The prevalence and influencing factors of multiple chronic diseases in the elderly in Taiyuan
-
摘要:
目的 了解太原市老年人多重慢病患病现状及其影响因素,为提升老年人健康水平、优化慢性病防治和管理提供参考。 方法 采用多阶段整群随机抽样的方法,在山西省太原市抽取3 637名年龄≥60岁的老年人,进行面对面问卷调查。采用χ2检验进行组间比较、多分类Logistic回归分析模型分析影响因素。 结果 3 637名调查对象中,慢性病患病率为68.8%,多重慢病患病率为21.0%;常见的二元疾病组合为:高血压+糖尿病、高血压+冠心病、高血压+类风湿性关节炎;常见的三元疾病组合为:高血压+糖尿病+冠心病、高血压+糖尿病+类风湿性关节炎、高血压+糖尿病+眼病。高龄、常住地为农村、低强度体力活动、有家族病史、超重或肥胖、饮食不规律(均有P < 0.05)的老年人是多重慢病高发人群。 结论 60岁及以上老年人慢性病患病率较高,多重慢病患病情况不容乐观,应针对患病特点和危险因素采取综合性的干预措施。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the prevalence and influencing factors of multiple chronic diseases in the elderly in Taiyuan, so as to provide references for improving the health level of the elderly and optimizing the prevention and management of chronic diseases. Methods Using multi-stage cluster random sampling method, 3 637 elderly persons aged 60 years or older were selected from Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province for face-to-face questionnaire survey. Chi-square test was used for comparison between groups and multinomial Logistic regression model was used to analyze the influencing factors. Results Among the 3 637 respondents, the prevalence of chronic diseases was 68.8%, and the prevalence of multiple chronic diseases was 21.0%; common dual disease combinations are: hypertension + diabetes, hypertension + coronary heart disease, hypertension + rheumatoid; common three disease combinations are: hypertension + diabetes + coronary heart disease, hypertension + diabetes + rheumatoid, hypertension + diabetes + eye disease. The elderly, who live in rural areas, with a family history, overweight or obesity, and an irregular diet (all P < 0.05), have a high incidence of multiple chronic diseases. Conclusions The prevalence of chronic diseases in the elderly aged 60 and above is relatively high, and the prevalence of multiple chronic diseases is not optimistic. Comprehensive intervention measures should be taken according to the characteristics of the disease and risk factors. -
Key words:
- Elderly /
- Multiple chronic diseases /
- Influencing factors /
- Health management
-
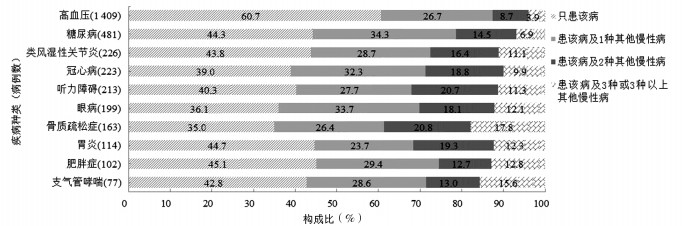
表 1 太原市不同性别老年人慢性病患病情况[n (%)]
Table 1. The prevalence of chronic diseases among the elderly of different genders in Taiyuan[n(%)]
慢性病种类 男 女 总计 患病人数 顺位 患病人数 顺位 患病人数 顺位 高血压 722(38.7) 1 687(38.7) 1 1 409(38.7) 1 糖尿病 227(12.2) 2 254(14.3) 2 481(13.2) 2 类风湿性关节炎a 88(4.7) 6 138(7.8) 3 226(6.2) 3 冠心病 128(6.9) 3 95(5.4) 7 223(6.1) 4 听力障碍 112(6.0) 4 101(5.7) 5 213(5.9) 5 眼病 90(4.8) 5 109(6.1) 4 199(5.5) 6 骨质疏松症b 65(3.5) 7 98(5.5) 6 163(4.5) 7 胃炎 54(2.9) 8 60(3.4) 8 114(3.1) 8 肥胖症b 41(2.3) 10 60(3.4) 8 102(2.8) 9 支气管哮喘 47(2.5) 9 30(1.7) 9 77(2.1) 10 注:表格中仅列出总患病率>2.00%的慢性病;a表示不同性别比较,P < 0.001;b表示不同性别比较,P < 0.05。 表 2 不同人口学资料分组的老年人多重慢病患病情况[n (%)]
Table 2. The prevalence of multiple chronic diseases in the elderly in different demographic data groups [n(%)]
变量 未患病(n=1 133) 单一慢性病(n=1 742) 多重慢病(n=762) χ2值 P值 性别 3.83 0.147 男 595(52.5) 902(51.8) 367(48.2) 女 538(47.5) 840(48.2) 395(51.8) 年龄(岁) 48.35 < 0.001 60~ 651(57.4) 844(48.5) 321(42.1) 70~ 362(32.0) 638(36.6) 315(41.3) ≥80 120(10.6) 260(14.9) 126(16.6) 婚姻状况 47.13 < 0.001 在婚 925(81.6) 1 410(80.9) 566(74.3) 未婚 36(3.2) 49(2.8) 20(2.6) 丧偶 147(13.0) 270(15.5) 172(22.6) 离异 25(2.2) 13(0.8) 4(0.5) 空巢情况 2.45 0.294 空巢 528(46.6) 837(48.0) 383(50.3) 非空巢 605(53.4) 905(52.0) 379(49.7) 文化程度 55.99 < 0.001 小学及以下 377(33.3) 634(36.4) 365(47.9) 初中 319(28.1) 507(29.1) 206(27.0) 高中 265(23.4) 384(22.0) 110(14.5) 大学及以上 172(15.2) 217(12.5) 81(10.6) 退休前职业 47.04 < 0.001 公务员 98(8.7) 150(8.6) 44(5.8) 企业及事业单位 459(40.5) 710(40.8) 264(34.6) 农民 280(24.7) 465(26.7) 286(37.5) 自由职业 247(21.8) 339(19.5) 130(17.1) 无业 49(4.3) 78(4.4) 38(5.0) 常住地 44.36 < 0.001 农村 396(35.0) 734(42.1) 383(50.3) 城市 737(65.0) 1 008(57.9) 379(49.7) 家庭人均月收入(元) 18.62 0.001 <1 000 154(13.6) 280(16.1) 148(19.4) 1 000~ 529(46.7) 773(44.4) 364(47.8) ≥3 000 450(39.7) 689(39.5) 250(32.8) 是否吸烟 0.31 0.856 是 286(25.2) 449(25.8) 201(26.4) 否 847(74.8) 1 293(74.2) 561(73.6) 是否饮酒 0.69 0.707 是 258(22.8) 374(21.5) 166(21.8) 否 875(77.2) 1 368(78.5) 596(78.2) BMI(kg/m2) 14.02 0.007 <18.5 89(7.9) 123(7.1) 53(7.0) 18.5~ 676(59.7) 986(56.6) 398(52.2) ≥24 368(32.4) 633(36.3) 311(40.8) 家族病史 107.71 < 0.001 无 1 114(98.3) 1 561(89.6) 654(85.8) 有 19(1.7) 181(10.4) 108(14.2) 体力活动强度 37.95 < 0.001 低 245(21.6) 429(24.6) 222(29.1) 中 435(38.4) 735(42.2) 335(44.0) 高 453(40.0) 578(33.2) 205(26.9) 注重饮食搭配 26.75 < 0.001 否 195(17.2) 317(18.2) 176(23.1) 一般 231(20.4) 375(21.5) 197(25.9) 是 707(62.4) 1 050(60.3) 389(51.0) 三餐规律 33.24 < 0.001 否 129(11.4) 207(11.9) 138(18.1) 一般 234(20.6) 417(23.9) 192(25.2) 是 770(68.0) 1 118(64.2) 432(56.7) 表 3 太原市老年人多重慢病的影响因素的多分类Logistic回归分析
Table 3. Multinomial Logistic regression analysis of influencing factors of multiple chronic diseases in the elderly in Taiyuan
变量 单一慢性病 多重慢性病 OR(95% CI)值 P值 OR(95% CI)值 P值 年龄(岁) 60~ 1.000 1.000 70~ 1.352(1.138~1.605) 0.001 1.728(1.393~2.143) < 0.001 ≥80 1.764(1.363~2.281) < 0.001 2.181(1.593~2.985) < 0.001 婚姻状况 在婚 1.000 1.000 未婚 0.833(0.519~1.337) 0.449 0.804(0.435~1.484) 0.485 丧偶 0.976(0.765~1.245) 0.844 1.399(1.057~1.853) 0.019 离异 0.268(0.130~0.551) < 0.001 0.201(0.066~0.611) 0.005 文化程度 大学及以上 1.000 1.000 小学及以下 1.264(0.946~1.689) 0.113 1.369(0.944~1.986) 0.980 初中 1.284(0.978~1.686) 0.072 1.126(0.787~1.609) 0.516 高中 1.083(0.829~1.416) 0.559 0.733(0.509~1.058) 0.097 退休前职业 无业 1.000 1.000 公务员 1.052(0.645~1.716) 0.839 0.846(0.451~1.586) 0.601 企业及事业单位 1.191(0.787~1.802) 0.408 1.284(0.770~2.139) 0.338 农民 0.951(0.635~1.424) 0.808 1.283(0.789~2.085) 1.283 自由职业 0.981(0.649~1.482) 0.926 0.934(0.561~1.555) 0.792 常住地 城市 1.000 1.000 农村 1.370(1.125~1.670) 0.002 1.458(1.140~1.863) 0.003 家庭人均月收入(元) ≥3 000 1.000 1.000 < 1 000 1.020(0.766~1.358) 0.893 0.944(0.667~1.336) 0.743 1 000~ 0.944(0.786~1.133) 0.537 1.060(0.838~1.341) 0.628 BMI(kg/m2) ≥24 1.000 1.000 18.5~ 0.870(0.737~1.027) 0.990 0.724(0.590~0.888) 0.002 <18.5 0.737(0.539~1.008) 0.560 0.539(0.363~0.802) 0.002 家族病史 无 1.000 1.000 有 7.389(4.543~12.091) < 0.001 11.329(6.794~18.893) < 0.001 体力活动强度 低 1.000 1.000 高 0.831(0.672~1.028) 0.088 0.649(0.497~0.848) 0.002 中 1.069(0.869~1.314) 0.528 1.044(0.815~1.338) 0.733 注重饮食搭配 是 1.000 1.000 否 0.960(0.769~1.199) 0.722 1.163(0.890~1.520) 0.268 一般 0.987(0.803~1.214) 0.904 1.244(0.967~1.601) 0.090 三餐规律 是 1.000 1.000 否 1.147(0.888~1.483) 0.294 1.840(1.369~2.474) < 0.001 一般 1.272(1.042~1.554) 0.018 1.385(1.080~1.776) 0.010 -
[1] Fortin M, Stewart M, Poitras ME, et al. A systematic review of prevalence studies onmultimorbidity: toward a more uniform methodology [J]. Ann Fam Med, 2012, 10(2):142-151. DOI: 10.1370/afm.1337. [2] Wang HH, Wang JJ, Wong SY, et al. Epidemiology of multimorbidity in China and implications for the healthcare system: cross-sectional survey among 162, 464 community household residents in southern China [J]. BMC Med, 2014, 12(1):188. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-014-0188-0. [3] 鲍欣雨, 谢易娴, 张晓霞, 等.多重慢病对社区居民健康相关生命质量的影响分析[J].中国卫生经济, 2019, 38(3):74-77. DOI: 10.7664/CHE20190320.Bao XY, Xie YX, Zhang XX, et al. Analysis on the effects of multimorbidity on health-related quality of life of community residents [J]. Chinese Health Economics, 2019, 38(3):74-77. DOI: 10.7664/CHE20190320. [4] 闫巍, 王杰萍, 张洪波, 等.老年共病患者在诊疗中面临的问题及应对策略[J].中国全科医学, 2018, 21(3):261-264. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2017.00.207.Yan W, Wang JP, Zhang HB, et al. Challenges and solutions for elderly patients with multimorbidity during receiving management in China [J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2018, 21(3):261-264. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2017.00.207. [5] 李洋.社区人群体力活动测量与促进[M].上海:复旦大学出版社, 2011:10-60, 114-117.Li Y. Measurement and promotion of community activities [M]. Shanghai: Fu Dan University Press, 2011:10-60, 114-117. [6] 樊萌语, 吕筠, 何平平.国际体力活动问卷中体力活动水平的计算方法[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2014, 35(8):961-964.Fan MY, Lv J, He PP. Chinese guidelines for data processing and analysis concerning the International Physical Activity Questionnaire [J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2014, 35(8):961-964. [7] 王晓波.国际体力活动长问卷在中国老年人群中应用的信度和效度[J].中国老年学杂志, 2015, 35(20):5912-5914. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2015.20.115.Wang XB. The reliability and validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire in the Chinese elderly [J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2015, 35(20):5912-5914. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2015.20.115. [8] 胡建平, 饶克勤, 钱军程, 等.中国慢性非传染性疾病经济负担研究[J].中国慢性病预防与控制, 2007, 15(3):189-193. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6194.2007.03.001.Hu JP, Rao KQ, Qian JC, et al. The study of economic burden of chronic non-communicable diseases in China [J]. Chin J Pre Contr Chron Non-commun Dis, 2007, 15(3):189-193. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6194.2007.03.001. [9] 国家卫生计生委统计信息中心. 2013年第五次国家卫生服务调查分析报告[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社, 2015.Center for Health Statistics and Information, NHFPC. An analysis report of national health service survey in China, 2013 [M]. Beijing: China Union Medical University Press, 2015. [10] 欧文森.社区多重慢病人群的健康现况及其社康服务管理评价——以深圳市某区为例[D].广州: 广州医科大学, 2018.Ou WS. Prevalence of multimorbidity among people with chronic diseases and evaluation of community health services in a district of Shenzhen city [D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Medical University, 2018. [11] 胡小兰.社区老年慢性病共病的现况调查[D].北京: 首都医科大学, 2015.Hu XL. Cross-sectional study of multimorbidity on chronic disease among the elderly in rural community [D]. Beijing: Capital Medical University, 2015. [12] 高杨, 平智广, 裴晓婷, 等. 2009年中国中老年人群慢性病共病现状及相关因素的多重对应分析[J].卫生研究, 2020, 49(5):844-849. DOI: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2020.05.026.Gao Y, Ping ZG, Pei XT, et al. Multi-correspondence analysis of the status and related factors of chronic diseases multimorbidity in middle-aged and elderly people in China in 2009 [J]. J Hygiene Res, 2020, 49(5):844-849. DOI: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2020.05.026. [13] Kearns K, Dee A, Fitzgerald AP, et al. Chronic disease burden associated with overweight and obesity in Ireland: the effects of a small BMI reduction at population level [J]. BMC Public Health, 2014, 14(1):143. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-143. [14] 李艳玲, 刘卫华, 白薇, 等.北京市某社区围绝经期骨量减少及骨质疏松症妇女干预效果观察[J].中华全科医师杂志, 2013(7):588-589. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2013.07.038.Li YL, Liu WH, Bai W, et al. Observation on the intervention effect of women with perimenopausal bone loss and osteoporosis in a community in Beijing [J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2013(7):588-589. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2013.07.038. [15] 吕宪玉, 刘淼, 李嘉琦, 等. 80岁以上高龄老年人主要慢性病的疾病谱调查与分析[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2016, 18(9):917-919. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2016.09.006.Lv XY, Liu M, Li JQ, et al. Spectrum of major chronic diseases in ≥80 years old people [J]. Chin J Geriatr Heart Brain Vessel Dis, 2016, 18(9):917-919. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2016.09.006. [16] Subramaniam M, Abdin E, Picco L, et al. Multiple chronic medical conditions: prevalenceand risk factors——results from the Singapore Mental Health Study [J]. Gen Hosp Psychiatry, 2014, 36(4):375-381. Doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2014.03.002. [17] Diouf I, Magliano DJ, Carrington MJ, et al. Prevalence, incidence, risk factors and treatment of atrial fibrillation in Australia: The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle (AusDiab) longitudinal, population cohort study [J]. Int J Cardiol, 2016, 205:127-132. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.12.013.Epub2015Dec15. [18] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Benefits of Physical Activity [EB/OL]. (2013-03-01) [2020-03-01]. http://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/everyone/health/index.html. [19] 薛雅卿, 张持晨, 赵慧宁, 等.基于结构方程模型的空巢老人抑郁现状及影响因素[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(10):1181-1185. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.10.005.Xue YQ, Zhang CC, Zhao HN, et al. Depression status and influencing factors of empty-nest elderly based on structural equation model [J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(10):1181-1185. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.10.005. [20] van Oostrom SH, Picavet HS, van Gelder BM, et al. Multimorbidity and comorbidity in the Dutch Population data from general practices [J]. BMC Public Health, 2012, 12(1):715. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-715. [21] Steinman MA, Lee SJ, John Boscardin W, et al. Patterns of multimorbidity in elderly veterans [J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2012, 60(10):1872-1880. DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.04158.x. [22] 游弋, 李宁, 吴明, 等.辽宁省城区居民主要慢性病流行现况及影响因素分析[J].预防医学, 2018, 30(1):35-40. DOI:10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2018.01.009.You Y, Li N, Wu M, et al. Prevalence and influencing factors of main chronic diseases among urban residents in Liaoning Province [J]. Prev Med, 2018, 30(1):35-40. DOI:10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087. 2018.01.009. DOI:10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2018.01.009. [23] 任仙龙, 胡冬梅, 王文娟, 等.关联规则在社区居民慢性病患病率分析中的应用[J].中国卫生统计, 2013, 30(6):818-820. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201306011.htmRen XL, Hu DM, Wang WJ, et al. Analysis of community residents with chronic disease using association rule mining [J]. Chin J Health Statistics, 2013, 30(6):818-820. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201306011.htm -





 下载:
下载: