Application of multiple seasonal ARIMA model for predicting the incidence trend of tuberculosis in Guangzhou City
-
摘要:
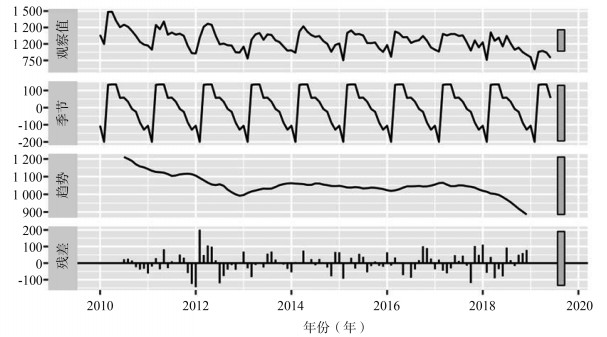
目的 探讨应用差分自回归移动平均(autoregressive intergrated moving average, ARIMA)乘积季节模型预测广州市肺结核月发病数的可行性,为制定防控措施提供参考依据。 方法 利用2010年1月至2019年6月广州市肺结核月发病数据建立ARIMA模型,并以2019年7-12月数据对模型的预测效果进行验证。 结果 2010-2019年广州市共报告肺结核124 311例,总体呈下降趋势。2月发病数最少,3-4月发病数最多。拟合出的最佳模型ARIMA (0, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12对广州市2019年7-12月肺结核月发病数预测结果显示实际值和预测值相对误差范围介于0.08%~11.33%,平均相对误差为1.46%。 结论 ARIMA (0, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12模型可用于广州市肺结核月发病数的短期预测。 -
关键词:
- 肺结核 /
- 差分自回归移动平均模型 /
- 时间序列 /
- 预测
Abstract:Objective To explore the feasibility of applying the multiple seasonal autoregressive intergrated moving average (ARIMA) model to predict the monthly incidence of tuberculosis in Guangzhou, and to provide evidence for developing prevention and control measures. Methods The ARIMA model was established based on the monthly incidence of tuberculosis in Guangzhou from January 2010 to June 2019, and the prediction effect of the model was verified with the data from July to December 2019. Results A total of 124 311 tuberculosis cases were reported during 2010-2019 in Guangzhou, showing an overall decreasing trend, with the lowest incidence in February and the hightest in March to April. Using the best fitted model ARIMA (0, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12 to predict the monthly incidence of tuberculosis in Guangzhou from July to December 2019, the results showed that the relative error between the actual value and predicted value ranged from 0.08% to 11.33%, and the average relative error was 1.46%. Conclusions The ARIMA (0, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12 model can be used for short-term prediction of the monthly incidence of tuberculosis in Guangzhou. -
Key words:
- Tuberculosis /
- ARIMA /
- Time series /
- Prediction
-
表 1 ARIMA(0, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12模型参数估计
Table 1. Parameters estimation of the ARIMA (0, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1)12 model
指标 参数估计 Ljung-Box残差检验 赤池信息准则值 β值 sx(β)值 统计量 P值 MA1 -0.656 0.085 19.514 0.552 1 178.540 SMA1 -0.692 0.100 表 2 2019年7-12月广州市肺结核发病数实际值与预测值比较
Table 2. Comparison between actual value and predicted value of the monthly number of tuberculosis cases in Guangzhou from July to December 2019
月份(月) 实际值(人) 预测值(95% CI值) 相对误差(%) 7 864 849.64(697.08~1002.19) 1.66 8 792 806.71(645.36~968.06) 1.86 9 734 744.50(574.82~914.19) 1.43 10 726 730.57(552.94~908.21) 0.63 11 698 698.59(513.35~883.83) 0.08 12 725 642.83(450.29~835.37) 11.33 -
[1] World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2019 [EB/OL]. (2019-10-17) [2020-2-15]. https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. [2] 言晨绮, 王瑞白, 刘海灿, 等. ARIMA模型预测2018-2019年我国肺结核发病趋势的应用[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2019, 40(6):633-637. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.06.006.Yan CQ, Wang RB, Liu HC, et al. Application of ARIMA model in predicting the incidence of tuberculosis in China from 2018 to 2019 [J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2019, 40(6):633-637. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.06.006. [3] 王燕.应用时间序列分析[M].北京:中国人民大学出版社, 2005.Wang Y. Applied time series analysis [M]. Beijing: Renmin University of China Press, 2005. [4] 杨仁东, 胡世雄, 邓志红, 等.湖南省手足口病发病趋势SARIMA模型预测[J].中国公共卫生, 2016, 32(1):48-52. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws2016-32-01-15.Yang RD, Hu SX, Deng ZH, et al. Predication of hand, foot and mouth disease incidence in Hunan Province using SARIMA model [J]. Chin J Public Health, 2016, 32(1):48-52. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws2016-32-01-15. [5] 孙振球, 徐勇勇.医学统计学[M].第2版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2006.Sun ZQ, Xu YY. Medical statistics [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2006. [6] Box GEP, Jenkins GM, Reinsel GC. Time series analysis: forecasting and control [M]. 4th ed. New Jersey: Wiley, 2008. [7] Hyndman R, Khandakar Y. Automatic time series forecasting: the forecast package for R [J]. J Stat Softw, 2008, 27(1):1-22. DOI: 10.18637/jss.v027.i03. [8] Liu Q, Li ZQ, Ji Y, et al. Forecasting the seasonality and trend of pulmonary tuberculosis in Jiangsu Province of China using advanced statistical time-series analyses [J]. Infect Drug Resist, 2019, 12:2311-2322. DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S207809. [9] Liao ZY, Zhang XN, Zhang YH, et al. Seasonality and trend forecasting of tuberculosis incidence in Chongqing, China [J]. Interdiscip Sci, 2019, 11(1):77-85. DOI: 10.1007/s12539-019-00318-x. [10] Ortblad KF, Salomon Joshua A, Bärnighausen Till, et al. Stopping tuberculosis: a biosocial model for sustainable development [J]. Lancet, 2015, 386(10010):2354-2362. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00324-4. [11] Reeves A, Basu S, McKee M, et al. Social protection and tuberculosis control in 21 European countries, 1995-2012: a cross-national statistical modelling analysis [J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2014, 14(11):1105-1112. DOI:https://doi.org/ 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70927-2. [12] 林玫, 崔哲哲, 林定文, 等.广西壮族自治区2010-2015年传染性肺结核时空特征分析[J].中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(9):1206-1211. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.09.013.Lin M, Cui ZZ, Lin DW, et al. Visual-spatial and temporal characteristics related to infectious tuberculosis epidemics in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 2012-2015 [J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(9):1206-1211. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.09.013. [13] 刘胜兰, 史宇晖, 申洋, 等.我国六省市流动人口结核病就诊意向分析[J].中国防痨杂志, 2018, 40(3):296-301. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6621.2018.03.016.Liu SL, Shi YH, Shen Y, et al. Analysis of the medical intention of TB and its influencing factors among floating population in six provinces in China [J]. Chin J Antituberc, 2018, 40(3):296-301. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6621.2018.03.016. [14] 李雪, 姜世闻, 高永鑫, 等.北京市流动人口肺结核患者确诊后未在首诊机构登记和治疗管理的原因分析[J].中国防痨杂志, 2017, 39(1):86-90. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6621.2017.01.019.Li X, Jiang SW, Gao YX, et al. Situation analysis on registration and treatment of migrant tuberculosis patients at tuberculosis dispensaries which initially confirmed diagnosis in Beijing [J]. Chin J Antituberc, 2017, 39(1):86-90. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6621.2017.01.019. [15] 魏珊, 陆一涵, 高眉扬, 等.中国主要法定报告传染病的"春节效应"研究[J].复旦学报(医学版), 2013, 40(2):153-158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2013.02.005.Wei S, Lu YH, Gao MY, et al. "Spring Festival effects" on the main notifiable communicable diseases in China [J]. Fudan Univ J Med Sci, 2013, 40(2):153-158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2013.02.005. [16] Li XX, Wang LX, Zhang J, et al. Exploration of ecological factors related to the spatial heterogeneity of tuberculosis prevalence in P. R. China [J]. Glob Health Action, 2014, 7:23620. DOI: 10.3402/gha.v7.23620. [17] 王晨, 郭倩, 周罗晶.基于R语言的ARIMA模型对流感样病例发病趋势的预测[J].中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(9):957-960. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.020.Wang C, Guo Q, Zhou LJ. Forecast of incidence trend of influenza-like illness by the ARIMA model based on R [J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(9):957-960. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.020. [18] 韩玲, 颜隆, 王鸿, 等. ARIMA乘积季节模型在天津市痢疾发病预测中的应用[J].中华中医药杂志, 2018, 33(7):2786-2789. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201807018.htmHan L, Yan L, Wang H, et al. Application of multiple seasonal ARIMA model on prediction of dysentery incidence in Tianjin [J]. Chin J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2018, 33(7):2786-2789. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201807018.htm -





 下载:
下载: