Serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from children in Suzhou from 2017 to 2019
-
摘要:
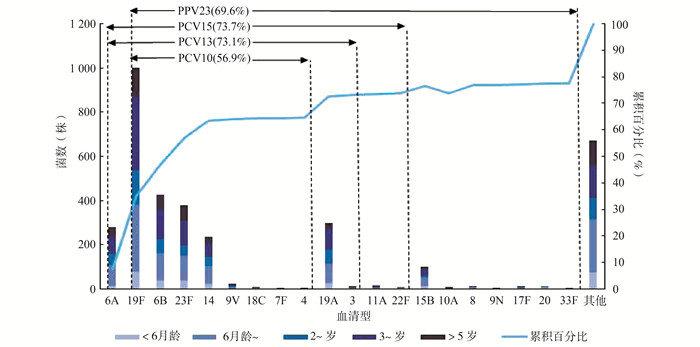
目的 了解苏州大学附属儿童医院呼吸道感染儿童肺炎链球菌菌株的血清型分布及耐药特征,为制定肺炎链球菌相关疾病的治疗和预防接种策略提供参考。 方法 采用乳胶凝集和荚膜肿胀试验对肺炎链球菌菌株进行血清分型,采用E-test法检测菌株对多种抗生素的耐药性。 结果 2017年1月-2019年7月共收集3 652株肺炎链球菌,主要来自于6月龄~2岁年龄段儿童,男女性别比为1.5:1。常见血清型为19F、6B、23F、19A及6A,13价肺炎球菌结合疫苗(13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, PCV13)的血清型覆盖率为73.1%(95% CI:71.6%~74.5%)。肺炎链球菌菌株对青霉素的耐药率为1.9%。青霉素不敏感肺炎链球菌(penicillin-non susceptible streptococcus pneumoniae, PNSP)(含中介和耐药菌株)对阿莫西林、红霉素、阿奇霉素等抗菌药物的耐药率高于青霉素敏感肺炎链球菌(penicillin-susceptible streptococcus pneumoniae, PSSP)菌株;PCV13疫苗血清型菌株的耐药率高于非疫苗血清型菌株。 结论 苏州地区儿童肺炎链球菌分离株PCV13疫苗血清型覆盖较高,且青霉素不敏感菌株大多为PCV13疫苗血清型。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumoniae) isolated from children with respiratory infectious diseases in Soochow University Affiliated Children's Hospital, so as to provide evidences for treatment and vaccination strategies of pneumococcal disease. Methods S. pneumoniae strains were serotyped by latex agglutination and quellung reactions, and were detected the susceptibility of multiple antibiotics with E-test method. Results From Jan 2017 to Jul 2019, a total of 3 652 pneumococci were collected. The strains were mainly isolated from 6-month to 2-year old children, with a male to female ratio of 1.5:1. The common serotypes were 19F, 6B, 23F, 19A and 6A, and the coverage of serotypes included in 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)was 73.1% (95% CI: 71.6%-74.5%). The penicillin resistance rate was 1.9%. Among the penicillin non-susceptible (PNSP) strains, the rates of resistant to amoxicillin, erythromycin and azithromycin were higher than those of the penicillin susceptible S. pneumoniae (PSSP) strains. The antibiotics resistance rate of strains included in PCV13 serotype was higher than that of the strains not covered by PCV13 vaccine serotype. Conclusions The coverage of PCV13 vaccine serotypes was high among the S. pneumoniae isolated from children in Suzhou, and most of the penicillin non-susceptible strains were covered by the PCV13 vaccine serotypes. -
Key words:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae /
- Serotype /
- Antimicrobial resistance /
- Children
-
表 1 2017—2019年苏州地区儿童肺炎链球菌菌株血清分型分布情况
Table 1. Serotype distribution of Streptococcus pneumoniae among children in Suzhou from 2017 to 2019
血清型 菌株数(株) 百分比(%) PCV10血清型 4 4 0.1 6B 425 11.6 7F 5 0.1 9V 23 0.6 14 236 6.5 18C 7 0.2 19F 1 000 27.4 23F 377 10.3 小计 2 077 56.9 PCV13添加血清型 3 14 0.4 19A 299 8.2 6A 279 7.6 小计 2 669 73.1 PCV15添加血清型 11A 15 0.4 22F 6 0.2 小计 2 690 73.7 PPV23添加血清型 10A 6 0.2 15B 101 2.8 17F 11 0.3 20 11 0.3 33F 1 0.0 8 10 0.3 9N 3 0.1 小计 2 554 69.9 非疫苗血清型 23A 148 4.1 6C 60 1.6 35F 55 1.5 15A 38 1.0 未分型 158 4.3 其他 639 17.5 合计 3 652 100.0 -
[1] Holl MJ, van den Bos EJ, et al. Burden of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in children in the era of conjugate vaccines: global, regional, and national estimates for 2000-15[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2018, 6(7):e744-e757. DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30247-X. [2] 中华医学会儿科学分会感染学组, 编辑委员会中华儿科杂志.儿童肺炎链球菌性疾病诊治与防控建议[J].中华儿科杂志, 2018, 56(8):564-570. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2018.08.002.Infectiology Group, Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association, Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Pediatrics. Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of Streptococcal pneumonia in children[J]. Chin J Pediatr, 2018, 56(8):564-570. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2018.08.002. [3] 中华预防医学会, 中华预防医学会疫苗与免疫分会.肺炎球菌性疾病免疫预防专家共识(2017版)[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(2):111-138. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.02.001.Chinese Preventive Medicine Association, Vaccine and Immunology Branch of Chinese Preventive Medicine Association. Expert consensus on immunization for prevention of pneumococcal disease in China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2018, 39(2):111-138. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.02.001. [4] Kyaw M, Lynfield R, Schaffner W, et al. Effect of introduction of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on drug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae[J]. N Engl J Med, 2006, 354(14):1455-1463. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa051642. [5] Mott MH, Caierão J, Rosa Da Cunha G, et al. Susceptibility profiles and correlation with pneumococcal serotypes soon after implementation of the 10-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Brazil[J]. Int J Infecti Dis, 2014, 20:47-51. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2013.11.009. [6] Ladhani SN, Collins S, Djennad A, et al. Rapid increase in non-vaccine serotypes causing invasive pneumococcal disease in England and Wales, 2000-17: a prospective national observational cohort study[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2018, 18(4):441-451. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30052-5. [7] Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). M100S. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility test; 26th informational supplement[S]. Wayne, PA: CLSI, 2018. [8] 陈凯乐, 邵雪君, 张锡彦, 等. 2013-2015年苏州地区儿童肺炎链球菌血清型与耐药监测[J].中国初级卫生保健, 2019, 33(8):106-109. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-568X.2019.08.0039Chen KL, Shao XJ, Zhang XY, et al. Surveillance on serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Streptococcus pneumonia in Suzhou from 2013 to 2015[J]. Chinese Primary Health Care, 2019, 33(8):106-109. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-568X.2019.08.0039 [9] Fu J, Yi R, Jiang Y, et al. Serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae causing invasive diseases in China: a meta-analysis[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2019, 19(1):424. DOI: 10.1186/s12887-019-1722-1. [10] 徐鑫鑫, 陈立凌, 田健美, 等. 2011-2018年苏州市住院儿童肺炎的常见病原分布及流行特征[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2020, 24(3):264-268. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.03.004Xu XX, Chen LL, Tian JM, et al. Analysis on distribution and epidemic characteristics of common pathogens of pneumonia among hospitalized children, Suzhou, 2011-2018[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2020, 24(3):264-268. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.03.004 [11] Zhao C, Li Z, Zhang F, et al. Serotype distribution and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates from 17 Chinese cities from 2011 to 2016[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2017, 17(1):804. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2880-0. [12] Shi W, Li J, Dong F, et al. Serotype distribution, antibiotic resistance pattern, and multilocus sequence types of invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in two tertiary pediatric hospitals in Beijing prior to PCV13 availability[J]. Expert Rev Vaccines, 2019, 18(1):89-94. DOI: 10.1080/14760584.2019.1557523. [13] Chen K, Zhang X, Shan W, et al. Serotype distribution of Streptococcus pneumoniae and potential impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2018, 14(6):1453-1463. DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1435224. [14] Lewnard JA, Hanage WP. Making sense of differences in pneumococcal serotype replacement[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2019, 19(6):e213-e220. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30660-1. [15] 胡付品, 郭燕, 朱德妹, 等. 2018年CHINET中国细菌耐药性监测[J].中国感染与化疗杂志, 2020, 20(1):1-10. DOI: 10.16718/j.1009-7708.2020.01.001.Hu FP, Guo Y, Zhu DS, et al. CHINET surveillance of bacterial resistance in China:2018 report[J]. Chin J Infect Chemother, 2020, 20(1):1-10. DOI: 10.16718/j.1009-7708.2020.01.001. [16] 吕志勇, 董方, 宋文琪, 等.儿童感染肺炎链球菌的血清型和耐药性分析[J].中国感染与化疗杂志, 2020, 20(4):417-422. DOI: 10.16718/j.1009-7708.2020.04.014Lv ZY, Dong F, Zhu WQ, et al. Analysis of the serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from children[J]. Chin J Infect Chemother, 2020, 20(4):417-422. DOI: 10.16718/j.1009-7708.2020.04.014 [17] 方潮, 陈学军, 周明明, 等. 2016年九家儿童医院肺炎链球菌感染的临床特征及分离株药物敏感性分析[J].中华儿科杂志, 2018, 56(8):582-586. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2018.08.005.Fang C, Chen XJ, Zhou MM, et al. Clinical characteristics and antimicrobial resistance of pneumococcal infections from 9 children's hospitals in 2016[J]. Chin J Pediatr, 2018, 56(8):582-586. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2018.08.005. [18] 杨晓华, 陈燕辉, 石冬梅, 等.儿童呼吸道标本肺炎链球菌的耐药性监测[J].中国感染与化疗杂志, 2018, 18(3):292-296. DOI: 10.16718/j.1009-7708.2018.03.009Yang XH, Chen YH, Shi DM, et al. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in the Streptococcus pneumoniae strains isolated from respiratory tract of children[J]. Chin J Infect Chemother, 2018, 18(3):292-296. DOI: 10.16718/j.1009-7708.2018.03.009 [19] Yao KH, Wang LB, Zhao GM, et al. Pneumococcal serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance in Chinese children hospitalized for pneumonia[J]. Vaccine, 2011, 29(12):2296-2301. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.01.027. [20] 陈素菜, 沈丽珍, 张颖, 等.温州地区青霉素不敏感肺炎链球菌临床分离株的血清分型及耐药性分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2019, 29(15):2247-2250. DOI: 10.11816/cn.ni.2019-186315Chen SC, Shen LZ, Zhang Y, et al. Serotyping and drug resistance analysis of clinical isolates of penicillin nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae in Wenzhou Area[J]. Chin J Nosocomil, 2019, 29(15):2247-2250. DOI: 10.11816/cn.ni.2019-186315 [21] Ubukata K, Takata M, Morozumi M, et al. Effects of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on genotypic penicillin resistance and serotype changes, Japan, 2010-2017[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2018, 24(11):2010-2020. DOI: 10.3201/eid2411.180326. -





 下载:
下载: