Development of a risk model for colon adenocarcinoma based on 3 methylation-regulated long non-coding RNA
-
摘要:
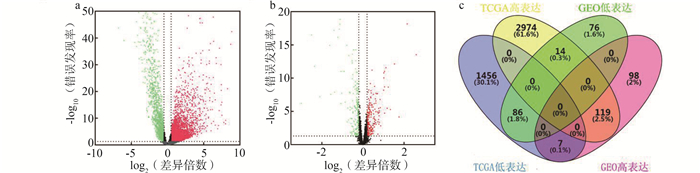
目的 本研究通过挖掘癌症基因组图谱(the cancer genome atlas, TCGA)数据库和基因表达公共数据库(gene expression omnibus, GEO),鉴定结肠腺癌(colon adenocarcinoma, COAD)中甲基化调控的长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA, lncRNA)并判断其预后价值。 方法 从TCGA数据库下载COAD患者的表达谱数据、DNA甲基化数据以及相应的临床数据。从GEO数据库下载GSE39582队列表达谱数据。使用R 4.0软件,通过“edgeR”和“limma”包筛选差异表达基因并通过Spearman秩次相关判断基因表达值和甲基化值的相关性。使用Cox回归模型构建风险模型。 结果 通过对TCGA和GEO数据库的联合分析,鉴定出23个甲基化调控的lncRNA。单因素Cox分析鉴定出4个甲基化调控的lncRNA(LINC00675、LINC01082、LINC01207和RP1-170O19.14)与COAD患者的总生存期(overall survival,OS)相关。采用逐步Cox回归分析构建风险模型,风险评分=(-0.148 19×表达量LINC01082)+(-0.120 50×表达量LINC01207)+(-0.120 46×表达量RP1-170O19.14)。 结论 本研究基于甲基化调控的lncRNA构建COAD患者的风险模型,可以促进对COAD患者OS的个体化预测。 Abstract:Objective The purpose of this study is to identify the methylation-regulated long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in patients with colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) and its prognostic value by mining the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) and gene expression omnibus (GEO). Methods Gene expression profile data, DNA methylation data and corresponding clinical data were obtained from the TCGA. The expression profile data of GSE39582 array was downloaded from the GEO. The edgeR and limma packages were used to screen differentially expressed genes. Spearman rank correlation was used to determine the correlation between gene expression values and methylation values. Cox regression model was used to construct risk model. Results Through joint analysis of TCGA and GEO databases, 23 methylation-regulated lncRNA were identified. Univariate Cox analysis identified 4 methylation-regulated lncRNA (LINC00675, LINC01082, LINC01207, and RP1-170O19.14) associated with overall survival (OS) in COAD patients. A risk model was constructed based on stepwise Cox regression analysis, risk score=(-0.148 19×expression valueLINC01082)+(-0.120 50×expression valueLINC01207)+(-0.120 46×expression valueRP1-170O19.14). Conclusion In this study, the risk model of COAD patients are constructed based on methylation-regulated lncRNA, which could promote the individual prediction of OS in COAD patients. -
Key words:
- Methylation /
- Colon adenocarcinoma /
- Risk model /
- Long non-coding RNA /
- TCGA
-
表 1 与COAD患者OS相关的四个甲基化调控的lncRNA
Table 1. Four methylation-regulated long noncoding RNA associated with OS of COAD patients
lncRNA HR(95% CI)值 P值 LINC00675 0.855(0.723~0.998) 0.047 LINC01082 0.824(0.694~0.978) 0.027 LINC01207 0.861(0.751~0.987) 0.031 RP1-170O19.14 0.842(0.721~0.983) 0.030 -
[1] Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492. [2] Islami F, Goding Sauer A, Miller KD, et al. Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(1): 31-54. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21440. [3] Li Y, He MZ, Zhou YY, et al. The prognostic and clinicopathological roles of PD-L1 expression in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 139. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00139. [4] Wang Y, He L, Du Y, et al. The long noncoding RNA lncTCF7 promotes self-renewal of human liver cancer stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2015, 16(4): 413-425. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.03.003. [5] Zhu YJ, Mao D, Gao W, et al. Peripheral whole blood lncRNA expression analysis in patients with eosinophilic asthma[J]. Medicine, 2018, 97(8): e9817. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009817. [6] Jones PA. Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2012, 13(7): 484-492. DOI: 10.1038/nrg3230. [7] Morgan AE, Davies TJ, Mc Auley MT. The role of DNA methylation in ageing and cancer[J]. Proc Nutr Soc, 2018, 77(4): 412-422. DOI: 10.1017/S0029665118000150. [8] Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019, 69(5): 363-385. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21565. [9] Mahna D, Puri S, Sharma S. DNA methylation signatures: Biomarkers of drug and alcohol abuse[J]. Mutat Res, 2018, 777: 19-28. DOI: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2018.06.002. [10] 钱伟明, 王海燕, 李可. 结肠癌组织RASGRF1蛋白表达与基因甲基化状态变化及其临床意义[J]. 山东医药, 2019, 59(19): 10-13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2019.19.003.Qian WM, Wang HY, Li K. Changes of RASGRF1 protein expression and gene methylation status in colon cancer tissues and their clinical significance[J]. Shandong Med J, 2019, 59(19): 10-13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2019.19.003. [11] Zheng RP, Gao D, He T, et al. Methylation of DIRAS1 promotes colorectal cancer progression and may serve as a marker for poor prognosis[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2017, 9: 50. DOI: 10.1186/s13148-017-0348-0. [12] Wang XY, Zhang DS, Zhang C, et al. Identification of epigenetic methylation-driven signature and risk loci associated with survival for colon cancer[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(6): 324. DOI: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.94. [13] Xiong W, Qin JY, Cai XY, et al. Overexpression LINC01082 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2019, 462(1-2): 33-40. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-019-03607-7. [14] Huang W, Liu Z, Li Y, et al. Identification of long noncoding RNAs biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis in patients with colon adenocarcinoma[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(3): 4121-4131. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.27697. [15] Chi DP, Zhang W, Jia YL, et al. LINC01207 predicts poor prognosis and suppresses cell growth and metastasis via regulating GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway in malignant glioma[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2020, 26: e923189. DOI: 10.12659/MSM.923189. [16] Wang SG, Qiu JG, Wang LP, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC01207 promotes prostate cancer progression by downregulating microRNA-1972 and upregulating LIM and SH3 protein 1[J]. IUBMB Life, 2020, 72(9): 1960-1975. DOI: 10.1002/iub.2327. [17] Zeng JH, Liang L, He RQ, et al. Comprehensive investigation of a novel differentially expressed lncRNA expression profile signature to assess the survival of patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(10): 16811-16828. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15161. [18] Ma SY, Deng XH, Yang Y, et al. The lncRNA LINC00675 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by affecting Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cervical cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 108: 1686-1693. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.011. [19] Yao MF, Shi XL, Li Y, et al. LINC00675 activates androgen receptor axis signaling pathway to promote castration-resistant prostate cancer progression[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(8): 638. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02856-5. [20] Liu X, Ke JW, Gu L, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00675 is associated with bladder cancer metastasis and patient survival[J]. J Gene Med, 2020, 22(9): e3210. DOI: 10.1002/jgm.3210. [21] Shan ZM, An N, Qin JL, et al. Long non-coding RNA Linc00675 suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer via acting on miR-942 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 101: 769-776. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.123. -





 下载:
下载: