Effectiveness of the Lanzhou lamp rotavirus vaccine against rovavirus gastroenteritis among children aged 2-35 months: a test-negative design study
-
摘要:
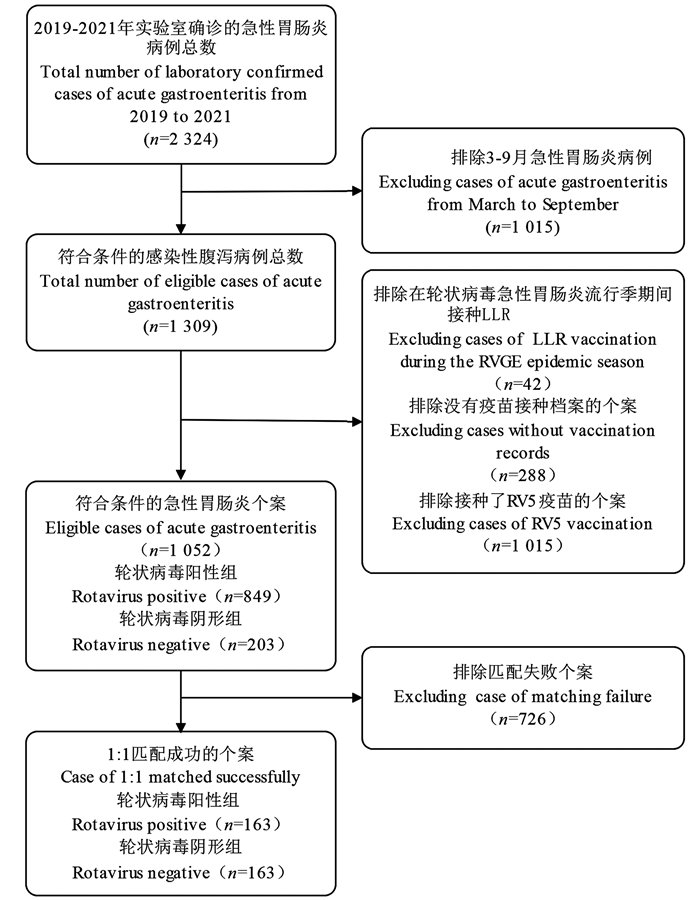
目的 评价兰州羔羊株轮状病毒(rotavirus,RV)(Lanzhou lamp rotavirus,LLR)疫苗对实验室确诊的儿童轮状病毒胃肠炎(rotacirus gastroenteritis,RVGE)的疫苗保护效果(vaccine effectiveness,VE),为疾病防控政策提供数据支持。 方法 采用检测阴性设计,通过中国疾病预防控制系统和预防接种信息管理系统收集深圳市龙华区2019―2021年RVGE流行季期间所有实验室确诊腹泻病例和LLR疫苗接种史,使用非条件和条件logistic回归分析模型计算并评价疫苗的校正OR值(adjusted odds ratio,aOR)和VE。 结果 共1 052例实验室确诊腹泻的患儿纳入研究,其中RV阳性组(RVGE+)849例和阴性对照组(RVGE-)203例,共326例匹配成功(RVGE+组163例,RVGE-组163例)。非条件和条件logistic回归分析模型中,≥1剂次LLR疫苗的VE分别为50.7% (95% CI: 28.2%~66.2%)和50.4%(95% CI: 11.7%~71.8%)。 结论 LLR疫苗对2~35月龄儿童在RVGE流行季提供中等程度的保护效果, 并提示LLR疫苗在2~11月龄儿童的接种率过低和第1剂接种年龄过晚。建议对于错过五价重配轮状病毒减毒活(pentavalent human-reassortant rotavirus, RV5)疫苗接种时间窗的儿童应鼓励尽早接种LLR疫苗。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of the Lanzhou lamp rotavirus vaccine (LLR) in mitigating laboratory-confirmed rotavirus gastroenteritis (RVGE) in children, with the objective of informing disease prevention and control policy-making. Methods Data pertaining to confirmed paediatric RVGE and the corresponding LLR vaccination history in Longhua District, Shenzhen City, from 2019-2021 during the RVGE epidemic season, were collected from the China Disease Prevention and Control Information System and the Vaccination Information Management System. A test-negative study design was employed. The adjusted odds ratios (aOR) for LLR vaccination rate and vaccine effectiveness (VE) were calculated using unconditional and conditional logistic regression analysis. Results Of the 1052 children with laboratory-confirmed RVGE included in the study, 849 were positive (RVGE+) and 203 were used as a negative control group (RVGE-), with 326 cases successfully matched (163 cases each in the RVGE+ and RVGE- groups). In the analysis model, the VE of ≥1 dose of LLR vaccine were 45.3 (95% CI: 17.8-63.6) and 50.4 (95% CI: 11.7-72.1) in the unconditional and conditional logistic regression models, respectively. Conclusions This suggests that the LLR vaccine offers moderate effectiveness in preventing RVGE in children aged 2-35 months during the epidemic season. However, the study also exposed a low coverage rate of LLR vaccination in children aged 2-11 months, indicating delayed first-dose inoculation. It is recommended that children who have missed the opportunity for pentavalent human-reassortant rotavirus vaccine should receive the LLR vaccine as soon as feasible. -
表 1 非匹配的RVGE+病例组和RVGE-对照组的基本特征描述
Table 1. Descriptive characteristics of unmatched RVGE+ cases group and RVGE- control group
变量 Variable 病例组[人数(占比/%)]
Cases [Number of people (proportion/%)]对照组[人数(占比/%)]
Controls[Number of people(proportion/%)]χ2值
valueP值
value性别Gender 0.625 0.429 男Male 497(58.5) 125(61.6) 女Female 352(41.5) 78(38.4) 发病年份Onset year 37.114 < 0.001 2019 472(51.7) 72(35.5) 2020 158(18.6) 36(17.7) 2021 314(29.8) 95(46.8) 发病月份Onset month 140.504 <0.001 10 81(9.5) 71(35.0) 11 85(10.0) 50(24.6) 12 209(24.6) 36(17.7) 次年1月Next January 265(27.8) 27(13.3) 次年2月Next February 209(24.6) 19(9.4) 月龄Age of months 0.324 0.850 2~ < 12 183(21.6) 44(21.7) 12~ < 24 480(56.5) 111(54.7) 24~ < 36 186(21.9) 48(23.6) 居住区域(街道)Residential area (subdistrict) 6.313 0.097 A街道 146(17.2) 40(19.7) B街道 192(22.6) 42(20.7) C街道 280(33.0) 52(25.6) D街道 231(27.2) 69(34.0) LLR疫苗接种LLR vaccination 19.025 <0.001 无Unvaccinated 698(82.2) 139(68.5) 有Vaccinated 151(17.8) 64(31.5) 接种剂次Vaccination 24.213 <0.001 0 698(82.2) 139(68.5) 1 134(15.8) 52(25.6) 2 17(2.0) 11(5.4) 3 0(0) 1(0.5) 合计Total 849(100.0) 203(100.0) 注:LLR, 兰州羔羊株轮状病毒。
Note: LLR, Lanzhou lamp rotavirus.表 2 按照出生日期(±1个月)、就诊日期(±1个月)匹配的RVGE+病例组和RVGE-对照组的基本特征描述
Table 2. Descriptive characteristics of RVGE+ cases group and RVGE-control group by matching age (±1 month)and clinic attending/hospital admission date (±1 month)
变量 Variable 病例组[人数(占比/%)]
Cases [Nnumber of people (proportion/%)]对照组[人数(占比/%)]
Controls[Nnumber of people(proportion/%)]χ2值
valueP值
value性别Gender 0.456 0.499 男Male 93(57.1) 99(60.7) 女Female 70(42.9) 64(39.3) 发病年份Onset year 0.096 0.953 2019 71(43.6) 71(43.6) 2020 31(19.0) 33(20.2) 2021 61(37.4) 59(36.3) 发病月份Onset month 4.703 0.319 10 35(21.5) 44(27.0) 11 37(22.7) 45(27.6) 12 42(25.8) 28(17.2) 次年1月Next January 29(17.8) 27(16.6) 次年2月Next February 20(12.0) 19(11.7) 月龄Age of months 0.079 0.961 2~ < 12 37(22.7) 35(21.5) 12~ < 24 85(52.1) 87(53.4) 24~ < 36 41(25.2) 41(25.2) 居住区域Residential area 3.009 0.390 A 29(17.8) 27(16.6) B 35(21.5) 33(20.2) C 52(31.9) 42(25.8) D 47(28.8) 61(37.4) LLR疫苗接种LLR vaccination 3.985 0.046 无Unvaccinated 127(77.9) 111(68.1) 有Vaccinated 36(22.1) 52(31.9) 接种剂次Vaccination 4.998 0.082 0 127(77.9) 111(68.1) 1 32(19.6) 42(25.8) 2 4(2.5) 10(6.1) 3 0(0) 0(0) 合计Total 163(100.0) 163(100.0) 注:LLR, 兰州羔羊株轮状病毒。
Note: LLR, Lanzhou lamp rotavirus.表 3 非条件logistic回归分析模型计算LLR疫苗对于2~35月龄儿童RVGE的保护效果
Table 3. LLR vaccine effectiveness against RVGE among children age 2~35 month calculated by unconditional logistic regression analysis
LLR疫苗接种剂次
Number of doses of LLR vaccine病例组[人数(占比/%)]
Cases [Number of people (proportion/%)]对照组[人数(占比/%)]
Controls[Number of people(proportion/%)]aOR值value
(95% CI)VE%(95% CI) P值
value接种月龄Vaccination months old 2~ < 12 1剂dose 9(4.9) 4(9.1) 0.697 (0.186~2.612) 30.7(-161.2~81.4) 0.593 12~ < 24 1剂dose 91(19.0) 37(34.9) 0.422 (0.250~0.711) 57.8(28.1~75.0) 0.001 2剂dose 1(0.3) 5(6.8) 0.019 (0.002~0.174) 81.0(72.6~99.8) <0.001 ≥1剂dose 92(19.2) 42(37.8) 0.361 (0.218~0.598) 63.9(40.3~78.2) <0.001 24~ < 35 1剂dose 34(20.0) 11(26.8) 0.734 (0.312~1.727) 26.6(-72.2~68.8) 0.479 2剂dose 16(10.5) 6(16.7) 0.795 (0.268~2.360) 20.5(-136.0~72.2) 0.680 ≥1剂dose 50(26.9) 18(37.5) 0.746 (0.356~1.563) 23.4(-56.3~64.4) 0.438 2~ < 35 ≥1剂dose 151(17.8) 64(31.5) 0.493 (0.338~0.718) 50.7(28.2~66.2) <0.001 合计Total 849(100.0) 203(100.0) 注:1. LLR, 兰州羔羊株轮状病毒。2. 3剂次LLR的比例过低,LLR所有剂次用≥1剂来表示;非条件logistic回归分析模型调整的部分混杂因素有:就诊年份、就诊月份。
Note: 1. LLR, Lanzhou lamp rotavirus.2. The proportion of LLR in 3 doses is too low, and all doses of LLR are represented by ≥1 dose; Some confounding factors adjusted by unconditioned logistic regression analysis model were: year of visit and month of visit.表 4 条件logistic回归模型评价LLR疫苗对于2~35月龄儿童RVGE的保护效果
Table 4. LLR vaccine effectiveness against RVGE among children age 2-35 month by conditional logistic regression model
LLR疫苗接种剂次
Number of doses of LLR vaccine病例组[人数(占比/%)]
Cases [Number of people (proportion/%)]对照组[人数(占比/%)]
Controls[Number of people(proportion/%)]cOR值value
(95% CI)①VE%(95% CI) P值
value接种月龄Vaccination months old 2~ < 12 1剂dose 4(10.8) 4(11.4) 0.958 (0.157~5.854) 4.2(-485.4~84.3) 0.958 12~ < 24 1剂dose 16(18.8) 30(34.5) 0.304(0.131~0.709) 69.6(19.1~86.9) 0.003 2剂dose 0(0) 5(5.7) ≥1剂dose 16(18.8) 35(40.2) 0.259(0.113~0.595) 74.1(40.5~88.7) 0.001 24~ < 35 1剂dose 13(31.0) 8(19.5) 1.333(0.463~3.843) -33.3(-284.3~53.7) 0.594 2剂dose 4(9.5) 5(12.2) 2.000(0.181~22.056) -100.0(-2105.6~81.9) 0.571 ≥1剂dose 16(39.0) 13(31.7) 1.429(0.544~3.753) -42.9(-265.3~45.6) 0.469 2~ < 35 ≥1剂dose 36(22.1) 52(31.9) 0.499(0.282~0.883) 50.1(11.7~71.8) 0.017 合计Total 163(100.0) 163(100.0) 注:LLR, 兰州羔羊株轮状病毒。①匹配后的条件logistic回归分析模型计算OR时,OR无需校正。Note: LLR, Lanzhou lamp rotavirus.① When the matched conditional logistic regression analysis model calculates OR, OR does not need to be corrected. -
[1] Luchs A, Timenetsky Mao C. Group A rotaviru gaitroenteritis: post-vaccine era, genotypes and zoonotic transmission[J]. Einstein(Sao Paulo), 2016, 14(2): 278-287. DOI: 10.1590/S1679-45082016RB3582. [2] Ansari SA, Springthorpe VS, Sattar SA. Survival and vehicular spread of human rotaviruses: possible relation to seasonality of outbreaks[J]. Rev Infect Dis, 1991, 13(3): 448-461. DOI: 10.1093/clinids/13.3.448. [3] Dennehy PH. Rotavirus infection: a disease of the past?[J]. Infect Dis North Am, 2015, 29(4): 617-635. DOI: 10.1016/j.idc.2015.07.002. [4] WHO. Rotavirus vaccines in routine immunization. Pocket Guide[Z]. Switzerland: World Health Organization. 2012. [5] 李丹地, 徐子乾, 谢广成, 等. 确认我国轮状病毒疫苗株LLR基因型为G10P[15][J]. 病毒学报, 2015, 31(2): 170-173. DOI: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.002642.Li DD, Xu ZQ, Xie GC, et al. Genotype of Rotavirus Vaccine Strain LLR in China is G10P[15][J]. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2015, 31(2): 170-173. DOI: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.002642. [6] 刘东磊, 杨洁, 李安, 等. 轮状病毒疫苗免疫效果及人体反应观察[J]. 中国计划免疫, 2002, 8(3): 138-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM200203006.htmLiu DL, Yang J, Li A, et al. Observation on immune effect and human reaction of rotavirus vaccine[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccine and Immunization, 2002, 8(3): 138-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM200203006.htm [7] Fu C, He Q, Xu J, et al. Effectiveness of the Lanzhou lamb rotavirus vaccine against gastroenteritis among children[J]. Vaccine, 2012, 31(1): 154-158. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.10.078. [8] Li J, Zhang Y, Yang Y, et al. Effectiveness of Lanzhou lamb rotavirus vaccine in preventing gastroenteritis among children younger than 5 years of age[J]. Vaccine, 2019, 37(27): 3611-3616. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.03.069. [9] 刘娜, 马智超, 李苑, 等. 深圳某接种点国产轮状病毒疫苗使用现况分析[J]. 中华实验和临床病毒学杂志, 2015, 29(2): 151-153. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9279.2015.02.019.Liu N, Ma ZC, Li Y, et al. The utility of Lanzhou Lamb Rotavirus Vaccine among two vaccination sites of Shenzhen[J]. Chin J Exp Clin Virol, 2015, 29(2): 151-153. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9279.2015.02.019. [10] 唐广心, 陈娅妮, 李苑, 等. 深圳市宝安区国产轮状病毒疫苗使用现况调查[J]. 国际病毒学杂志, 2020, 27(5): 417-420. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4092.2020.05.015.Tang GX, Chen YN, Li Y, et al. Survey on the usage of the domestic attenuated rotavirus vaccine in Baoan Districut of Shenzhen[J]. Int J Virol, 2020, 27(5): 417-420. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4092.2020.05.015. [11] Hsieh YC, Wu FT, Hsiung CA, et al. Comparison of virus shedding after lived attenuated and pentavalent reassortant rotavirus vaccine[J]. Vaccine, 2014, 32(10): 1199-1204. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.08.041. [12] Mo Z, Mo Y, Li M, et al. Efficacy and safety of a pentavalent live human-bovine reassortant rotavirus vaccine (RV5) in healthy Chinese in fants: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Vaccine, 2017, 35(43): 5897-5904. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.08.081 [13] Zhen SS, Li Y, Wang SM, et al. Effectiveness of the live attenuated rotavirus vaccine produced by a domestic manufacturer in China studied using a population-based case-control design[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2015, 4(10): e64. DOI: 10.1038/emi.2015.64. [14] Fu C, Tate JE, Jiang B, et al. Effectiveness of Lanzhou lamb rotavirus vaccine against hospitalized gastroenteritis: further analysis and update[J]. Hum Vaccin, 2010, 6(11): 953. DOI: 10.4161/hv.6.11.12847. [15] 陈茜, 张颖, 钱智勇, 等. 口服轮状病毒减毒活疫苗对轮状病毒腹泻保护效果的病例对照研究[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2014, 20(1): 55-58. DOI: 10.19914/j.cjvi.2014.01.012.Chen Q, Zhang Y, Qian ZY, et al. Case-control Study on Effect of Oral Rotavirus Attenuated Live Vaccine against Rotavirus Diarrhea[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccine and Immunization, 2014, 20(1): 55-58. DOI: 10.19914/j.cjvi.2014.01.012. [16] Fang ZY, Wang B, Kilgore PE, et al. Sentinel hospital surveillance for rotavirus diarrhea in the People's Republic of China, August 2001-July 2003[J]. J Infect Dis, 2005, 192: S94-S99. DOI: 10.1086/431505. [17] Velázquez FR, Matson DO, Calva JJ, et al. Rotavirus infection in infants as protection against subsequent infections[J]. N Engl J Med, 1996, 335(14): 1022-1028. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199610033351404. [18] Fischer TK, Valentiner-Branth P, Steinsland H, et al. Protective immunity after natural rotavirus infection: a community cohort study of newborn children in Guinea-Bissau, West Africa[J]. J Infect Dis, 2002, 186(5): 593-597. DOI: 10.1086/342294. [19] Gladstone BP, Ramani S, Mukhopadhya I, et al. Protective effect of natural rotavirus infection in an Indian birth cohort[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011, 365(4): 337-346. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1006261. [20] WHO. Rotavirus vaccines: WHO position paper-July 2021[J]. Weekly Epidemiological Record, 2021, 96(28): 301-320. [21] Jackson ML, Rothman KJ. Effects of imperfect test sensitivity and specificity on observational studies of influenza vaccine effectiveness[J]. Vaccine, 2015, 33(11): 1313-1316. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.01.069. [22] 张力, 金鹏飞, 李靖欣, 等. 检测阴性设计在疫苗效果评价中的应用[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(2): 280-283. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.024.Zhang L, Jin PF, Li JX, et al. Application of test-negative design in vaccine efficacy evaluation[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2020, 41(2): 280-283. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.024. -





 下载:
下载: