The study of college students' physical exercise behavior phase and process of change based on the Transtheoretical model
-
摘要:
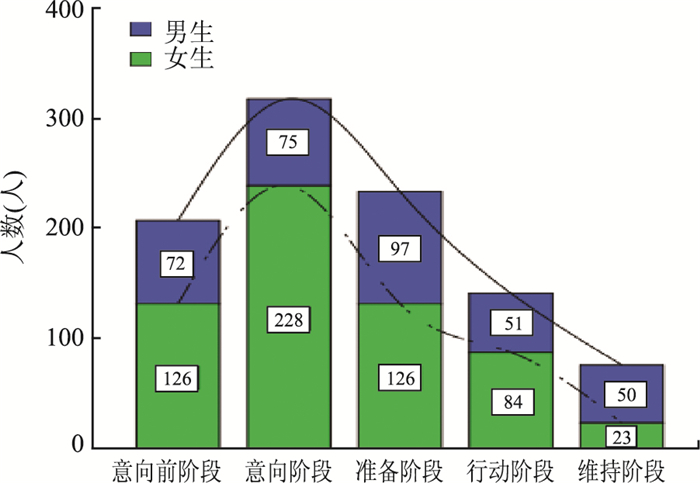
目的 本研究基于跨理论模型,对大学生在改善体育锻炼行为过程中不同阶段的特征进行分析,探求变化程序在体育锻炼行为改变过程中的作用,为大学生体育锻炼行为阶段匹配干预提供参考依据。 方法 采用分层随机整群抽样方法对山西省5类高校932名大学生进行问卷调查。大学生锻炼行为阶段现状采用描述性分析;利用方差分析及多因素Logistic回归分析模型探讨不同体育锻炼变化阶段的变化程序差异;利用多因素方差分析个体一般情况对变化程序的影响。 结果 89.4%大学生明确体育锻炼的重要性,但对自身锻炼状况感到满意仅占29.4%;运动阶段分布呈左偏峰倒U型分布,且存在性别差异(χ2=54.657,P < 0.001);大学生体育锻炼变化程序存在阶段特征。性别对互助关系、意识控制具有主效应(F性别=7.400,P=0.007;F性别=7.778,P=0.005)。年级和性别对社会释放具有交互效应(F年级*性别=3.614,P=0.013)。 结论 大学生体育锻炼行为呈现"知而不行"的特点,且符合跨理论模型的结构。研究者应根据大学生体育行为的阶段特征,制定针对性的干预策略。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the stage characteristics in the exercise behavior improvement of college students and explore the role of Process in the exercise behavior change based on the transtheoretical model, providing basis for the stage-matched intervention for the exercise behavior of college students. Methods There were 932 students who completed the questionnaires, from 5 universities in Shanxi Province were selected by using a stratified random cluster sampling method. Descriptive analysis was used to describe the exercise behavior of college students. Variance analysis and multivariate Logistic regression model were used to analyze the difference of the process of with stage of change among college students' physical exercise. Multivariate variance analysis was used to analyze how personal characteristics affect process of change. Results Among all participants, 89.4% students knew the importance of physical exercise, and 29.4% students were satisfied with their physical exercise condition. The distribution of students' physical exercise stage showed an inverted U-shape with left-side peak, and there was a significant difference between gender(χ2=54.657, P < 0.001). There were significant stage characteristics in the process of students' exercise behavior, gender had a significant main effects on mutual aid relation(F=7.400, P=0.07)and conscious control (F=7.778, P=0.005), gender and grade had interaction effects on social release (F=3.614, P=0.013). Conclusions The college students' exercise behavior showed the characteristics of "knowing but not to do", which conformed to the Transtheoretical model. It is essential to develop targeted phased exercise intervention strategies according to the relationship between change of phase and change of procedure. -
表 1 不同行为阶段大学生体育锻炼变化程序的比较
Table 1. Comparison of the process of change with stage of change among college students' physical exercise
变化程序 意向前阶段 意向阶段 准备阶段 行动阶段 维持阶段 F值 自我释放 14.80±4.30 15.77±3.10 17.50±3.24 18.10±3.08 19.86±4.19 42.741a 互助关系 11.00±3.64 11.04±2.85 12.30±2.76 12.97±2.67 13.53±2.95 21.172a 效果评估 11.83±3.31 12.26±2.87 13.16±2.67 13.16±2.55 13.22±3.49 8.497a 社会释放 16.33±3.65 16.82±3.11 17.03±2.93 17.80±2.97 18.07±3.81 6.411a 自我管理 15.88±4.21 17.28±3.42 18.38±3.23 18.36±3.13 19.93±3.97 23.970a 意识控制 16.03±5.33 16.30±4.29 18.39±4.04 18.69±3.59 20.81±4.55 26.077a 总分 85.78±20.64 89.49±14.86 96.75±14.48 99.08±13.63 105.42±18.48 31.296a 注:a表示P < 0.001。 表 2 不同体育锻炼行为阶段变化程序影响因素多因素Logistic回归分析
Table 2. Multifactor Logistic regression analysis of different stages of different physical exercise behavior
影响因素 β sx Wald/χ2值 OR(95% CI)值 P值 前意向阶段(否=0,是=1) 自我释放 -0.153 0.040 14.336 0.858(0.793~0.929) < 0.001 社会释放 0.100 0.036 7.591 1.106(1.029~1.187) 0.006 自我管理 -0.127 0.036 12.607 0.881(0.822~0.945) < 0.001 意向阶段(否=0,是=1) 自我释放 -0.106 0.034 9.839 0.900(0.842~0.961) 0.002 互助关系 -0.078 0.034 5.291 0.925(0.866~0.989) 0.021 准备阶段(否=0,是=1) 社会释放 -0.121 0.034 12.822 0.886(0.829~0.947) < 0.001 自我管理 0.066 0.034 3.892 1.069(1.000~1.141) 0.049 行动阶段(否=0,是=1) 自我释放 0.148 0.046 10.376 1.160(1.060~1.270) 0.001 互助关系 0.113 0.045 6.448 1.120(1.026~1.222) 0.011 维持阶段(否=0,是=1) 自我释放 0.255 0.064 15.757 1.290(1.138~1.463) < 0.001 效果评估 -0.172 0.053 10.540 0.842(0.759~0.934) 0.001 意识控制 0.109 0.045 5.916 1.115(1.021~1.217) 0.015 -
[1] 李晶, 王文军, 顾怀婷, 等. 济宁市社区老年人休闲体育活动与抑郁、生存质量的关系[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2016, 20(8): 817-820. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.08.016.Li J, Wang WJ, Gu HT, et al. Correlation of physical activities with depression and the quality of life in elders from urban community in Jining City[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2016, 20(8): 817-820. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.08.016. [2] 姜媛, 张力为, 毛志雄. 体育锻炼与心理健康: 情绪调节自我效能感与情绪调节策略的作用[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2018, 16(4): 570-576. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2018.04.020Jiang Y, Zhang LW, Mao ZX. Physical exercise and mental health: the effect of emotion regulation self-efficacy and emotion regulation strategy[J]. Stud Psychol Behav, 2018, 16(4): 570-576. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2018.04.020 [3] Eisho Y, Daisuke N, Yutaka JM. Association between regular physical exercise and depressive symptoms mediated through social support and resilience in Japanese company workers: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2016, 16(553): 1-8. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-3251-2. [4] Zhang C, Zhang J, Long C, et al. Analyze of research on the health of college students based on a perspective of knowledge mapping[J]. Public Health, 2016, 137: 188-191. DOI: 10.1016/j.puhe.2015.11.002. [5] 张立敏, 张力为, 杨宁, 等. 长期健身活动对大学生印象管理及心理健康的影响[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 2013, 36(9): 108-112. DOI: 10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2013.09.020.Zhang LM, Zhang LW, Yang N, et al. Effects of long term exercise movements on exercisers' impression management and their mental health[J]. J Beijing Sport Univ, 2013, 36(9): 108-112. DOI: 10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2013.09.020. [6] 徐明. 肥胖与体育锻炼[J]. 成都体育学院学报, 2002, 28(5): 80-83. DOI: 10.15942/j.jcsu.2002.05.026.Xu M. Obesity and physical exercises[J]. J Chengdu Sport Univ, 2002, 28(5): 80-83. DOI: 10.15942/j.jcsu.2002.05.026. [7] 王佃娥, 杜发强, 韩亚娟. 我国城市青少年校外体育锻炼行为变化阶段与变化程序关系的研究[J]. 广州体育学院学报, 2018, 38(1): 11-16. DOI: 10.13830/j.cnki.cn44-1129/g8.2018.01.004.Wang DE, Du FQ, Han YJ. Relationship between the stage and process of exercise behavior of teenagers[J]. J Guangzhou Sport Univ, 2018, 38(1): 11-16. DOI: 10.13830/j.cnki.cn44-1129/g8.2018.01.004. [8] Zhang CC, Zheng X, Huang H, et al. A study on the applicability of the health action process approach to the dietary behavior of university students in Shanxi, China[J]. J Nutr Educ Behav, 2018, 50(4): 388-395. DOI: 10.1016/j.jneb.2017.09.024. [9] 尹博. 运用跨理论模型对大学生体育锻炼行为改变的实证研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2007. DOI: 10.7666/d.y1073880.Yi B. An empirical study on the change of college students' physical exercise behavior using a transtheoretical model[D]. Shanghai: Huadong Normal University, 2007. DOI: 10.7666/d.y1073880. [10] 杨廷忠, 于文平, 黄丽. 行为改变的一种策略和方法: 行为分阶段转变理论模型介绍[J]. 中国行为医学科学, 2002, 11(3): 352-353. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6554.2002.03.064.Yang TZ, Yu WP, Huang L. A strategy and approach to behavioral change: an introduction to the behavioral transition theory model: The transtheoretical model and stages of change[J]. Chin J Beha Med & Sci, 2002, 11(3): 352-353. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6554.2002.03.064. [11] 李娜娜. 计划行为理论和跨理论模型预测锻炼行为的差异研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉体育学院, 2014.Li NN. The differences between the theory of planned behavior (TPB) and the trans theoretical model (TTM)'s predictive power of physical activity[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Sports University, 2014. [12] Lippke S, Ziegelmann JP. Understanding and modeling health behavior: the multi-stage model of health behavior change[J]. J Health Psychol, 2006, 11(1): 37-50. DOI: 10.1177/1359105306058845. [13] Marcus BH, Selby VC, Niaura RS, et al. Self-efficacy and the stages of exercise behavior change[J]. Res Q Exercise Sport, 1992, 63(1): 60-66. DOI: 10.1080/02701367.1992.10607557. [14] 江铁峰. 大学生体育锻炼变化阶段(连续性测量)量表的修正研究[J]. 浙江体育科学, 2007, 29(2): 113-118. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3624.2007.02.036.Jiang TF. Modification of exercise stage of change (continuous measure) scale for college students[J]. Zhejiang Sport Sci, 2007, 29(2): 113-118. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3624.2007.02.036. [15] 程小虎, 卢标. 一、二年级大学生体育锻炼行为阶段性特点的调查研究[J]. 武汉体育学院学报, 1998, 2(125): 44-47. DOI: 10.15930/j.cnki.wtxb.1998.02.011.Cheng XH, Lu B. The stages character of exercise behavior change in 1-2 grades undergraduates[J]. J Wuhan Inst Physi Edu, 1998, 2(125): 44-47. DOI: 10.15930/j.cnki.wtxb.1998.02.011. [16] 司琦, 于可红, 陈谦, 等. 阶段变化模型在身体活动领域应用研究的综述: 1998年至2012年[J]. 体育科学, 2013, 33(5): 74-83. DOI: 10.16469/j.css.2013.05.010.Si Q, Yu KH, Chen Q, et al. A systematic review of physical activity study based on the transtheoretical model in the China from1998 to 2012[J]. China Sport Sci, 2013, 33(5): 74-83. DOI: 10.16469/j.css.2013.05.010. [17] 张中江, 陈善平, 潘秀刚. 大学生体育锻炼行为和锻炼动机的性别差异[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 2009, 32(9): 50-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD200909018.htmZhang ZJ, Chen SP, Pan XG. Gender differences on exercise behavior and exercise motivation of university students[J]. J Beijing Sport Univ, 2009, 32(9): 50-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD200909018.htm [18] 方敏, 孙影. 大学生锻炼行为阶段变化模式研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2009, 24(5): 453-456. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0000.2009.05.023.Fang M, Sun Y. The stages of exercise behavior change of undergraduates[J]. J Tianjin Univ of Sport, 2009, 24(5): 453-456. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0000.2009.05.023. -





 下载:
下载: