Change trend analysis of the disease burden of low back pain and its risk factors in China from 1990 to 2019
-
摘要:
目的 分析1990—2019年中国人群腰背痛及其危险因素疾病负担的变化趋势。 方法 利用2019年全球疾病负担研究开放数据, 选用发病人数与发病率、患病人数与患病率、伤残损失寿命年(years lived with disability, YLDs)与YLDs率、人群归因分值(population attributable fraction, PAF)等指标对1990—2019年中国人群腰背痛及其危险因素疾病负担的变化趋势进行分析。 结果 1990—2019年中国人群腰背痛的发病人数与发病率、患病人数与患病率、YLDs与YLDs率分别增长20.85%、0.57%、21.30%、0.95%、20.83%、0.55%, 标化发病率、标化患病率、标化YLDs率分别下降28.15%、29.13%、28.97%;女性腰背痛的疾病负担高于男性, 且差距逐渐增大; ≥70岁组的疾病负担高于其他年龄组。与腰背痛相关的3种危险因素中, 归因于职业工效学因素的疾病负担下降17.98%, 归因于吸烟、高BMI的疾病负担分别增长35.80%、196.27%。 结论 腰背痛仍是造成中国人群伤残负担的主要原因, 中国未来减轻腰背痛疾病负担的形势十分严峻, 建议从相关危险因素出发对女性、高龄等重点人群采取针对性措施以降低腰背痛的疾病负担。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to analyze the changing trend in the disease burden of low back pain and its risk factors in Chinese residents from 1990 to 2019. Methods The data were extracted from the database of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.We used case numbers, incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), YLDs rate, and population attributable fraction (PAF) to describe the burden of low back pain and its risk factors, and the changes from 1990 to 2019. Results From 1990 to 2019, the number of incidence cases and incidence rate, the number of prevalence cases and prevalence rate, YLDs and YLDs rate of low back pain increased by 20.85%, 0.57%, 21.30%, 0.95%, 20.83% and 0.55%, respectively.However, the standardized incidence rate, standardized prevalence rate, and standardized YLDs rate decreased by 28.15%, 29.13%, and 28.97%, respectively.The disease burden was higher in females than males, with the difference gradually increasing.Additionally, the disease burden was highest in the 70-year-old age group.Among the three risk factors associated with low back pain (occupational ergonomics, smoking, and high BMI), the disease burden attributable to occupational ergonomics decreased by 17.98%, while the burden attributable to smoking and high BMI increased by 35.80% and 196.27%, respectively. Conclusions Low back pain continues to be a major cause of disability burden among the Chinese population, with the situation being especially serious.Interventions to control the prevalence of risk factors should be formulated, and further measures should be taken to reduce the disease burden of low back pain, particularly among women and older people. -
Key words:
- Low back pain /
- Risk factors /
- Disease burden /
- Change trends
-
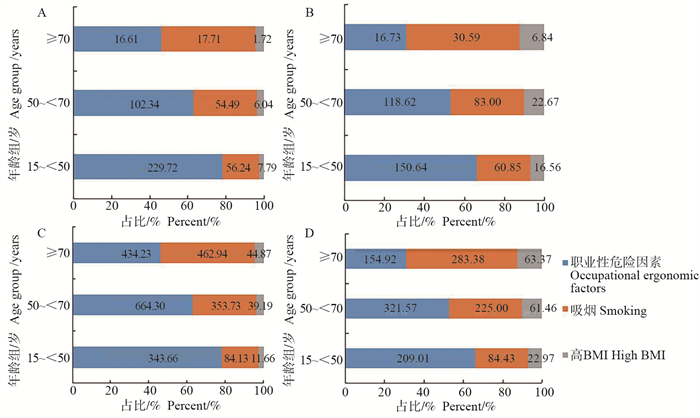
图 1 不同年龄组腰背痛危险因素的归因疾病负担
1. BMI: 体质指数。
2. A:1990年不同年龄组腰背痛危险因素归因YLDs分布情况;B:2019年不同年龄组腰背痛危险因素归因YLDs分布情况;C:1990年不同年龄组腰背痛危险因素归因YLDs率分布情况;D:2019年不同年龄组腰背痛危险因素归因YLDs率分布情况。Figure 1. Attributed disease burden to risk factors of low back pain in different age groups
1. BMI: body mass index.
2. A: YLDs attribute to risk factors in 1990; B: YLDs attribute to risk factors in 2019; C: YLDS rate attribute to risk factors in 1990; D: YLDS rate attribute to risk factors in 2019.表 1 1990—2019年中国人群腰背痛的疾病负担及其变化趋势
Table 1. Disease burden and trend of low back pain in Chinese residents from 1990 to 2019
变量 Variable 男
Male女
Female合计
Total发病人数 Numberof incidence cases 1990年/万人 1990 year/×104 1 458.69 1 864.25 3 322.93 2019年/万人 2019 year/×104 1 662.43 2 353.41 4 015.84 变化率/% Change rate/% 13.97 26.24 20.85 AAPC/% 0.46 ① 0.81 ① 0.68 ① 发病率 Incidence rate 1990年/10万-1 1990 year/100 000-1 2 390.56 3 250.68 2 807.29 2019年/10万-1 2019 year/100 000-1 2 293.57 3 373.92 2 823.38 变化率/% Change rate/% -4.06 3.79 0.57 AAPC/% -0.14 ① 0.13 ① 0.04 标化发病率
Age-standardized incidence rate1990年/10万-1 1990 year/100 000-1 2 738.75 3 621.49 3 174.26 2019年/10万-1 2019 year/100 000-1 1 941.68 2 611.58 2 280.67 变化率/% Change rate/% -29.10 -27.89 -28.15 AAPC/% -1.17 ① -1.12 ① -1.16 ① 患病人数
Number of prevalence cases1990/万人 1990/×104 3 237.36 4 292.48 7 529.84 2019/万人 2019/×104 3 756.75 5 377.19 9 133.94 变化率/% Change rate/% 16.04 25.27 21.30 AAPC/% 0.52 ① 0.78 ① 0.68 ① 患病率 Prevalence rate 1990年/10万-1 1990 year/100 000-1 5 305.52 7 484.78 6 361.37 2019年/10万-1 2019 year/100 000-1 5 183.00 7 708.91 6 421.72 变化率/% Change rate/% -2.31 2.99 0.95 AAPC/% -0.08 ① 0.10 ① 0.04 标化患病率
Age-standardized prevalence rate1990年/10万-1 1990 year/100 000-1 6 131.89 8 375.33 7 245.29 2019年/10万-1 2019 year/100 000-1 4 328.76 5 915.76 5 134.73 变化率/% Change rate/% -29.41 -29.37 -29.13 AAPC/% -1.18 ① -1.18 ① -1.21 ① YLDs 1990/万人年 1990/×104 372.01 483.27 855.29 2019/万人年 2019/×104 430.73 602.68 1 033.41 变化率/% Change rate/% 15.78 24.71 20.83 AAPC/% 0.51 ① 0.77 ① 0.67 ① YLDs率 YLDs rate 1990年/10万-1 1990 year/100 000-1 609.67 842.68 722.56 2019年/10万-1 2019 year/100 000-1 594.26 864.02 726.55 变化率/% Change rate/% -2.53 2.53 0.55 AAPC/% -0.08 ① 0.09 ① 0.04 标化YLDs率
Age-standardized YLDs rate1990年/10万-1 1990 year/100 000-1 697.09 936.36 815.20 2019年/10万-1 2019 year/100 000-1 493.40 662.76 579.05 变化率/% Change rate/% -29.22 -29.22 -28.97 AAPC/% -1.18 ① -1.18 ① -1.20 ① 注:AAPC, 平均年度变化百分比;YLDs, 伤残损失寿命年。
① P<0.05。
Note: AAPC, average annual percentage change; YLDs, years lived with disability.
① P<0.05.表 2 1990—2019年中国不同年龄居民腰背痛的疾病负担及其变化趋势
Table 2. The trends of age-specific burden of low back pain in Chinese residents from 1990 to 2019
变量 Variable 1990年
1990 year2019年
2019 year变化率/%
Change rate/%AAPC/% 年龄组/岁 Age group/years 15~<50 发病人数/万人 Number of incidence cases/×104 1 773.64 1 529.82 -13.75 -0.53 发病率/10万-1 Incidence rate/100 000-1 2 653.31 2 122.62 -20.00 -0.79 患病人数/万人 Number of prevalence cases/×104 4 040.75 3 484.00 -13.78 -0.51 患病率/10万-1 Prevalence rate/100 000-1 6 044.85 4 834.01 -20.03 -0.76 YLDs/万人年 YLDs/×104 years 467.58 406.32 -13.10 -0.48 YLDs率/10万-1 YLDs rate/100 000-1 699.49 563.76 -19.40 -0.73 50~<70 发病人数/万人 Number of incidence cases/×104 1 000.42 1 642.55 64.19 1.74 发病率/10万-1 Incidence rate/100 000-1 6 494.05 4 452.77 -31.43 -1.29 患病人数/万人 Number of prevalence cases/×104 2 316.47 3 781.62 63.25 1.73 患病率/10万-1 Prevalence rate/100 000-1 15 036.86 10 251.55 -31.82 -1.30 YLDs/万人年 YLDs/×104 years 262.84 430.82 63.91 1.74 YLDs率/10万-1 YLDs rate/100 000-1 1 706.20 1 167.92 -31.55 -1.28 ≥70 发病人数/万人 Number of incidence cases/×104 358.05 712.38 98.96 2.41 发病率/10万-1 Incidence rate/100 000-1 9 358.78 6 598.22 -29.50 -1.21 患病人数/万人 Number of prevalence cases/×104 871.01 1 662.65 90.89 2.27 患病率/10万-1 Prevalence rate/100 000-1 22 766.50 15 399.91 -32.36 -1.36 YLDs/万人年 YLDs/×104 years 91.81 173.68 89.17 2.24 YLDs率/10万-1 YLDs rate/100 000-1 2 399.79 1 608.67 -32.97 -1.39 注:YLDs, 伤残损失寿命年; AAPC, 平均年度变化百分比。
Note: YLDs, years lived with disability; AAPC, average annual percentage change.表 3 1990—2019中国人群腰背痛危险因素的归因疾病负担
Table 3. Attributed disease burden to risk factors of low back pain in Chinese residents from 1990 to 2019
变量 Variable YLDs/万人年
YLDs/×104 yearPAF/% YLDs率/10万-1
YLDs rate/100 000-1男 Male 职业工效学因素
Occupational ergonomic factors1990年 year 164.93 0.44 270.29 2019年 year 131.13 0.30 180.91 变化率/% Change rate/% -20.49 -31.82 -33.07 吸烟 Smoking 1990年 year 115.57 0.31 189.40 2019年 year 148.43 0.34 204.79 变化率/% Change rate/% 28.43 9.68 8.13 高BMI High BMI 1990年 year 6.20 0.02 10.16 2019年 year 18.64 0.04 25.71 变化率/% Change rate/% 200.64 100.00 153.05 女 Female 职业工效学因素
Occupational ergonomic factors1990年 year 183.75 0.38 320.40 2019年 year 154.86 0.26 222.01 变化率/% Change rate/% -15.72 -31.58 -30.71 吸烟 Smoking 1990年 year 12.88 0.03 22.45 2019年 year 26.01 0.04 37.29 变化率/% Change rate/% 101.94 33.33 66.10 高BMI High BMI 1990年 year 9.35 0.02 16.31 2019年 year 27.43 0.05 39.33 变化率/% Change rate/% 193.37 150.00 141.14 合计 Total 职业工效学因素
Occupational ergonomic factors1990年 year 348.67 0.41 294.57 2019年 year 285.99 0.28 201.07 变化率/% Change rate/% -17.98 -31.71 -31.74 吸烟 Smoking 1990年 year 128.45 0.16 108.51 2019年 year 174.44 0.17 122.64 变化率/% Change rate/% 35.8 6.25 13.02 高BMI High BMI 1990年 year 15.55 0.02 13.14 2019年 year 46.07 0.04 32.39 变化率/% Change rate/% 196.27 100.00 1.46 注:YLDs, 伤残损失寿命年;PAF, 人群归因分值。
Note: YLDs, years lived with disability; PAF, population attributable fraction. -
[1] Warfield CA, Bajwa ZH. 疼痛医学原理与实践[M]. 第2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2009: 132-138.Warfield CA, Bajwa ZH. Principles and Practice of Pain Medicine[M]. Version 2. Beijing: People's Health Press, 2009: 132-138. [2] Vlaeyen JWS, Maher CG, Wiech K, et al. Low back pain[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2018, 4(1): 52. DOI: 10.1038/s41572-018-0052-1. [3] Chen S, Chen M, Wu X, et al. Global, regional and national burden of low back pain 1990—2019: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2019[J]. J Orthop Translat, 2021, 32: 49-58. DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2021.07.005. [4] Wu AM, Dong WL, Liu SW, et al. The prevalence and years lived with disability caused by low back pain in China, 1990 to 2016: findings from the global burden of disease study 2016[J]. Pain, 2019, 160(1): 237-245. DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001396. [5] Hartvigsen J, Hancock MJ, Kongsted A, et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10137): 2356-2367. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30480-X. [6] GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990—2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10258): 1204-1222. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9. [7] GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990—2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10258): 1223-1249. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30752-2. [8] 袁空军, 赵创艺, 杨媛, 等. 中国人群1990—2019年高低密度脂蛋白胆固醇归因疾病负担趋势分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2022, 22(4): 444-449. DOI: 10.7507/1672-2531.2021/2052.Yuan KJ, Zhao CY, Yang Y, et al. Burden trend analysis of disease attributable to high low density lipoprotein cholesterol in Chinese population from 1990 to 2019[J]. Chin J Evid Based Med, 2022, 22(4): 444-449. DOI: 10.7507/1672-2531.2021/2052. [9] Hoy D, March L, Brooks P, et al. The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2014, 73(6): 968-974. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204428. [10] 国家统计局, 国务院第七次全国人口普查领导小组办公室. 第七次全国人口普查公报(第五号)——第七次全国人口普查工作基本情况[J]. 中国统计, 2021, 473(5): 10-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTJ202105003.htmNational Bureau of Statistics, Office of the Seventh National Population Census Leading Group of The State Council. Bulletin of the seventh national population census (No. 5) -population age composition[J]. China Stat, 2021, 473(5): 10-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTJ202105003.htm [11] Wang YXJ. Menopause as a potential cause for higher prevalence of low back pain in women than in age-matched men[J]. J Orthop Transl, 2017, 8: 1-4. DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2016.05.012. [12] 周志强, 李佐凡, 陈躐, 等. 无痛胃镜患者疼痛敏感度相关因素调查[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2016, 24(5): 381-383. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2016.05.021.Zhou ZQ, Li ZF, Chen L, et al. Pain sensitivity factors survey of patient undergoing painless gastroscopy[J]. J Clin Surg, 2016, 24(5): 381-383. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2016.05.021. [13] Gibson L. Pregnancy related low back pain[J]. Int J Childb Edu, 2017, 32(1): 27-29. [14] Chen S, Liu S, Ma K, et al. TGF-β signaling in intervertebral disc health and disease[J]. Osteoarthr Cartil, 2019, 27(8): 1109-1117. DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.05.005. [15] 肖琳, 南奕, 邸新博, 等. 2018年中国15岁及以上人群吸烟现况及变化趋势研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2022, 43(6): 811-817. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20211130-00934.Xiao L, Nan Y, Di XB, et al. Study on smoking behavior and its changes among Chinese people aged 15 years and above in 2018[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2022, 43(6): 811-817. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20211130-00934. [16] 张圆媛, 张忠彬, 高子清, 等. 工作场所职业工效相关因素及其管理初探[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2018, 14(3): 174-179. DOI: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2018.03.026.Zhang YY, Zhang ZB, Gao ZQ, et al. Exploration on related factors and their management of occupational ergonomics at workplaces[J]. J Saf Sci Technol, 2018, 14(3): 174-179. DOI: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2018.03.026. -





 下载:
下载: