Analysis of urine volume and dietary salt intake assessed by two 24 hours urine specimens
-
摘要:
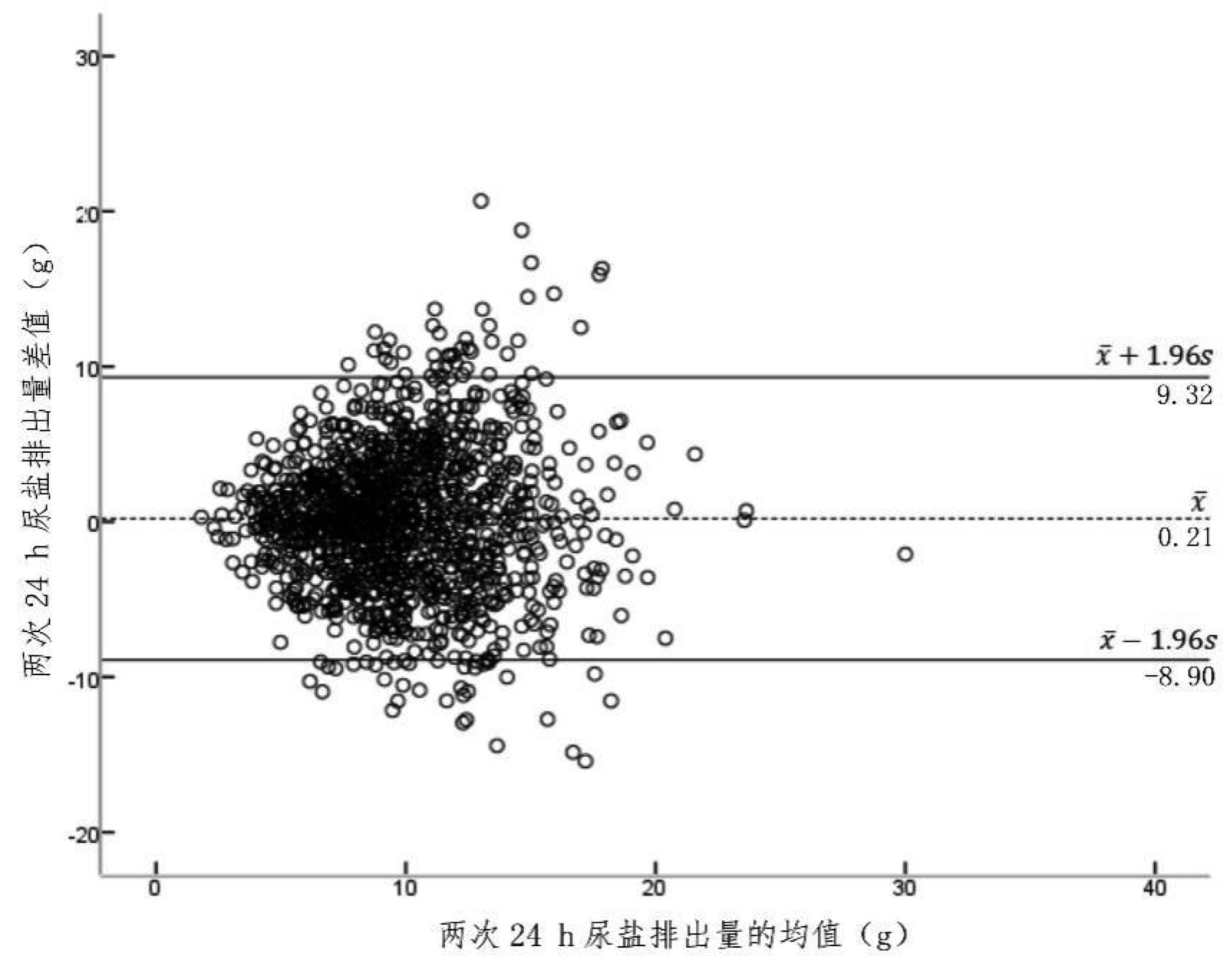
目的 分析两次24 h尿量和尿盐排出量, 探讨24 h尿用于评估群体和个体食盐摄入量的价值。 方法 于2013-2014年在山东省和江苏省4个项目县, 采用多阶段整群随机抽样的方法, 抽取18~69岁调查对象进行问卷调查并收集间隔1 d两次24 h尿液, 比较两次24 h尿量的差异, 从个体和群体两个层面分析两次24 h尿盐排出量的差异。 结果 1 288名研究对象年龄为(42.3±14.0)岁, 男性626名(48.6%)。24 h平均尿量为(1 462±437)ml, 第1次24 h尿量(1 427±488)ml低于第2次24 h尿量(1 498±552)ml(t=-4.439, P < 0.001)。调查对象每日食盐摄入量为(9.8±3.3)g, 男性每日食盐摄入量(10.1±3.5)g高于女性(9.5±3.1)g(t=3.09, P=0.002), 不同年龄组人群每日食盐摄入量差异有统计学意义(F=7.57, P < 0.001), 1 136名(88.2%)研究对象每日食盐摄入量高于推荐值。从个体层面比较, 调查对象两次24 h尿盐排出量绝对差异 < 1 g, 人数为279(21.7%), 而有48.5%的调查对象差异 > 3 g。从群体层面比较, 调查对象两次24 h尿盐排出量分别为(9.9±4.1)g和(9.7±4.0)g, 差异无统计学意义(P=0.102), 两次24 h尿盐排出量的组内相关系数为0.508(95% CI:0.451~0.559)。 结论 本研究结果提示24 h尿钠能较好评估人群食盐摄入量, 但不能准确反映个体食盐摄入量。 Abstract:Objective To analyze urine volume and dietary salt intake assessed by two 24 h urine specimens, to discuss its application value for evaluating population level and individual level dietary salt intake. Methods The subjects aged 18-69 years were selected from four counties in Shandong Province and Jiangsu Province from 2013 to 2014 by using multi-stage stratified cluster random sampling method. A questionnaire survey was conducted and two 24 h urine with an interval of one day were collected. The differences between two 24 h urine volume, and the dietary salt intake between two 24 h urine were assessed at individual level and population level. Results A total of 1 288 subjects was(42.3±14.0)years old, of which 626(48.6%) were males. The average urine volume of the subjects was(1 462±437) ml. The first 24 h urine volume(1 427±488) ml was lower than the second 24 h urine volume(1 498±552) ml(t=-4.439, P < 0.001). The dietary salt intake was(9.8±3.3) g, and the dietary salt intake of males(10.1±3.5) g was higher than that of females(9.5±3.1) g(t=3.09, P=0.002). There was a significant difference in dietary salt intake among different age groups(F=7.57, P < 0.001). The dietary salt intake of 1 136(88.2%) subjects was higher than the recommended level. At the individual level, the participants with the absolute difference with 1 g between the subjects' two 24 h urinary salt excretion was 279(21.7%), and the participants with the absolute difference with > 3 g was 48.5%. At the population level, the first 24 h urinary salt excretions(9.9 ± 4.1) g was similar to that in the second 24 h urine and(9.7±4.0) g(P=0.1021). The intraclass correlation coefficients between salt excretions in the two 24 h urine was 0.508(95% CI:0.451-0.559). Conclusion The results of this study suggest that 24 h urinary salt excretion can better assess the salt intake at population level, but cannot accurately reflect the individual's salt intake. -
Key words:
- Urine volume /
- Salt /
- 24 h urine
-
表 1 调查对象基本情况
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of participants
特征 例数 构成比(%) 性别 男 626 48.6 女 662 51.4 年龄(岁) 18~ 301 23.4 30~ 558 43.3 50~69 429 33.3 文化程度 小学及以下 486 37.7 初中 528 41.0 高中及以上 274 21.3 职业 农林牧渔劳动者 527 40.9 生产运输工人 211 16.4 家务人员 223 17.3 商业服务业人员 97 7.5 专业技术人员 64 5.0 其他 166 12.9 体重状况 正常 567 44.0 超重 480 37.3 肥胖 241 18.7 表 2 研究对象两次24 h尿量情况比较
Table 2. Comparison of two 24 h urine volume of participants
变量 平均尿量(ml) 第1次24 h尿量(ml) 第2次24 h尿量(ml) t值 P值 性别 男 1 504±468 1 470±522 1 538±597 -2.733 0.006 女 1 423±401 1 386±450 1 460±504 -3.627 < 0.001 年龄(岁) 18~ 1 328±353 1 325±418 1 330±432 -0.187 0.851 30~ 1 482±418 1 443±482 1 522±535 -3.186 0.002 50~69 1 531±491 1 478±530 1 584±622 -3.594 < 0.001 合计 1 462±437 1 427±488 1 498±552 -4.439 < 0.001 表 3 研究对象两次24 h尿盐排出量情况比较
Table 3. Comparison of two 24-hour urinary salt excretions of study subjects
变量 每日盐摄入量(g) 第1次24 h尿盐排出量(g) 第2次24 h尿盐排出量(g) t值 P值 性别 男 10.1±3.5 10.3±4.3 9.9±4.1 2.356 0.019 女 9.5±3.1 9.5±3.8 9.5±3.9 -0.024 0.980 年龄(岁) 18~ 10.4±3.4 10.6±4.2 10.1±4.1 1.963 0.051 30~ 9.8±3.3 9.9±4.1 9.7±4.1 1.284 0.200 50~69 9.4±3.2 9.4±3.9 9.5±3.9 -0.335 0.738 合计 9.8±3.3 9.9±4.1 9.7±4.0 1.636 0.102 -
Liu Y, Li H, Hong S, et al. Salt reduction and hypertension in China: a concise state-of-the-art review[J]. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther, 2015, 5(3): 191-196. DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-3652.2015.05.01. He FJ, Li J, Macgregor GA. Effect of longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials[J]. BMJ, 2013, 346: f1325. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f1325. Shao S, Hua Y, Yang Y, et al. Salt reduction in China: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Risk Manag Healthc Policy, 2017, 10: 17-28. DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S75918. McLean RM. Measuring population sodium intake: a review of methods[J]. Nrtrients, 2014, 6(11): 4651-4662. DOI: 10.3390/nu6114651. Lerchl K, Rakova N, Dahlmann A, et al. Agreement between 24-hour salt ingestion and sodium excretion in a controlled environment[J]. Hypertension, 2015, 66(4): 850-857. DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05851. Xu J, Chen X, Ge Z, et al. Associations of usual 24-Hour sodium and potassium intakes with blood pressure and risk of hypertension among adults in China's Shandong and Jiangsu Provinces[J]. Kidney Blood Press Res, 2017, 42(1): 188-200. DOI: 10.1159/000475486. 丁心悦, 于冬梅, 赵丽云. 24小时尿钠法评估食盐摄入量的应用与评价[J].卫生研究, 2018, 47(1): 156-159. DOI: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2018.01.038.Ding XY, Yu DM, Zhao LY. Application and evaluation of 24-hour urine sodium method for assessing salt intake[J]. J Hygiene Res, 2018, 47(1): 156-159. DOI: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2018.01.038. 唐俊利, 马冠生, 李剑虹, 等.山东省成年居民24 h尿量的调查分析[J].中国慢性病预防与控制, 2015, 23(11): 842-844. DOI: 10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1004-6194.2015.11.011.Tang JL, Ma GS, Li JH, et al. Analysis of 24 h urine volume of adult residents in Shandong Province[J]. Chin J Prev Contr Chron Dis, 2015, 23(11): 842-844. DOI: 10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1004-6194.2015.11.011. 夏玉婷, 尚莉, 何颖霞, 等.江苏省黄泛平原不同人群连续两日24 h尿量调查结果分析[J].中华地方病学杂志, 2016, 35(11): 830-833. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4255.2016.11.011.Xia YT, Shang L, He YX, et al. Results analysis of 24 h urine volume for two consecutive days in different populations in Huangfan plain of Jiangsu Province[J]. Chin J Endemiol, 2016, 35(11): 830-833. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4255.2016.11.011. Powles J, Fahimi S, Micha R, et al. Global, regional and national sodium intakes in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis of 24 h urinary sodium excretion and dietary surveys worldwide[J]. BMJ Open, 2013, 3(12): e003733. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003733. 李玉青, 刘秀荣, 刘枫, 等.北京市居民食盐摄入水平现况调查[J].中国健康教育, 2008, 24(5): 345-346. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9982.2008.05.022.Li YQ, Liu XR, Liu F, et al. The level of common salt of Beijing residents[J]. Chin J Health Education, 2008, 24(5): 345-346. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9982.2008.05.022. Zhang JY, Yan LX, Tang JL, et al. Estimating daily salt intake based on 24 h urinary sodium excretion in adults aged 18-69 years in Shandong, China[J]. BMJ Open, 2014, 4(7): e005089. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005089. 国家卫生计生委疾病预防控制局.中国居民营养与慢性病状况报告(2015年)[M].北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016: 57-58.Disease Prevention and Control Bureau of National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. Report on Chinese Residents'Chronic Disease and Nutrition[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2016: 57-58. 颜流霞, 徐建伟, 张梅, 等. 2010年我国家庭人均自报食盐消费情况分析[J].中国健康教育, 2014, 30(5): 387-389. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2014.05.002.Yan LX, Xu JW, Zhang M, et al. Analysis on self-reported daily salt intake per capital ofresident households in China, 2010[J]. Chin J Health Education, 2014, 30(5): 387-389. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2014.05.002. 朱圣陶.日常摄入量估计方法研究进展[J].国外医学(卫生学分册), 2009, 36(1): 58-63.Zhu ST, Research progress on usual intake estimation methods[J]. Section of Hygiene, 2009, 36(1): 58-63. Mente A, Dagenais G, Wielgosz A, et al. Assessment of dietary sodium and potassium in Canadians using 24-hour urinary collection[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2016, 32(3): 319-326. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjca.2015.06.020. Murakami K, Sasaki S, Takahashi Y, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of published strategies using urinary creatinine to identify incomplete 24-h urine collection[J]. Nutrition, 2008, 24(1): 16-22. DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2007.09.001. -





 下载:
下载: