Prediction and analysis of death of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou based on time series model
-
摘要:
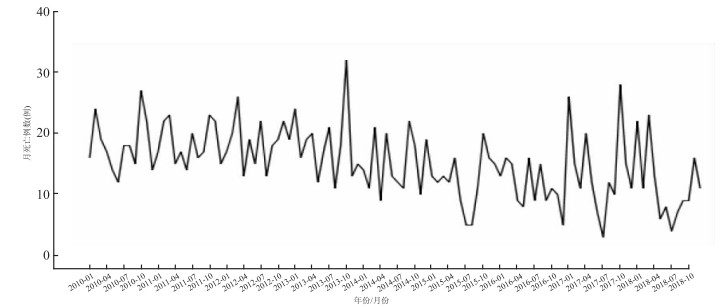
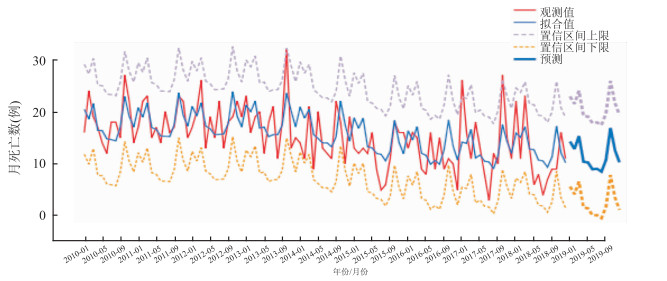
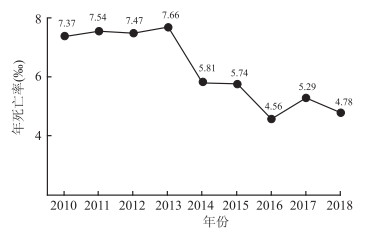
目的 分析2010-2018年兰州市5岁以下儿童死亡情况,构建时间序列模型预测2019年兰州市5岁以下儿童死亡趋势。 方法 采用描述流行病学方法综合分析兰州市2010年1月-2018年12月5岁以下儿童死亡情况,利用SPSS 21.0软件构建时间序列分析模型,筛选最佳模型并预测2019年兰州市5岁以下儿童死亡情况。 结果 兰州市2010-2018年共报告5岁以下儿童死亡病例1 650例,男、女报告死亡例数分别为871例和774例,年均死亡率为6.23‰。近几年兰州市5岁以下儿童死亡率总体呈下降趋势;5岁以下儿童死亡以新生儿为主,占65.27%;通过不同模型比较发现简单季节性指数平滑模型为最优模型,该模型较好的拟合了兰州市2010-2018年5岁以下儿童月死亡例数,预测2019年兰州市5岁以下儿童总死亡例数为140例,与2018年的死亡例数相近。 结论 兰州市5岁以下儿童死亡率总体呈逐年下降趋势,简单季节性指数平滑模型可以较好的反映兰州市5岁以下儿童的死亡趋势并进行短期预测。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the death trend of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou and establish the time series model to predict the mortality and incidence of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou in 2019. Methods Descriptive epidemiological method was used to analyze the mortality of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou from January 2010 to December 2018. SPSS 21.0 software was used to construct time series analysis model, selecting the best model and predict the mortality of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou in 2019. Results A total of 1 650 deaths of children under 5 years old were reported in Lanzhou from 2010 to 2018. The number of deaths reported by boys and girls was 871 and 774 respectively, with an average annual mortality rate of 6.23‰. In recent years, the overall mortality rate of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou had declined. The majority of deaths among children under 5 years old were neonates, accounting for 65.27%. Simple seasonal model was the best model by comparing different models. The model could well fit the monthly death cases of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou from 2010 to 2018. It is predicted that the total number of deaths of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou will be 140 in 2019, which is similar to the number of deaths in 2018. Conclusions The mortality rate of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou is decreasing year by year. Simple seasonal model can better reflect the mortality trend of children under 5 years old in Lanzhou and make short-term prediction. -
表 1 各模型拟合参数估计
Table 1. Estimation of fitting parameters for each model
模型类型 平稳R2 R2 RMSE MAPE 正态化BIC Box-Ljung Q统计量 P值 简单季节性 0.723 0.374 4.226 28.073 2.978 13.928 0.604 Winters加法 0.739 0.408 4.133 25.519 2.981 12.325 0.654 Winters乘法 0.712 0.362 4.289 26.444 3.055 12.280 0.658 SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(1, 1, 1)12 0.637 0.145 5.121 32.443 3.533 12.279 0.584 SARIMA(0, 0, 0)(0, 1, 1)12 0.274 0.169 4.928 32.176 3.295 12.924 0.741 表 2 各指数平滑模型参数设置
Table 2. Parameter settings of exponential smoothing models
模型类型 指标 估计值 sx t值 P值 简单季节性 Alpha (水平) 0.100 0.045 2.204 0.030 Delta (季节) 0.000 0.072 0.000 1.000 Winters加法 Alpha (水平) 0.005 0.011 0.480 0.632 Delta (季节) 0.000 0.083 0.000 1.000 Gamma (趋势) 0.000 0.086 0.000 1.000 Winters乘法 Alpha (水平) 0.001 0.010 0.057 0.954 Delta (季节) 0.088 0.067 1.320 0.190 Gamma (趋势) 0.001 0.641 0.002 0.999 表 3 兰州市2018年5岁以下儿童月死亡数实际值与预测值比较
Table 3. Comparison of actual and predicted monthly mortality of children under 5 years of age in Lanzhou in 2018
月份 实际死亡数 预测死亡数 95% CI值 相对误差(%) 1月 22 15 6~23 31.82 2月 11 15 6~23 36.36 3月 23 16 7~24 30.43 4月 13 12 3~20 7.69 5月 6 12 4~21 100.00 6月 8 11 2~19 37.50 7月 4 11 3~20 175.00 8月 7 10 2~19 42.86 9月 9 12 4~21 33.33 10月 9 19 11~28 111.11 11月 16 14 5~23 12.50 12月 11 12 3~21 9.09 -
[1] 胡波波, 傅克本, 胡碧波. 2013-2017年余姚市5岁以下儿童死亡分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(2): 176-179. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.02.011.Hu BB, Fu KB, Hu BB. Mortality analysis on children under 5 years old in Yuyao County from 2013 to 2017[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(2):176-179. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.02.011. [2] World Health Organization. Child health, under-five mortality rate[EB/OL]. (2018-04-15)[2019-05-15]. https://www.who.int/gho/child_health/mortality/mortality_under_five/en/ [3] Maternal and Child Department of National Health Commission. National maternal and child health monitoring and annual report newsletter[EB/OL]. (2019-04-15)[2019-05-15].
国家卫生健康委妇幼司. 全国妇幼卫生监测及年报通讯[EB/OL]. (2019-04-15)[2019-05-15]. Maternal and Child Department of National Health Commission. National maternal and child health monitoring and annual report newsletter[EB/OL]. (2019-04-15)[2019-05-15].[4] 张文彤, 董伟. SPSS统计分析高级教程[M]. 第3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2018.Zhang WT, Dong W. SPSS advanced course on statistical analysis[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2018. [5] Su Y, Gao W, Guan D, et al. Dynamic assessment and forecast of urban water ecological footprint based on exponential smoothing analysis[J]. J Clean Prod, 2018, 195: 354-364. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.184. [6] 孙振球, 徐勇勇. 医学统计学[M]. 第4版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014.Sun ZQ, Xu YY. Medical statistics[M]. 4rd ed. Beijing: People's Health Publishing House, 2014. [7] 唐广心, 张飞飞, 鲁苇葭, 等. 指数平滑法在麻疹发病率预测中的应用[J]. 实用预防医学, 2018, 25(6): 123-125. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2018.06.034.Tang GX, Zhang FF, Lu WJ, et al. Application of exponential smoothing method to forecasting the incidence rate of measles[J]. Pract Prev Med, 2018, 25(6): 123-125. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2018.06.034. [8] 王雅文, 沈忠周, 严宝湖. ARIMA模型和ARIMA-GRNN模型在AIDS发病预测中的应用[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(12): 1287-1290. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.020.Wang YW, Shen ZZ, Yan BH. Application of ARIMA and hybrid ARIMA-GRNN models in forecasting AIDS incidence in China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(12): 1287-1290. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.020. [9] He Z, Tao H. Epidemiology and ARIMA model of positive-rate of influenza viruses among children in Wuhan, China: a nine-year retrospective study[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2018, 74: 61-70. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.07.003. [10] 韩玲, 颜隆, 郝宇, 等. 山西省痢疾发病趋势的时间序列分析[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2018, 41(5): 413-417. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2018.05.010.Han L, Yan L, Hao Y, et al. Time series analysis on incidence trend of dysentery in Shanxi Province[J]. J Beijing Univ Chin Med, 2018, 41(5): 413-417. DOI:10.3969/j.issn. 1006-2157.2018.05.010. [11] 兰州市人民政府, 兰州市儿童发展规划(2011-2020年)[R]. 兰州, 2012.Lanzhou Municipal People's Government, Lanzhou Children's Development Plan (2011-2020)[R]. Lanzhou, 2012. [12] Ayoade MA. Spatio-temporal patterns of under 5 mortality in Nigeria[J]. SSM Popul Health, 2018, 6: 116-124. DOI: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2018.09.004. [13] 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018.National Bureau of Statistics. China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House, 2018. [14] 孙振高, 王天琪, 杨毅, 等. 年龄相关性生殖功能减退的卵泡液代谢组学研究[J]. 现代妇产科进展, 2018, 27(8): 561-565. DOI: 10.13283/j.cnki.xdfckjz.2018.08.001.Sun ZG, Wang TQ, Yang Y, et al. Study on the follicular fluid metabolomics of age-related reproductive dysfunction[J]. Current Adv Obstetr Gynecol, 2018, 27(8): 561-565. DOI: 10.13283/j.cnki.xdfckjz.2018.08.001. [15] 周建新, 阮焱. 3484例高龄孕妇妊娠结局分析[J]. 中国医刊, 2018, 53(9): 69-73. DOI:10.13283/j.cnki.xdfckjz.2018.08.001.Zhou JX, Ruan Y. Pregnancy outcome analysis of 3484 advanced maternal age[J]. Chin J Med, 2018, 53(9): 69-73. DOI: 10.13283/j.cnki.Xdfckjz.2018.08.001. [16] 罗波艳, 梁芳, 赵丽婷, 等. 兰州市2010-2014年5岁以下儿童死亡分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2016, 20(7): 683-686. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.07.010.Luo BY, Liang F, Zhao LT, et al. Mortality analysis on children under 5 years old in Lanzhou City from 2010 to 2014[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2016, 20(7): 683-686. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.07.010. [17] 中华人民共和国国务院. "健康中国2030"规划纲要[R]. 北京, 2016.The State Council of the People's Republic of China. Outline of "Healthy China 2030" program[R]. Beijing, 2016. 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王广俊,马燕,于宗君,尹莉. 肾图在中/高危急性淋巴细胞白血病儿童大剂量甲氨蝶呤化疗中的应用探析. 中国医药导刊. 2019(10): 579-582 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 马健娟,吴莎莎. 大剂量甲氨蝶呤治疗儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病的安全性与疗效研究. 当代医学. 2018(26): 57-59 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 彭九兰. 健康教育在儿童白血病甲氨蝶呤化疗期间的应用. 实用临床护理学电子杂志. 2018(40): 188+191 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 季妍. 大剂量甲氨蝶呤治疗儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病(ALL)延迟排泄的发生率分析. 海峡药学. 2018(09): 130-131 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 吴大海,刘鹏,卢远强,刘瑜,于涛. 大剂量甲氨蝶呤治疗儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病不良反应的效果分析. 北方药学. 2017(05): 157-158 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-





 下载:
下载: