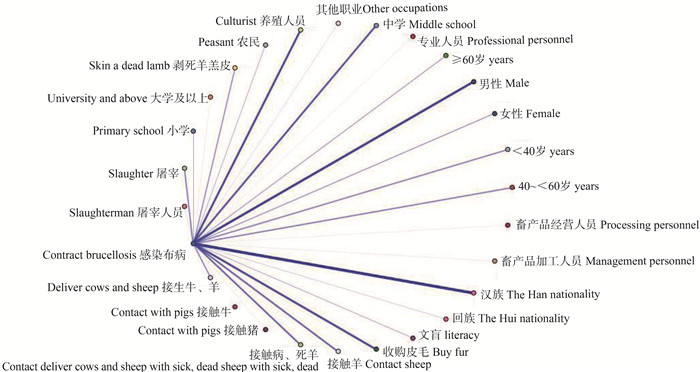
图 1 布病相关危险因素关联性网络视图
图中线的粗细和代表联系的强弱,线条越粗越深表示它们之间的关联性越强,线条越细越浅表示关联性越弱。
Figure 1. Network view of risk factors associated with brucellosis
The thickness of the lines in the figure represents the strength of the connection. The thicker and deeper the lines are, the stronger the correlation between them, and the thinner and shallower the lines are, the weaker the correlation.
表 1 变量原始信息表
Table 1. Original information of variables
编号 No. 属性名称 Attribute name 特征值 Eigenvalue 赋值 Assign 1 性别 Sex Woman(女性);Man(男性) Woman(Woman); Man(Man) 女=0,男=1 Woman=0, Man=1 2 年龄组/岁 Age group/years A1(< 40); A2(40~<60); A3(≥60) < 40=1,40~<60=2,≥60=3 3 民族 Nation HAN(汉族);HUI(回族) HAN(The Han nationality); HUI(The Hui nationality) 汉族=1,回族=0 The Han nationality=1, The Hui nationality=0 4 文化程度 Educational level E1(文盲);E2(小学);E3(中学);E4(大学及以上) E1(Illiteracy); E2(Primary school); E3(Middle school); E4(University and above) 文盲=1,小学=2,中学=3,大学及以上=4 Illiteracy=1, Primary school=2, Middle school=3, University and above=4 5 职业 Occupation O1、2(专业人员);O3(养殖人员);O4(屠宰人员);O5(畜产品加工人员);O6(畜产品经营人员);O7(农民);O8(其他) O1, 2(Professional personnel); O3(Culturist); O4(Slaughterman); O5(Processing personnel); O6(Management personnel); O7(Peasant); O8(Other occupations) 专业人员=1、2,养殖人员=3,屠宰人员=4,畜产品加工人员=5,畜产品经营人员=6,农民=7,其他=8 Professional personnel=1, 2, Culturist=3, Slaughterman=4, Processing personnel=5, Management personnel=6, Peasant=7, Other occupations=8 6 危险动物 Dangerous animal Cow(牛);Sheep(羊);Pig(猪);Dog(狗) Cow(Cow); Sheep(Sheep); Pig(Pig); Dog(Dog) 未感染=0,感染=1 Not infected with brucellosis=0, Contract brucellosis=1 7 危险行为 Dangerous behavior B1(接触病、死羊);B2(养貂等);B3(剥死羊羔皮);B4(接生牛、羊);B5(收购皮毛);B6(屠宰) B1(Contact with sick or dead sheep); B2(Raising mink etc); B3(Skin a dead lamb); B4(Deliver cows and sheep); B5(Buy fur); B6(Slaughter) 未感染=0,感染=1 Not infected with brucellosis=0, Contract brucellosis=1 8 布病感染情况 Contract brucellosis 结果 Result 未感染=0,感染=1 Not infected with brucellosis=0, Contract brucellosis=1 表 2 布鲁菌病调查问卷研究对象一般情况
Table 2. General situation of the subjects completed the brucellosis questionnaire
调查项目 Investigation item 感染布鲁菌病(n=279) Infectious brucellosis (n=279) 未感染布鲁菌病(n=2 613) Not infected with brucellosis (n=2 613) 人数 Number of people 占比/% Proportion/% 人数 Number of people 占比/% Proportion/% 性别 Sex 男 Male 202 72.40 1 562 59.78 女 Female 77 27.60 1 051 40.22 年龄组/岁 Age group/years < 40 104 37.28 880 33.68 40~< 60 107 38.35 1 032 39.49 ≥60 68 24.37 701 26.83 民族 Nation 汉族 The Han nationality 247 88.53 2 378 91.01 回族 The Hui nationality 32 11.47 235 8.99 文化程度 Educational level 文盲 Illiteracy 53 19.00 445 17.03 小学 Primary school 59 21.15 695 26.60 中学 Middle school 160 57.35 1 286 49.22 大学及以上 University and above 7 2.51 187 7.16 职业 Occupation 专业人员 Professional personnel 1 0.36 66 2.53 养殖人员 Culturist 178 63.80 848 32.45 屠宰人员 Slaughterman 19 6.81 287 10.98 畜产品加工 Processing personnel 9 3.23 91 3.48 畜产品经营 Management personnel 5 1.79 63 2.41 农民 Peasant 49 17.56 1 059 40.53 其他 Other occupations 18 6.45 199 7.62 表 3 布鲁菌病调查问卷研究对象一般情况
Table 3. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of brucellosis infection as dependent variable
变量 Variable β sx OR值(95% CI) OR value (95% CI) P值 P value 变量 Variable β sx OR值(95% CI) OR value (95% CI) P值 P value 性别 Sex 0.440 0.146 0.644(0.484~0.859) 0.003 农民 Peasant 0.799 0.207 0.450(0.300~0.675) < 0.001 年龄/岁 Age /years 0.007 0.004 0.993(0.985~1.001) 0.087 其他 Other 0.008 0.269 1.008(0.595~1.708) 0.978 民族 Nation 0.142 0.212 1.152(0.760~1.747) 0.505 接触羊 Contact sheep 1.201 0.156 3.323(2.448~4.511) < 0.001 文盲 Illiteracy 0.429 0.206 0.651(0.435~0.975) 0.037 接触牛 Contact cattle 0.298 0.561 0.743(0.247~2.229) 0.596 小学 Primary school 1.071 0.431 0.343(0.147~0.797) 0.013 接触猪 Contact with pigs 1.124 1.146 3.078(0.192~49.377) 0.427 中学 Middle school 0.049 0.186 0.952(0.662~1.371) 0.793 接触病、死羊 Contact with sick or dead sheep 0.266 0.246 0.766(0.473~1.241) 0.279 养殖人员 Culturist 0.878 0.169 2.406(1.726~3.353) < 0.001 剥死羊羔皮 Skin a dead lamb 1.465 0.479 0.231(0.090~0.591) 0.002 屠宰人员 Slaughterman 0.889 0.253 0.411(0.250~0.675) < 0.001 接生牛、羊 Deliver cows and sheep 0.283 0.385 0.754(0.355~1.602) 0.463 畜产品加工人员 Processing personnel 0.255 0.369 0.775(0.376~1.598) 0.490 收购皮毛 Buy fur 3.051 0.205 21.141(14.154~31.577) < 0.001 畜产品经营人员 Management personnel 0.330 0.485 0.719(0.278~1.860) 0.496 屠宰 Slaughter 0.045 0.256 1.047(0.634~1.729) 0.859 注:文化程度、职业、接触危险动物、危险行为变量,分别以大学及其以上、专业人员、接触狗、养貂等为对照设置为哑变量。
Note: The variables of education level, occupation, contact with dangerous animals and risky behavior were set as dumb variables with university or above, professional personnel, contact with dogs and raising minks as controls respectively.表 4 布病感染的部分强关联规则
Table 4. Partial strong association rules of brucellosis infection
序号 No. 前项个数 Number of Antecedent 规则前项 Antecedent 规则后项 Consequent 支持度/% Support/% 置信度/% Confidence/% 提升比 Lift leverage 1 9 汉族,羊,养殖人员,女性,剥死羊羔皮,接生牛、羊,收购皮毛,屠宰,接触病、死羊 The Han nationality, Sheep, Culturist, Woman, Skin a dead lamb, Deliver cows and sheep, Buy fur, Slaughter, Contact with sick or dead sheep 感染布病 Contract brucellosis 0.14 100.00 10.37 2 9 ≥60岁,羊,农民,剥死羊羔皮,接生牛、羊,收购皮毛,屠宰,接触病、死羊,男性 ≥60 years, Sheep, Peasant, Skin a dead lamb, Deliver cows and sheep, Buy fur, slaughtering, Contact with sick or dead sheep, Man 感染布病 Contract brucellosis 0.10 66.67 6.91 3 8 汉族,羊,养殖人员,女性,剥死羊羔皮,接生牛、羊,收购皮毛,屠宰 The Han nationality, Sheep, Culturist, Woman, Skin a dead lamb, Deliver cows and sheep, Buy fur, Slaughter 感染布病 Contract brucellosis 0.14 100.00 10.37 4 8 汉族,羊,养殖人员,剥死羊羔皮,接生牛、羊,收购皮毛,屠宰,接触病、死羊 The Han nationality, Sheep, Culturist, Woman, Skin a dead lamb, Deliver cows and sheep, Duy fur, Slaughter, Contact with sick or dead sheep 感染布病 Contract brucellosis 0.21 83.33 8.64 5 8 汉族,羊,女性,剥死羊羔皮,接生牛、羊,收购皮毛,屠宰,接触病、死羊 The Han nationality, Sheep, Woman, Skin a dead lamb, Deliver cows and sheep, Buy fur, slaughter, Contact with sick or dead sheep 感染布病 Contract brucellosis 0.31 66.67 6.91 …… 35 3 其他职业,羊,收购皮毛 Other occupations, Sheep, Buy fur 感染布病 Contract brucellosis 0.45 61.54 6.38 注:本文仅列出了前5条具有代表性的强关联规则。
Note: This article only lists the first 5 representative strong association rules. -
[1] Jean C. The changing nature of the Brucella-containing vacuole[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2015, 17(7): 951-958. DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12452. [2] Perez A, Berhe M. Brucella, a bacterium with multiple ways of causing infection[J]. Bayl Univ Med Cent Proc, 2021, 34(1): 99-101. DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2020.1805674. [3] 赵媛, 郭忠琴, 梁沛枫. 基于自回归滑动平均混合模型的布鲁菌病流行趋势预测[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(8): 932-937. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.08.010.Zhao Y, Guo ZQ, Liang PF. Prediction of brucellosis epidemic trend based on ARIMA model[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(8): 932-937. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.08.010. [4] 刘维量, 寇增强, 陈保立, 等. 山东省2014-2016年布鲁氏菌病空间分布特征和空间自相关分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(9): 897-901. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.007.Liu WL, Kou ZQ, Chen BL, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and spatial autocorrelation analysis of human brucellosis in Shandong Province from 2014 to 2016[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(9): 897-901. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.007. [5] 张雪梅. 2018年济宁市重点职业病监测及职业人群健康状况分析[J]. 中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2020, 38(1): 41-44. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2020.01.009.Zhang XM. Surveillance of key occupational diseases and analysis of health status of occupational population in Jining City in 2018[J]. Chin J Ind Hyg Occup Dis, 2020, 38(1): 41-44. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2020.01.009. [6] 刘小燕, 邱明, 康家豪, 等. 泸州市青少年膳食模式与超重肥胖的相关性研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2022, 26(3): 280-284. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2022.03.007.Liu XY, Qiu M, Kang JH, et al. Association between dietary patterns and overweight/obesity among adolescents in Luzhou[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2022, 26(3): 280-284. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2022.03.007. [7] Yan D, Xuan Zhao X, Lin R, et al. PPQAR: parallel PSO for quantitative association rule mining[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2019, 12(5): 1433-1444. DOI: 10.1007/s12083-018-0698-1. [8] 钱振宇, 姜霞, 刘晓丽, 等. 河北省2006-2013年布鲁氏菌病流行特征及影响因素分析[J]. 医学动物防制, 2015, 31(8): 846-848. DOI: 10.7629/yxdwfz201508007.Qian ZY, Jiang X, Liu XL, et al. Brucellosis epidemiological characteristics and influencing actors analysis of Hebei Province during 2006-2013[J]. J Med Pest Contrl, 2015, 31(8): 846-848. DOI: 10.7629/yxdwfz201508007. [9] 郝丽萍, 李岩青, 杨爱, 等. 关联规则算法在布鲁氏菌病危险因素分析中的应用[J]. 中国卫生信息管理杂志, 2018, 15(5): 541-545. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5166.2018.05.013.Hao LP, Li YQ, Yang A, et al. Application of apriori algorithm in the analysis of brucellosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Informatics and Management, 2018, 15(5): 541-545. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5166.2018.05.013. [10] 施旭光, 孙继民, 任江萍, 等. 浙江省职业人群布鲁氏菌病流行病学调查及危险因素分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2017, 28(3): 262-264. DOI: 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2017.03.017.Shi XG, Sun JM, Ren JP, et al. Epidemiological survey and risk factors analysis of brucellosis among occupational population in Zhejiang Province[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2017, 28(3): 262-264. DOI: 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2017.03.017. [11] 祝寒松, 谢忠杭, 许志斌, 等. 福建省2011-2015年人间布鲁氏菌病疫情分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2017, 21(8): 818-821. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.08.016.Zhu HS, Xie ZH, Xu ZB, et al. Epidemic situation analysis of human brucellosis in Fujian Province, 2011-2015[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2017, 21(8): 818-821. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.08.016. [12] 郝丽萍, 侯敏, 傅宗, 等. 回归分析在布鲁氏菌病数据挖掘中的应用[J]. 中国数字医学, 2018, 13(2): 45-47. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7571.2018.02.015.Hao LP, Hou M, Fu Z, et al. Application of regression analysis in data mining of brucellosis[J]. China Digit Medicine, 2018, 13(2): 45-47. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7571.2018.02.015. -





 下载:
下载: