Study on the combined effects of sleep and obesity on functional loss in middle-aged and elderly people
-
摘要:
目的 了解中老年人睡眠、肥胖的联合作用对中老年人功能损失的影响。 方法 数据来源于北京大学2015年中国健康与养老追踪调查(China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study, CHARLS)数据库。采用logistic回归分析模型分析睡眠、肥胖对功能损失的联合作用。 结果 以腰围(waist circumference, WC)正常+夜间睡眠6~ < 8 h组为参照,腹型肥胖+夜间睡眠0~ < 4 h组功能损失患病风险最高(OR=1.655, P < 0.001)。以WC正常+午睡0~ < 30 min组为参照,腹型肥胖+无午睡组功能损失患病风险最高(OR=3.360, P=0.008)。以非全身性肥胖+夜间睡眠6~ < 8 h组为参照,全身性肥胖+夜间睡眠4~ < 6 h组功能损失患病风险最高(OR=2.359, P < 0.001)。以非全身性肥胖+午睡0~ < 30 min组为参照,全身性肥胖+午睡30~ < 90 min组功能损失患病风险最高(OR=1.905, 95% CI: 1.237~2.933, P=0.003)。 结论 夜间睡眠时间短、无午睡或午睡时间长分别与腹型肥胖或全身性肥胖共存会增加功能损失的患病风险,提示夜间睡眠时间短、无午睡或午睡时间长的中老年人控制BMI和WC有利于改善日常生活活动能力。 Abstract:Objective The aim of this study was to investigate the combined effect of sleep and obesity on the prevalence of functional disability among middle-aged and older adults. Methods Data were collected from the 2015 China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). The logistic regression model was performed to estimate the combined effect of sleep and obesity on the prevalence of functional disability. Results Compared to participants with normal waist circumference (WC) and 6- < 8 hours of nocturnal sleep, those with abdominal obesity and 0- < 4 hours of nocturnal sleep exhibited an increased risk of functional disability (OR=1.655, P < 0.001). Similarly, participants with abdominal obesity and no afternoon nap, compared to those with normal WC and 0- < 30 minutes of afternoon nap, showed an elevated risk of functional disability (OR=3.360, P=0.008). When compared to non-systemically obese individuals with 6- < 8 hours of nocturnal sleep, those with systemic obesity and 4- < 6 hours of nocturnal sleep had an increased risk of functional disability (OR=2.359, P < 0.001). Additionally, systemically obese individuals with 30- < 90 minutes of afternoon nap, compared to non-systemically obese individuals with 0- < 30 minutes of afternoon nap, showed an increased risk of functional disability (OR=1.905, 95% CI: 1.237-2.933, P=0.003). Conclusions The concurrent presence of short nocturnal sleep duration, absence of an afternoon nap or extended afternoon nap duration, and either abdominal or systemic obesity, increases the risk of functional disability. This suggests that controlling body mass index (BMI) and WC among middle-aged and older adults with short nocturnal sleep duration, absence of an afternoon nap, or extended afternoon nap duration could be beneficial in preventing functional disability. -
Key words:
- Sleep /
- Body mass index /
- Waist circumference /
- Functional disability
-
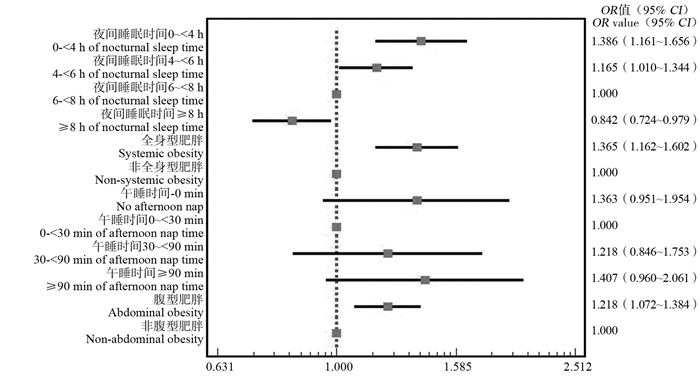
图 1 中老年人功能损失影响因素的logistic回归分析模型
校正的变量有性别、年龄、婚姻状态、文化程度、跌倒、抑郁、视力、听力、自评健康、生活满意度。
Figure 1. Logistic regression analysis of the influencing factors on the prevalence of functional disability among middle-aged and older adults
Adjusting variables included sex, age, marital status, education level, falls, depression, vision, hearing, health self-assessment, and life satisfaction.
表 1 2015年中国不同特征的中老年人功能损失情况的比较
Table 1. Comparison of the prevalence of functional disability among Chinese middle-aged and older adults with different characteristics in 2015
变量 Variable 调查人数[人数(占比/%)]
Number of respondents [Number (proportion/%)]功能损失[人数(占比/%)]
Functional disability [Number (proportion/%)]功能未损失[人数(占比/%)]
Non-functional disability [Number (proportion/%)]χ2值
valueP值
value性别 Gender 28.271 < 0.001 男 Male 2 952(41.79) 751(25.44) 2 201(74.56) 女 Female 4 112(58.21) 1 285(31.25) 2 827(68.75) 年龄组/岁 Age group/years 67.108 < 0.001 40~ < 60 2 852(40.37) 669(23.46) 2 183(76.54) ≥60 4 212(59.63) 1 367(32.45) 2 845(67.55) 跌倒 Fall 261.335 < 0.001 是 Yes 1 543(21.84) 699(45.30) 844(54.70) 否 No 5 521(78.16) 1 337(24.22) 4 184(75.78) 文化程度 Education 17.359 < 0.001 小学及以下 Primary school and below 5 038(71.32) 1 497(29.71) 3 541(70.29) 初中 Middle school 1 325(18.76) 384(28.98) 941(71.02) 高中及以上 High school and above 701(9.92) 155(22.11) 546(77.89) 婚姻状况 Marital status 36.372 < 0.001 已婚/同居 Married/cohabitated 5 510(78.00) 1 493(27.10) 4 017(72.90) 离婚/分居/丧偶/未婚 Divorced/separated/widowed/unmarried 1 554(22.00) 543(34.94) 1 011(65.06) 夜间睡眠/h Nocturnal sleep time/h 132.090 < 0.001 0~ < 4 866(12.26) 365(42.15) 501(57.85) 4~ < 6 1 888(26.73) 618(32.73) 1 270(67.27) 6~ < 8 2 466(34.91) 626(25.39) 1 840(74.61) ≥8 1 844(26.10) 427(23.16) 1 417(76.84) 吸烟 Smoking 0.017 0.895 是 Yes 410(5.80) 117(28.54) 293(71.46) 否 No 6 654(94.20) 1 919(28.84) 4 735(71.16) 饮酒 Drinking 0.314 0.575 是 Yes 1 330(18.83) 375(28.20) 955(71.80) 否 No 5 734(81.17) 1 661(28.97) 4 073(71.03) 午睡/min Nap/min 12.732 0.005 0 3 370(47.71) 1 020(30.27) 2 350(69.73) 0~ < 30 202(2.86) 45(22.28) 157(77.72) 30~ < 90 2 496(35.33) 672(26.92) 1 824(73.08) ≥90 996(14.10) 299(30.02) 697(69.98) 抑郁 Depression 263.228 < 0.001 是 Yes 3 498(49.52) 1 317(37.65) 2 181(62.35) 否 No 3 566(50.48) 719(20.16) 2 847(79.84) 视力 Eyesight 96.494 < 0.001 好及以上 Good and above 2 545(36.03) 554(21.77) 1 991(78.23) 一般及以下 General and below 4 519(63.97) 1 482(32.79) 3 037(67.21) 听力 Hearing 104.648 < 0.001 好及以上 Good and above 2 000(28.31) 401(20.05) 1 599(79.95) 一般及以下 General and below 5 064(71.69) 1 635(32.29) 3 429(67.71) BMI/(kg·m-2) 27.665 < 0.001 < 18.50 380(5.38) 121(31.84) 259(68.16) 18.50~ < 24.00 3 252(46.04) 966(29.70) 2 286(70.30) 24.00~ < 28.00 2 441(34.55) 618(25.32) 1 823(74.68) ≥28.00 991(14.03) 331(33.40) 660(66.60) WC 9.317 0.002 腹型肥胖 Abdominal obesity 4 794(67.87) 1 436(29.95) 3 358(70.05) 正常 Normal 2 270(32.13) 600(26.43) 1 670(73.57) 自评健康状况 Health self-assessment 389.839 < 0.001 极好 Excellent 51(0.72) 1(1.96) 50(98.04) 很好 Very good 420(5.95) 64(15.24) 356(84.76) 好 Good 613(8.68) 136(22.19) 477(77.81) 一般 General 3 617(51.20) 808(22.34) 2 809(77.66) 不好 Poor 2 363(33.45) 1 027(43.46) 1 336(56.54) 生活满意度 Life satisfaction 155.100 < 0.001 满意 Satisfaction 6 277(88.86) 1 660(26.45) 4 617(73.55) 不满意 Dissatisfaction 787(11.14) 376(47.78) 411(52.22) 表 2 夜间睡眠与腹型肥胖的联合作用对功能损伤影响的logistic回归分析模型
Table 2. Logistic regression analysis of the combined effect of nocturnal sleep and central obesity on the prevalence of functional disability
夜间睡眠时间/h
Nocturnal sleep time/h非腹型肥胖 Non-abdominal obesity 腹型肥胖 Abdominal obesity OR值(95% CI) OR value(95% CI) P值 value OR值(95% CI) OR value(95% CI) P值 value 0~ < 4 1.182(0.868~1.608) 0.288 1.655(1.280~2.141) < 0.001 4~ < 6 1.033(0.798~1.337) 0.805 1.355(1.085~1.692) 0.007 6~ < 8 1.000 1.120(0.903~1.390) 0.303 ≥8 0.715(0.542~0.944) 0.018 1.032(0.820~1.298) 0.791 注:调整的变量有性别、年龄、婚姻状态、文化程度、跌倒、抑郁、视力、听力、自评健康、生活满意度。
Note: Adjusted variables include gender, age, marital status, educational level, falls, depression, vision, hearing, health self-assessment, and life satisfaction.表 3 午睡与腹型肥胖的联合作用对功能损伤影响的logistic回归分析模型
Table 3. Logistic regression analysis of the combined effect of afternoon nap and central obesity on the prevalence of functional disability
午睡时间/min
Afternoon nap time/min非腹型肥胖 Non-abdominal obesity 腹型肥胖 Abdominal obesity OR值(95% CI) OR value(95% CI) P值 value OR值(95% CI) OR value(95% CI) P值 value 0 2.482(1.014~6.072) 0.046 3.360(1.379~8.186) 0.008 0~ < 30 1.000 2.926(1.114~7.690) 0.029 30~ < 90 2.303(0.933~5.684) 0.070 2.885(1.183~7.040) 0.020 ≥90 2.885(1.141~7.296) 0.025 3.118(1.266~7.679) 0.013 注:调整的变量有性别、年龄、婚姻状态、文化程度、跌倒、抑郁、视力、听力、自评健康、生活满意度。
Note: Adjusted variables included gender, age, marital status, educational level, falls, depression, vision, hearing, health self-assessment, and life satisfaction.表 4 夜间睡眠与全身性肥胖的联合作用对功能损伤影响的logistic回归分析模型
Table 4. Logistic regression analysis of the combined effect of nocturnal sleep time and systemic obesity on the prevalence of functional disability
夜间睡眠时间/h
Nocturnal sleep time/h非全身性肥胖 Non-systemic obesity 全身性肥胖 Systemic obesity OR值(95% CI) OR value(95% CI) P值 value OR值(95% CI) OR value(95% CI) P值 value 0~ < 4 1.519(1.258~1.835) < 0.001 1.020(0.621~1.675) 0.936 4~ < 6 1.115(0.955~1.302) 0.167 2.359(1.750~3.180) < 0.001 6~ < 8 1.000 1.551(1.208~1.993) 0.001 ≥8 0.878(0.744~1.036) 0.122 1.087(0.811~1.458) 0.576 注:调整的变量有性别、年龄、婚姻状态、文化程度、跌倒、抑郁、视力、听力、自评健康、生活满意度。
Note: Adjusted variables included gender, age, marital status, educational level, falls, depression, vision, hearing, health self-assessment, and life satisfaction.表 5 午睡与全身性肥胖的联合作用对功能损伤影响的logistic回归分析模型
Table 5. Logistic regression model of the combined effect of afternoon nap and systemic obesity on the prevalence of functional disability
午睡时间/min
Afternoon nap time/min非全身性肥胖 Non-abdominal obesity 全身性肥胖 Abdominal obesity OR值(95% CI) OR value(95% CI) P值 value OR值(95% CI) OR value(95% CI) P值 value 0 1.348(0.919~1.975) 0.126 1.606(1.036~2.492) 0.034 0~ < 30 1.000 1.744(0.616~4.936) 0.295 30~ < 90 1.123(0.762~1.655) 0.558 1.905(1.237~2.933) 0.003 ≥90 1.304(0.868~1.959) 0.202 1.868(1.138~3.066) 0.014 注:调整的变量有性别、年龄、婚姻状态、文化程度、跌倒、抑郁、视力、听力、自评健康、生活满意度。
Note: Adjusted variables included gender, age, marital status, educational level, falls, depression, vision, hearing, health self-assessment, and life satisfaction. -
[1] 李真真, 汤哲. 老年人失能的流行病学研究进展[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2016, 37(7): 1047-1050. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.07.028.Li ZZ, Tang Z. Epidemiological studies of disability in the elderly[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2016, 37(7): 1047-1050. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.07.028. [2] Zhang L, Fu S, Fang Y. Prediction of the number of and care costs for disabled elderly from 2020 to 2050: a comparison between urban and rural areas in China[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(7): 2598. DOI: 10.3390/su12072598. [3] 李慧琦, 周艳凤, 潘安. 中老年人BMI与日常生活活动能力关联[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 25(3): 335-340. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.03.016.Li HQ, Zhou YF, Pan A. Association of body mass index with activities of daily life among middle-aged and older Chinese[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2021, 25(3): 335-340. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.03.016. [4] 龚健, 古正涛, 苏磊. 褪黑素在热打击诱导细胞凋亡中可能的保护作用[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2019, 31(5): 658-661. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.05.028.Gong J, Gu ZT, Su L. Possible protective role of melatonin on heat stress induced apoptosis[J]. Chin Crit Care Med, 2019, 31(5): 658-661. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.05.028. [5] 李亚梅, 张凯强, 彭壮, 等. 大叶千斤拔对慢性盆腔炎大鼠的抗炎作用及机制研究[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2019, 54(11): 874-880. DOI: 10.11669/cpj.2019.11.004.Li YM, Zhang KQ, Peng Z, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect and mechanisms of flemingia macrophylla merr. for chronic pelvic inflammatory disease in rats[J]. Chin Pharm J, 2019, 54(11): 874-880. DOI: 10.11669/cpj.2019.11.004. [6] 张蕴超, 贾英杰, 朱津丽, 等. 消岩汤对肺癌恶病质小鼠肌肉蛋白质降解的影响[J]. 中医杂志, 2016, 57(9): 775-778. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2016.09.015.Zhang YC, Jia YJ, Zhu JL, et al. Impact of Xiaoyan decoction on muscle protein degradationin lung cancer cachexia mice[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2016, 57(9): 775-778. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2016.09.015. [7] 雷映红, 陈辉, 刘菊. 老年男性2型糖尿病患者骨密度与炎症因子相关性研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2017, 23(2): 213-215, 243. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2017.02.016.Lei YH, Chen H, Liu J. Correlation between bone mineral density and inflammatory cytokines in elderly male diabetic patients[J]. Chin J Osteopor, 2017, 23(2): 213-215, 243. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2017.02.016. [8] Kunutsor SK, Laukkanen JA. Should inflammatory pathways be targeted for the prevention and treatment of hypertension?[J]. Heart, 2019, 105(9): 665-667. DOI: 10.1136/heartjnl-2018-314625. [9] 张晗, 王志会, 王丽敏, 等. 中国社区老年居民日常生活活动能力失能状况调查[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2019, 40(3): 266-271. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.03.003.Zhang H, Wang ZH, Wang LM, et al. Study on activities of daily living disability in community-dwelling older adults in China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2019, 40(3): 266-271. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.03.003. [10] Corona LP, Alexandre T, Duarte Y, et al. Abdominal obesity as a risk factor for disability in Brazilian older adults[J]. Public Health Nutr, 2017, 20(6): 1046-1053. DOI: 10.1017/S1368980016003505. [11] 母蕾, 巫嘉陵. 衰弱与炎症[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2020, 20(1): 61-64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2020.01.010.Mu L, Wu JL. Frailty and inflammation[J]. Chin J Contemp Neurol Neurosurg, 2020, 20(1): 61-64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2020.01.010. [12] Smith CJ, Perfetti TA, Hayes AW, et al. Obesity as a source of endogenous compounds associated with chronic disease: a review[J]. Toxicol Sci, 2020, 175(2): 149-155. DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa042. [13] Koren D, Taveras EM. Association of sleep disturbances with obesity, insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome[J]. Metabolism, 2018, 84: 67-75. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.04.001. [14] 曾繁杰, 杨宝霞, 黎萍. 睡眠和心血管代谢性疾病相关的研究进展[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2021, 25(6): 929-931. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2021.06.039.Zeng FJ, Yang BX, Li P. Advances in sleep and cardiovascular metabolic diseases[J]. Chin J Lab Diagn, 2021, 25(6): 929-931. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2021.06.039. [15] 宋孟娜, 程潇, 孔静霞, 等. 我国中老年人超重、肥胖变化情况及影响因素分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(8): 804-808. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.08.010.Song MN, Cheng X, Kong JX, et al. Prevalence and influencing factors of overweight and obesity among middle-aged and elderly people in China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(8): 804-808. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.08.010. [16] Kowall B, Lehnich AT, Erbel R, et al. Associations between sleep characteristics and weight gain in an older population: results of the Heinz Nixdorf Recall Study[J]. Nutr Diabetes, 2016, 6(8): e225. DOI: 10.1038/nutd.2016.32. [17] Maugeri A, Medina-Inojosa JR, Kunzova S, et al. Sleep duration and excessive daytime sleepiness are associated with obesity independent of diet and physical activity[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(9): 1219. DOI: 10.3390/nu10091219. [18] 张娴, 陈宏. 新型脂肪因子与肥胖相关代谢性疾病[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志, 2018, 38(3): 171-175. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4157.2018.03.007.Zhang X, Chen H. Novel adipokines and obesity-related metabolic diseases[J]. Int J Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 38(3): 171-175. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4157.2018.03.007. -





 下载:
下载: