-
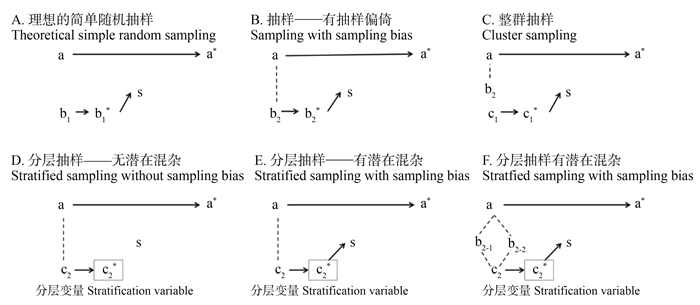
摘要: 本研究从因果图和因果模型的角度解释了简单随机抽样、整群抽样和分层抽样的结构和原理,清晰呈现了抽样偏倚的产生和调整过程。发现当研究的目标属性与是否抽中有关联时,样本对总体的代表性将产生偏差,即抽样偏倚或抽样的系统误差。整群抽样和分层抽样是两种对抽样偏倚的不同调整策略; 前者找到一个目标无关变量作为分群变量,而后者直接调整了引起抽样偏倚且与研究属性关联的变量。在抽样方法的选择上,整群抽样要求群内异质且群间同质,分层抽样则正好相反。最后,本研究为实际研究工作中对抽样方法的选择提供了路线参考,可帮助读者提高对随机抽样的认识,考量研究方法的选择。Abstract: This article explained the structure and principle of simple random sampling, cluster sampling, and stratification sampling from the perspective of causal graphs. The process of generation and adjustment of sampling bias was clearly presented. We found that: when the target attribute of the study was related to other attributes which affected the selection of the samples, the representative of the sample would be biased. In other words, the sampling bias or the systematic error of sampling would appear. When selecting sampling methods, cluster sampling requires heterogeneity within clusters but homogeneity among clusters. In contrast, stratified sampling requires the opposite way. Finally, this paper provides a route for the selection of sampling methods in practical research work, which can help readers to improve the acknowledgment of random sampling and consider the best sampling method.
-
Key words:
- Sampling /
- Causal graphs /
- Sampling bias /
- Stratification sampling /
- Cluster sampling
-
[1] Acharya AS, Prakash A, Saxena P, et al. Sampling: why and how of it?[J]. Indian J Med Spec, 2013, 4(2): 330-333. DOI: 10.7713/ijms.2013.0032. [2] Jun SJ, Lee S. Causal inference under outcome-based sampling with monotonicity assumptions[M]. arXiv preprint, 2020: 1-169. [3] Gabriel EE, Sachs MC, Sjölander A. Causal bounds for outcome-dependent sampling in observational studies[J]. J Am Stat Assoc, 2020, 117(538): 939-950. DOI: 10.1080/01621459.2020.1832502. [4] Hernan MA, Robins JM. Causal Inference: What If[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2020: 1-389. [5] Pearl J. Causality: Models, reasoning, and inference[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2009: 1-477. [6] 郑英杰, 赵耐青. 有向无环图: 语言、规则及应用[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(8): 1140-1144. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.01.019.Zheng YJ, Zhao NQ. Directed acyclic graphs: languages, rules and applications[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(8): 1140-1144. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.01.019. [7] Cochran WG. Sampling techniques[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1977: 1-11. [8] Kish L. Survey Sampling[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1965: 1-29. [9] Neyman J. Contribution to the theory of sampling human populations[J]. J Am Stat Assoc, 1938, 33(201): 101-116. DOI: 10.1080/01621459.1938.10503378. -





 下载:
下载: