Analysis of the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Zhongshan City from 2013 to 2018
-
摘要:
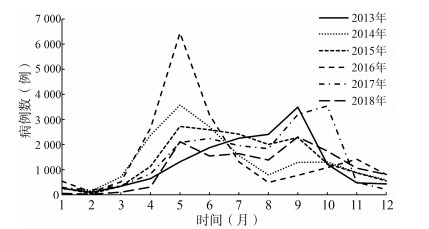
目的 分析2013―2018年中山市手足口病(hand-foot-and-mouth disease, HFMD)发病的时空聚集性,为防控工作提供理论依据。 方法 收集中山市2013―2018年HFMD流行病学数据,结合空间自相关分析与时空扫描实现时空聚集分析,并对分析结果进行可视化处理。 结果 2013―2018年中山市共报告HFMD病例97 214例,年均发病率为493.40/10万。发病人群主要为5岁及以下儿童,占发病总数的95.38%,时间上呈现双峰分布。空间自相关分析结果显示,2015―2016年HFMD发病存在空间正相关。逐年时空扫描结果显示,2013―2018年之间均存在高风险聚集区域,主要是位于中心城区西侧的市郊边缘乡镇,聚集时段与发病曲线变化趋势基本一致。 结论 2013―2018年中山市HFMD发病存在一定的时空聚集性,在春夏、夏秋交替之际聚集程度更高,今后的防控工作应有所侧重。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the temporal-spatial clustering of hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) in Zhongshan City from 2013 to 2018, so as to provide a theoretical basis for prevention and control of HFMD. Methods The epidemic data of HFMD in Zhongshan City from 2013 to 2018 was collected. Combining spatial autocorrelation analysis and spatial-temporal scanning to realize spatial-temporal analysis, and visualize the analysis results. Results A total of 97 214 cases of HFMD were reported in Zhongshan City from 2013 to 2018, with an average annual incidence of 493.40/100 000. Children aged 0-5 years old accounted for 95.38% of the total cases. The distribution over time was obviously bimodal. Spatial autocorrelation analysis results showed that there was an obvious positive spatial correlation in HFMD incidence from 2015 to 2016. High risk clusterings were detect by year-by-year time-space scanning from 2013 to 2018, mainly in the suburban border towns on the west side of the central city. The high-incidence aggregation period was basically consistent with the trend of the incidence curve. Conclusions A certain characteristic of spatiotemporal clustering is shown in the HFMD incidence in Zhongshan City from 2013 to 2018. The clustering degree is higher at the turn of spring and summer, summer and autumn. And future prevention and control work should be strengthen at that time.. -
表 1 2013―2018年中山市HFMD逐年时空扫描结果
Table 1. Result of spatial-temporal scanning analysis of HFMD in Zhongshan City from 2013 to 2018
项目 覆盖乡镇数[半径(km)] 聚集时间(月/日―月/日) 实际发病数(例) 期望发病数(例) LLR值 RR值 P值 2013年 Ⅰ类 5(10.99) 6/1―9/30 2 614 893 1 195.65 3.34 < 0.001 Ⅱ类 4(13.38) 5/1―9/30 2 678 1 056 968.98 2.87 < 0.001 2014年 Ⅰ类 2(11.77) 4/1―7/31 2 056 721 877.35 3.12 < 0.001 Ⅱ类 5(10.99) 4/1―6/30 2 026 727 833.02 3.04 < 0.001 2015年 Ⅰ类 5(24.32) 5/1―9/30 3 026 1 243 1 018.13 2.76 < 0.001 Ⅱ类 3(8.47) 5/1―9/30 2 109 1 286 242.68 1.73 < 0.001 2016年 Ⅰ类 4(10.78) 4/1―6/30 3 467 681 3 072.75 5.98 < 0.001 Ⅱ类 4(13.38) 4/1―6/30 2 612 808 1 351.32 3.58 < 0.001 2017年 Ⅰ类 2(11.77) 5/1―10/31 2 934 1 149 1 066.65 2.87 < 0.001 Ⅱ类 5(10.99) 5/1―10/31 3 370 1 571 879.04 2.42 < 0.001 Ⅱ-1类 4(8.97) 5/1―6/30 812 413 154.08 2.01 < 0.001 2018年 Ⅰ类 5(10.99) 5/1―10/31 2 919 1 193 1 016.77 2.86 < 0.001 Ⅱ类 4(8.47) 5/1―10/31 1 714 953 268.89 1.92 < 0.001 -
[1] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 手足口病诊疗指南(2018年版)[J]. 中国病毒病杂志, 2018, 8(5): 347-352. DOI: 10.16505/j.2095-0136.2018.0063.National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hand foot and mouth disease (2018 version)[J]. Chin J Viral Dis, 2018, 8(5): 347-352. DOI: 10.16505/j.2095-0136.2018.0063. [2] 胡跃华, 肖革新, 郭莹, 等. 2008-2011年中国大陆手足口病流行特征分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2014, 18(8): 693-697, 747. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201408001Hu YH, Xiao GX, Guo Y, et al. The epidemic features of the hand, foot, and mouth disease during 2008-2011 in China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2014, 18(8): 693-697, 747. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201408001 [3] 邓坤仪, 范汉恭, 黄桑, 等. 中山市2011-2015年儿童手足口病流行病学调查及分子病原学研究[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2017, 33(11): 1861-1864. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2017.11.037.Deng KY, Fan HG, Huang S, et al. Epidemiological investigation and molecular etiology of hand-foot-mouth disease of children in Zhongshan City from 2011 to 2015[J]. The J Pract Med, 2017, 33(11): 1861-1864. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2017.11.037. [4] Nguyen HX, Chu C, Nguyen HL T, et al. Temporal and spatial analysis of hand, foot, and mouth disease in relation to climate factors: a study in the Mekong Delta Region, Vietnam[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2017, 581-582: 766-772. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.006. [5] Gui J, Liu Z, Zhang T, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and spatial-temporal clusters of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Zhejiang Province, China, 2008-2012[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(9): e0139109. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139109. [6] 胡文穗, 刘伟, 侯建荣, 等. 2010-2019年广州市肺结核流行特征及时空聚集性[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2020, 24(9): 1037-1041. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.09.009.Hu WS, Liu W, Hou JR, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and temporal-spatial clustering analysis of tuberculosis in Guangzhou City from 2010 to 2019[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2020, 24(9): 1037-1041. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.09.009. [7] 张驰, 张旭彬, 姚丽君, 等. 2009-2018年汕头市手足口病流行特征与时空聚集性[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2020, 24(5): 573-578, 596. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.05.015.Zhang C, Zhang XB, Yao LJ, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and temporalspatial clustering analysis of hand, foot and mouth disease in Shantou City[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2020, 24(5): 573-578, 596. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.05.015. [8] Kulldorff M. A spatial scan statistic[J]. Communications in Statistics, 1997, 26(6): 1481-1496. DOI: 10.1080/03610929708831995. [9] 刘伟, 董智强, 胡文穗, 等. 2013-2017年广州市手足口病流行特征及时空聚集性分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2019, 46(14): 2526-2529, 2537.Liu W, Dong ZQ, Hu WS, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and temporal-spatial clustering analysis of hand-food-and-mouth disease in Guangzhou between 2013 and 2017[J]. Modern Prevent Med, 2019, 46(14): 2526-2529, 2537. [10] 李媛, 张振, 路滟, 等. 2008-2016年广东省深圳市手足口病流行病学及病原学特征分析[J]. 医学动物防制, 2019, 35(6): 536-539, 543. DOI: 10.7629/yxdwfz201906007.Li Y, Zhang Z, Lu Y, et al. Epidemiological and etiological characteristics of hand-foot-mouth disease in Shenzhen of Guangdong Province from 2008 to 2016[J]. J Med Pest Control, 2019, 35(6): 536-539, 543. DOI: 10.7629/yxdwfz201906007. [11] 朱琦, 郝元涛, 于石成. 广东省2008-2010年手足口病流行特征分析及时空聚集性研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2011, 38(10): 1824-1826, 1831.Zhu Q, Hao YT, Yu SC. Epidemiological characteristics and space-time analysis of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Guangdong Province from 2008 to 2010[J]. Modern Prevent Med, 2011, 38(10): 1824-1826, 1831. [12] 薛莉萍, 范慧, 郭静. 流动人口健康教育现状及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国健康教育, 2017, 33(9): 771-774, 796. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2017.09.001.Xue LP, Fan H, Guo J. Current situation of health education and its influencing factors among migrant population[J]. Chin J Health Education, 2017, 33(9): 771-774, 796. DOI: 10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2017.09.001. [13] 黄颖. 我国流动人口子女的教育总体特征[J]. 教育科学, 2015, 31(4): 14-25.Huang Y. The overall characteristics of education for children of floating population in China[J]. Education Science, 2015, 31(4): 14-25. [14] 李欣欣, 侯文平, 米卓, 等. 2012-2015年北京市大兴区手足口病时空聚集性分析[J]. 国际病毒学杂志, 2016, 23(5): 311-313. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4092.2016.05.007.Li XX, Hou WP, Mi Z, et al. Tempoarl and spatial clustering characteristic of hand-foot-mouth disease in Daxing, 2012-2015[J]. International Journal of Virology, 2016, 23(5): 311-313. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4092.2016.05.007. [15] Zhang Q, Zhou M, Yang Y, et al. Short-term effects of extreme meteorological factors on childhood hand, foot, and mouth disease reinfection in Hefei, China: a distributed lag non-linear analysis[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2019, 653: 839-848. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.349. [16] Chao S, Xun S, Yanchen B, et al. Exploring spatiotemporal nonstationary effects of climate factors on hand, foot, and mouth disease using Bayesian spatiotemporally varying coefficients (STVC) model in Sichuan, China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2019, 648: 550-560. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.114. [17] Xu M, Yu W, Tong S, et al. Non-linear association between exposure to ambient temperature and children's hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Beijing, China[J]. PloS one, 2015, 10 (5): e0126171. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126171. [18] 蔡韵, 蒋露芳, 史妍, 等. 介质表面的肠道病毒71型在不同气候条件下存活情况调查[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2012, 30(7): 398-401. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6680.2012.07.005.Cai Y, Jiang LF, Shi Y, et al. Survey on the enterovirus 71 survival ability on different surfaces under different climate[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2012, 30(7): 398-401. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6680.2012.07.005. -





 下载:
下载: