Study on the relationship between the incidence of hand-foot-mouth disease and meteorological factors in Nanning City based on the distribution lag nonlinear model
-
摘要:
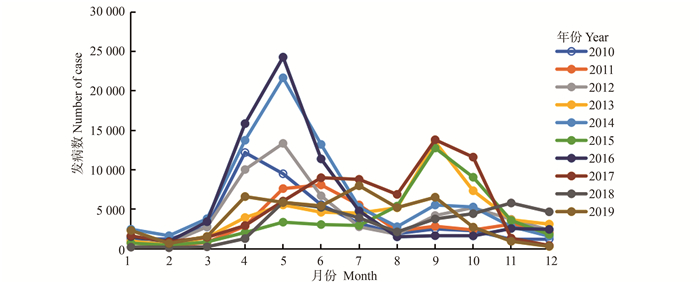
目的 探讨气象因素对手足口病(hand-foot-mouth disease, HFMD)发病的影响与滞后效应。 方法 收集整理南宁市2010—2019年HFMD日发病数据及同期气象资料,运用分布滞后非线性模型(distributed lag non-linear models, DLNM)分析南宁市HFMD发病与气象因素的相关性。 结果 南宁市2010—2019年HFMD累计报告508 984例,发病主高峰在每年4—6月,次高峰在9—10月;男女报告发病率之比为1.57∶1,以幼托儿童和散居儿童为主。HFMD发病与气温、相对湿度和日照时数呈正相关,与气压呈负相关。气温为35.0 ℃,滞后d 9时RR值最大(RR=1.058,95% CI:1.037~1.079);相对湿度为86.0%,滞后d 14时RR值最大(RR=1.011,95% CI:1.007~1.014);气压呈“双峰”现象,气压为990.0 hpa滞后d 4时RR值最大(RR=1.022,95% CI:1.017~1.027),气压为1 030.0 hpa滞后d 5时RR值最大(RR=1.054,95% CI:0.988~1.124);日照时数为7.0 h/d,滞后d 5时RR值最大(RR=1.017,95% CI:1.009~1.025);极高温、极高压、极低温和极低湿度对HFMD发病也有明显滞后效应。 结论 南宁市HFMD发病与气象因素相关,可利用气象因素预测HFMD发展趋势。 Abstract:Objective This study aims to investigate the influence and lag effects of meteorological factors on the incidence of hand-foot-mouth disease disease (HFMD). Methods Daily HFMD incidence data and concurrent meteorological data from 2010 to 2019 were collected and analyzed. The distributed lag non-linear model (DLNM) was utilized to examine the correlation between HFMD incidence and meteorological factors in Nanning. Results From 2010 to 2019, a total of 508 984 HFMD cases were reported in Nanning, with primary peaks observed from April to June and secondary peaks from September to October. The incidence rate for males to females was 1.57∶1, primarily among nursery-aged and home-based children. HFMD incidence exhibited a positive correlation with average temperature, relative humidity, and sunshine duration, and a negative correlation with atmospheric pressure. At 35.0 ℃, the mean temperature exhibited the highest RR value on the 9th day (RR=1.058, 95% CI: 1.037-1.079); At 86.0%, the relative humidity peaked on the 14th day (RR=1.011, 95% CI: 1.007-1.014); Atmospheric pressure displayed a "double peak" phenomenon, with the highest RR value at 990.0 hPa on the 7th day (RR=1.022, 95% CI: 1.017-1.027), and at 1 030.0 hPa on the 5th day (RR=1.054, 95% CI: 0.988-1.124); At 7.0 h/d, the sunshine duration revealed the maximum RR value on the 5th lag day (RR=1.017, 95% CI: 1.009-1.025). Notably, extreme heat, high-pressure, cold, and dry effects also demonstrated a significant lag effect on the onset of HFMD. Conclusions HFMD presents a severe epidemic situation in Nanning. The incidence of HFMD is significantly associated with meteorological factors. Meteorological factors can be leveraged to predict the disease′s development trend. -
表 1 2010—2019年南宁市HFMD与气象因素分布情况
Table 1. Distribution of HFMD and meteorological factors in Nanning from 2010 to 2019
气象指标
Meteorological indicator平均值
Average values Min Max P2.5 P25 M P75 P97.5 日发病数 Number of daily cases 139.00 145.00 0 1 026.00 7.00 45.00 92.00 181.00 582.00 日降水量/mm Daily precipitation/mm 2.29 5.09 0 23.74 0 0 0 2.29 22.87 日均风速/(m·s-1) Daily average wind speed/(m·s-1) 1.87 0.86 0.20 7.00 0.70 1.20 1.70 2.30 3.90 日均气压/hpa Daily average atmospheric pressure/hpa 997.03 7.29 978.85 1 023.20 984.43 991.40 996.60 1 002.40 1 011.17 日均气温/℃ Daily average temperature/℃ 21.78 6.49 3.80 31.80 8.10 16.70 23.40 27.30 30.10 日均水汽压/hpa Daily average water vapor pressure/hpa 21.87 8.02 3.60 35.80 7.30 14.70 22.60 29.50 33.20 日均相对湿度/% Daily average relative humidity/% 79.63 10.04 30.50 99.00 55.00 75.00 80.95 86.30 95.00 日照时数/h Sunshine duration/h 4.21 3.82 0 12.20 0 0 3.80 7.90 10.90 日均最低气压/hpa Daily minimum atmospheric pressure/hpa 994.29 7.22 973.00 1 018.90 981.70 988.70 993.80 999.70 1 008.40 日均最高气压/hpa Daily average maximum atmospheric pressure/hpa 999.40 7.62 980.70 1 027.10 986.30 993.40 999.00 1 005.10 1 014.00 日均最低气温/℃ Daily minimum temperature/℃ 18.70 6.34 -1.20 28.10 5.40 13.60 20.20 24.30 26.60 日均最高气温/℃ Daily maximum temperature/℃ 26.34 7.25 5.40 38.90 10.70 21.30 28.20 32.40 35.70 注: HFMD, 手足口病。
Note: HFMD, hand-foot-mouth disease.表 2 2010—2019年南宁市HFMD日发病数与气象因素Spearman相关分析结果
Table 2. Spearman correlation analysis results of daily incidence of HFMD and meteorological factors in Nanning from 2010 to 2019
气象指标
Meteorological indicator发病数
Number of incidents降水量/mm
Precipitation/mm风速/(m·s-1)
Wind speed/(m·s-1)气压/hpa
Atmospheric pressure/hpa气温/℃
Temperature/℃水汽压/hpa
Water vapor pressure/hpa相对湿度/%
Relative humidity/%日照时数/h
Sunshine duration/h最低气压/hpa
Minimum atmospheric pressure/hpa最高气压/hpa
Maximum atmospheric pressure/hpa最低气温/℃
Minimum temperature/℃发病数 Number of incidents 1.000 降水量/mm Precipitation/mm 0.063 ③ 1.000 风速/(m·s-1) Wind speed/(m·s-1) 0.041 ① 0.052 ② 1.000 平均气压/hpa Mean atmospheric pressure/hpa -0.502 ③ -0.101 ③ -0.216 ③ 1.000 平均气温/℃ Mean temperature/℃ 0.580 ③ -0.036 ② 0.082 ③ -0.864 ③ 1.000 水汽压/hpa Water vapor pressure/hpa 0.580 ③ 0.142 ③ 0.088 ③ -0.886 ③ 0.937 ③ 1.000 相对湿度/% Relative humidity/% 0.052 ② 0.545 ③ -0.027 -0.153 ③ -0.062 ③ 0.244 ③ 1.000 日照时数/h Sunshine duration/h 0.254 ③ -0.441 ③ -0.043 ② -0.329 ③ 0.523 ③ 0.325 ③ -0.520 ③ 1.000 最低气压/hpa Minimum atmospheric pressure/hpa -0.490 ③ -0.095 ③ -0.232 ③ 0.991 ③ -0.851 ③ -0.868 ③ -0.134 ③ -0.332 ③ 1.000 最高气压/hpa Maximum atmospheric pressure/hpa -0.507 ② -0.112 ③ -0.209 ③ 0.997 ③ -0.869 ③ -0.893 ③ -0.160 ③ -0.322 ③ 0.983 ③ 1.000 最低气温/℃ Minimum temperature/℃ 0.579 ② 0.095 ③ 0.139 ③ -0.870 ③ 0.962 ③ 0.957 ③ 0.070 ③ 0.357 ③ -0.852 ③ -0.880 ③ 1.000 最高气温/℃ Maximum temperature/℃ 0.545 ② -0.125 ③ 0.007 -0.811 ③ 0.963 ③ 0.871 ③ -0.151 ③ 0.653 ③ -0.806 ③ -0.812 ③ 0.879 ③ 注:HFMD, 手足口病。
① P < 0.05; ② P < 0.01; ③ P < 0.001。
Note: HFMD, hand-foot-mouth disease.
① P < 0.05; ② P < 0.01; ③ P < 0.001.表 3 气象因素对HFMD的滞后效应
Table 3. The lag effect of meteorological factors on HFMD
气象指标
Meteorological indicators参考值
Reference value累积效应最大
Maximum cumulative effect累积RR值
Accumulated RR值value95% CI 滞后天数 Lag days 滞后天数
Lag daysRR值
value95% CI 气温/℃ Temperature/℃ 23.40 35.0 1.597 1.289~1.978 d 9 1.058 1.037~1.079 相对湿度/% Relative humidity/% 80.95 86.0 1.094 1.069~1.120 d 14 1.011 1.007~1.014 气压/hpa Atmospheric pressure/hpa 996.60 990.0 1.213 1.152~1.278 d 7 1.022 1.017~1.027 996.60 1 030.0 1.383 0.647~2.957 d 5 1.054 0.988~1.124 日照时数/h Sunshine duration/h 3.80 7.0 1.159 1.060~1.266 d 5 1.017 1.009~1.025 注:1. HFMD, 手足口病。
2. 以各项指标的中位数为参考值。
Note: 1. HFMD, hand-foot-mouth disease.
2. Using the median of each indicator as a reference value.表 4 低端气候对HFMD的滞后效应
Table 4. Lag effect of extreme climate on HFMD
气象指标
Meteorological indicator参考值
Reference value滞后天数
Lag daysRR值 value
(95% CI)极高温/℃ Extreme high temperature/℃ 30.10 d 9 1.020(1.007~1.033) 极低温/℃ Extreme low temperature/℃ 8.10 d 3 1.065(1.046~1.084) 极高湿/% Extreme high humidity/% 95.00 — — 极低湿% Extreme low humidity/% 55.00 d 0 1.055(0.992~1.122) 极高压/hpa Extreme high pressure/hpa 1 011.17 d 5 1.081(1.025~1.139) 极低压/hpa Extreme low pressure/hpa 984.43 — — 极高日照/h Extreme high sunlight/h 10.90 — — 极低日照/h Extreme low sunlight/h 0 — — 注:1. HFMD, 手足口病。
2. 极端值分别以气象指标中97.5%位点和2.5%位点所对应的值为参考。
3.“—”滞后期内无发病风险。
Note: 1. HFMD, hand-foot-mouth disease.
2. The extreme values are based on the values corresponding to 97.5% and 2.5% of the meteorological indicators, respectively.
3.“—”No risk during the lag period. -
[1] 蒋丽娜, 谭毅, 王晶, 等. 2008-2015年广西手足口病流行病学特征及时空聚集性分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2017, 21(4): 340-344. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.04.005.Jiang LN, Tan Y, Wang J, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and temporal-spatial clustering of hand, foot and mouth disease in Guangxi from 2008 to 2015[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2017, 21(4): 340-344. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2017.04.005. [2] 林健燕, 陈婷, 汤洪洋, 等. 南宁市手足口病流行病学特征分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2011, 38(20): 4258-4260.Lin JY, Chen T, Tang HY, et al. Analysis of the epidemiologicai characteristics of hand-foot-mouth disease in Nanning[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2011, 38(20): 4258-4260. [3] 刘峰, 刘凤仁, 李刚. 深圳市龙岗区2011-2014年手足口病特征及与气象因素相关性[J]. 中国热带医学, 2016, 16(7): 688-691. DOI: 10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2016.07.16.Liu F, Liu FR, Li G. Epidemiological characteristics of hand foot and mouth disease(HFMD)and correlation with meteorological factors in Longgang District, Shenzhen City, 2011-2014[J]. China Tropical Medicine, 2016, 16(7): 688-691. DOI: 10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2016.07.16. [4] 韩微笑. 2009~2013年广州市气温对常见传染病的短期影响[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017.Han WX. Short-term impacts of temperature on major infectious diseases in Guangzhou City, 2009-2013[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2017. [5] 贺楠. 广西手足口病时空分布与环境暴露滞后效应研究[D]. 开封: 河南大学, 2019.He N. Spatiotemporal distribution of hand-foot-mouth disease and environmental exposure-lag effect in Guangxi[D]. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2019. [6] 朱建明, 李澜, 莫平华, 等. 基于气象因素的上海市金山区手足口病多元线性回归预测模型[J]. 实用预防医学, 2016, 23(1): 115-116. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2016.01.036.Zhu JM, Li L, Mo PH, et al. Multiple linear regression prediction model of hand, foot and mouth disease in Jinshan District of Shanghai based on meteorological factors[J]. Pract Prev Med, 2016, 23(1): 115-116. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2016.01.036. [7] 杨琼英. 广州市流行性腮腺炎流行病学特征及与气象因子关联性研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2015.Yang QY. Study on the relationship between the epidemiology of mumps and meteorological factors in Guangzhou[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2015. [8] Bertrand I, Schijven JF, Sánchez G, et al. The impact of temperature on the inactivation of enteric viruses in food and water: a review[J]. J Appl Microbiol, 2012, 112(6): 1059-1074. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05267.x. [9] 杜君, 王宝强, 韩璐. 定西市2010-2020年手足口病发病与气象因素的相关性分析[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2022, 35(6): 1055-1059. DOI: 10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2022.06.071.Du J, Wang BQ, Han L. Correlation analysis between hand foot mouth disease and meteorological factors in Dingxi City from 2010 to 2020[J]. The Journal of Medical Theory and Practice, 2022, 35(6): 1055-1059. DOI: 10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2022.06.071. [10] 彭丽, 叶晓芳, 阚海东, 等. 气温对上海市浦东新区手足口病发病的短期效应[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2018, 35(8): 690-695. DOI: 10.13213/j.cnki.jeom.2018.18173.Peng L, Ye XF, Kan HD, et al. Short-term effects of temperature on incidence of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Pudong New Area, Shanghai[J]. Journal of Environmental and Occuptional Medicine, 2018, 35(8): 690-695. DOI: 10.13213/j.cnki.jeom.2018.18173. [11] Zhang Z, Xie X, Chen X, et al. Short-term effects of meteorological factors on hand, foot and mouth disease among children in Shenzhen, China: Non-linearity, threshold and interaction[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2016, 539: 576-582. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.027. [12] 吕世峰, 王惠君, 刘慧玲, 等. 山东日照市2009-2012年手足口病与气象因素的时间序列分析[J]. 华南预防医学, 2014, 40(4): 312-317. DOI: 10.13217/j.scjpm.2014.0312.Lyu SF, Wang HJ, Liu HL, et al. Time series analysis of weather and hand, foot, and mouth disease in Rizhao, Shandong, 2009-2012[J]. South China J Prev Med, 2014, 40(4): 312-317. DOI: 10.13217/j.scjpm.2014.0312. [13] Yang H, Wu J, Cheng J, et al. Is high relative humidity associated with childhood hand, foot, and mouth disease in rural and urban areas[J]. Public Health, 2017, 142: 201-207. DOI: 10.1016/j.puhe.2015.03.018. [14] Qi H, Chen Y, Xu D, et al. Impact of meteorological factors on the incidence of childhood hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) analyzed by DLNMs-based time series approach[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2018, 7(1): 7. DOI: 10.1186/s40249-018-0388-5. [15] 刘琦, 陈益平. 温州市儿童手足口病与气象因素相关性研究[J]. 浙江预防医学, 2015, 27(10): 1020-1022. DOI: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn1007-0931.2015.10.013.Liu Q, Chen YP. Correlation between hand foot mouth disease and meteorological factors in children in Wenzhou[J]. Zhejiang Prev Med, 2015, 27(10): 1020-1022. DOI: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn1007-0931.2015.10.013. [16] 王琳轶, 舒艳婷, 刘练. 重庆大学城区域2018-2019年度儿童手足口病流行情况及时空相关性分析[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2021, 34(18): 3278-3281. DOI: 10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2021.18.077.Wang LY, Shu YT, Liu L. Prevalence of hand foot mouth disease among children in Chongqing University Town in 2018-2019 and analysis of temporal and spatial correlation[J]. The Journal of Medical Theory and Practice, 2021, 34(18): 3278-3281. DOI: 10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2021.18.077. -





 下载:
下载: