The epidemiological characteristics of rash and fever syndrome in Gansu Province from 2009 to 2019
-
摘要:
目的 了解2009―2019年甘肃省发热伴出疹症候群(rash and fever syndrome, RFS)的病原构成及季节流行性分布特征,为进一步疾病监测和科学防控提供参考。 方法 采用描述性流行病学方法分析2009―2019年甘肃省RFS病原构成及主要病原的季节性变化特征。 结果 甘肃省RFS病原构成以病毒为主,主要是肠道病毒(56.04%)、麻疹病毒(19.14%)、水痘-带状疱疹病毒(16.85%)和风疹病毒(7.33%);主要病原在不同年龄段、不同季节间的阳性率差异均有统计学意义(均有P<0.05)。肠道病毒在0~<5岁和5~<15岁组阳性率较高(χ2 =393.04, P<0.001),麻疹病毒在35~<50岁组阳性率最高(χ2 =150.13, P<0.001),风疹病毒在15~<35岁组阳性率最高(χ2 =327.89, P<0.001),而水痘-带状疱疹病毒在0~<5岁组最低(χ2 =221.53, P<0.001);冬季肠道病毒阳性率低于其他季节(χ2 =173.97, P<0.001);春季麻疹病毒(χ2 =164.46, P<0.001)和风疹病毒(χ2 =68.90, P<0.001)阳性率较高;而冬季水痘-带状疱疹病毒阳性率高于其他季节(χ2 =32.90, P<0.001)。 结论 2009―2019年甘肃省RFS病原构成以病毒为主,且主要病原具有明显的季节性特征,应对重点人群采取季节性针对性预防措施。 Abstract:Objective To understand the compositions of pathogens and seasonal distribution characteristics of rash and fever syndrome (RFS) in Gansu Province from 2009 to 2019, so as to provide references for further disease surveillance and scientific prevention and control. Methods Descriptive epidemiological methods were used to analyze the composition of pathogens of RFS in Gansu Province from 2009 to 2019 and the seasonal variation characteristics of the main pathogens. Results The compositions of pathogens of RFS in Gansu Province were dominated by viruses, mainly enterovirus (56.04%), measles virus (19.14%), varicella-zoster virus (16.85%) and rubella virus (7.33%). The differences of positive rate of the main pathogens in different age groups and different seasons were statistically significant (all P < 0.05). The positive rate of enterovirus was higher in the 0-year-old and 5-year-old groups (χ2 =393.04, P < 0.001). The positive rate of measles virus was the highest in the 35-year-old group (χ2 =150.13, P < 0.001). The positive rate of rubella virus was the highest in the 15-year-old group (χ2 =327.89, P < 0.001), while the varicella-zoster virus had the lowest positive rate in the 0-year-old group (χ2 =221.53, P < 0.001). The positive rate of enterovirus in winter was lower than those in other seasons (χ2 =173.97, P < 0.001). The positive rate of measles virus (χ2 =164.46, P < 0.001) and rubella virus (χ2 =68.90, P < 0.001) were higher in spring, and the positive rate of varicella-zoster virus in winter was higher than those in other seasons (χ2 =32.90, P < 0.001). Conclusions From 2009 to 2019, the compositions of pathogens of RFS in Gansu Province were mainly viruses and the main pathogens have obvious seasonal characteristics. Seasonal and targeted proventive methods should be adopted for high-risk populations. -
表 1 2009―2019年甘肃省RFS病例病原检出情况
Table 1. Pathogenic detection results of RFS cases in Gansu Province from 2009 to 2019
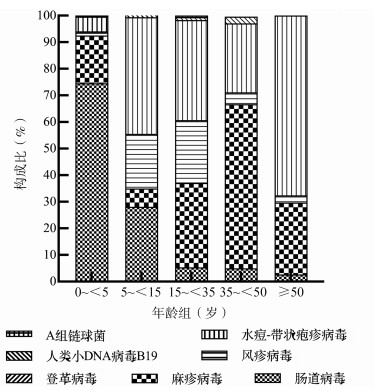
病原 阳性数(例) 检测数(例) 阳性率(%) 构成比(%) 肠道病毒 1 666 3 514 47.41 56.04 麻疹病毒 569 3 244 17.54 19.14 风疹病毒 218 3 206 6.80 7.33 水痘-带状疱疹病毒 501 1 877 26.69 16.85 人类小DNA病毒B19 15 1 154 1.30 0.50 登革病毒 2 808 0.25 0.07 A组链球菌 2 380 0.53 0.07 表 2 2009―2019年甘肃省主要病原分年龄组检出情况
Table 2. The detection results of main pathogens in different age groups in Gansu Province from 2009 to 2019
病原 年龄组(岁) χ2值 P值 0~<5 5~<15 15~<35 35~<50 ≥50 肠道病毒 2 430(57.41) a 756(32.28) a 270(8.15) 46(8.70) 39(2.56) 393.04 <0.001 麻疹病毒 1 617(21.77) 792(5.43) 557(20.29) 133(37.59) b 10(7.59) 150.13 <0.001 风疹病毒 1 591(1.76) 785(9.81) 553(19.53) c 132(3.03) 145(0.69) 327.89 <0.001 水痘-带状疱疹病毒 854(11.65) d 209(36.30) 311(44.69) 25(46.30) 27(51.92) 221.53 <0.001 注:检出情况以n(%)表示,n为检测数,%为阳性率; a经Bonferroni法校正,0~<5岁、5~<15岁组与其他年龄组两两比较均有P<0.05; b经Bonferroni法校正,35~<50岁组与其他年龄组两两比较均有P<0.05; c经Bonferroni法校正,15~<35岁组与其他年龄组两两比较均有P<0.05; d经Bonferroni法校正,0~<5岁组与其他年龄组两两比较有P<0.05。 表 3 2009―2019年甘肃省主要病原季节检出情况
Table 3. The detection results of main pathogens in different seasons in Gansu Province from 2009 to 2019
病原 季节 χ2值 P值 春季 夏季 秋季 冬季 肠道病毒 1 035(41.45) 1 437(58.73) 753(42.76) 316(22.47) a 173.97 <0.001 麻疹病毒 1 117(27.31) b 905(12.60) 627(4.63) 595(20.34) 164.46 <0.001 风疹病毒 1 094(11.06) c 897(7.02) 623(0.96) 592(4.73) 68.90 <0.001 水痘-带状疱疹病毒 504(27.78) 647(23.96) 405(20.49) 321(38.32) d 32.90 <0.001 注:检出情况以n(%)表示,n为检测数,(%)为阳性率; a经Bonferroni法校正,冬季肠道病毒阳性率与春、夏、秋季两两比较均有P<0.05; b经Bonferroni法校正,春季麻疹病毒阳性率与夏、秋、冬季两两比较均有P<0.05; c经Bonferroni法校正,春季风疹病毒阳性率与夏、秋、冬季两两比较均有P<0.05; d经Bonferroni法校正,冬季水痘-带状疱疹病毒阳性率与春、夏、秋季两两比较均有P<0.05。 -
[1] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 艾滋病和病毒性肝炎等重大传染病防治科技重大专项传染病监测技术平台项目: 发热伴出疹症候群监测实施方案[Z]. 北京: 中华人民共和国卫生部, 2008.Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. AIDS and viral hepatitis and other major infectious diseases prevention and control technology major special infectious disease monitoring technology platform project: implementation plan for monitoring fever with rash syndrome[Z]. Beijing: Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China, 2008. [2] 琚雄飞, 许岸高, 方巧云, 等. 2010—2012年广东省发热伴出疹症候群的病原学研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2013, 17(8): 670-673. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201308008Ju XF, Xu AG, Fang QY, et al. Etiology study on rash and fever illness in Guangdong Province, 2010-2012[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2013, 17(8): 670-673. http://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201308008 [3] 徐胜平. 九种发热伴出疹病原体基因芯片检测方法的建立[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2017.Xu SP. Development of a DNA-based microarray for detection of nine pathogens causing rash and fever illness[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2017. [4] 周广恩, 华华, 陈淑红, 等. 黑龙江省2015—2016年发热伴出疹症候群流行特征及病原学分析[J]. 中国公共卫生管理, 2020, 36(4): 544-546. DOI:10.19568/j.cnki.23-1318.2020.04.028.Zhou GE, Hua H, Chen SH, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and etiology analysis of fever with rash syndromes among residents in Heilongjiang Province, 2015-2016[J]. Chin J of PHM, 2020, 36(4): 544-546. DOI: 10.19568/j.cnki.23-1318.2020.04.028.j.cnki.23-1318.2020.04.028. [5] 费怡, 邓鹏飞, 杨天, 等. 2010―2017年上海市浦东新区发热伴出疹性疾病病原学分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2019, 23(5): 550-554. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.05.012.Fei Y, Deng PF, Yang T, et al. Study on the etiology of rash and fever illness in Pudong New Area of Shanghai from 2010 to 2017[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2019, 23(5): 550-554. DOI:10.16462 /j.cnki.zhjbkz.2019.05.012. [6] 邱琪, 柴志凯, 郜慧, 等. 2009—2015年中国山西省发热伴出疹症候群病毒性病原谱流行特征[J]. 病毒学报, 2017, 33(2): 169-175. DOI: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.003117.Qiu Q, Chai ZK, Gao H, et al. Viral pathogenic spectrum and epidemiological features of rash and fever syndrome in Shanxi Province, China, during 2009-2015[J]. Chin J Virol, 2017, 33(2): 169-175. DOI: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.003117. [7] 刘光远, 肖岩, 吴可亚. 2009-2015年营口市发热伴出疹症候群病原谱与流行特征研究[J]. 航空航天医学杂志, 2016, 27(8): 1028-1030. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1434.2016.08.055.Liu GY, Xiao Y, Wu KY. Subject study on the epidemiology and etiology of rash and fever illness in Yingkou City, 2009-2015[J]. Journal Aerospace Medicine, 2016, 27(8): 1028-1030. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1434.2016.08.055. [8] 沈月华, 纪蕾, 朱晓娟, 等. 2011年-2013年湖州市儿童手足口病病原学监测分析[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2015, 25(9): 1439-1441. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ201509051.htmShen YH, Ji L, Zhu XJ, et al. Etiological surveillance of children with hand foot and mouth disease in Huzhou City during 2011-2013[J]. Chin J Heal Lab Technol, 2015, 25(9): 1439-1441. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ201509051.htm [9] 尹志英, 来时明, 钟建跃, 等. 2006—2014年浙江省衢州市水痘疫情流行特征及水痘疫苗免疫效果分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2016, 31(4): 308-313. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2016.04.011.Yin ZY, Lai SM, Zhong JY, et al. Epidemiology of varicella and effect of varicella immunization in Quzhou, Zhejiang, 2006-2014[J]. Dis Surveillance, 2016, 31(4): 308-313. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2016.04.011. [10] Schröder C, Enders D, Schink T, et al. Incidence of herpes zoster amongst adults varies by severity of immunosuppression[J]. J Infect, 2017, 75(3): 207-215. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2017.06.010. [11] 张晓萌, 郝利新, 王华庆. 中国2005—2014年15~49岁人群麻疹流行病学特征分析[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2015, 21(3): 248-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201503004.htmZhang XM, Hao LX, Wang HQ. Epidemiological characteristics of measles among people 15 to 49 years of age in China, 2005-2014[J]. Chin J Vaccines Immun, 2015, 21(3): 248-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201503004.htm [12] 王琼, 邹翠容, 王林中, 等. 自然和人工免疫状况下母婴麻疹抗体水平研究[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2018, 24(6): 628-631, 641. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201806005.htmWang Q, Zou CR, Wang LZ, et al. Measles antibody levels of mothers and their infants under natural-infection and vaccine-induced immunity[J]. Chin J Vaccines Immun, 2018, 24(6): 628-631, 641. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201806005.htm [13] Coates SJ, Davis MDP, Andersen LK. Temperature and humidity affect the incidence of hand, foot, and mouth disease: a systematic review of the literature - a report from the International Society of Dermatology Climate Change Committee[J]. Int J Dermatol, 2019, 58(4): 388-399. DOI: 10.1111/ijd.14188. [14] 马超, 郝利新, 温宁, 等. 中国2019年麻疹流行病学特征[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2020, 26(5): 493-497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM202005002.htmMa C, Hao LX, Wen N, et al. Epidemiology of measles in China, 2019[J]. Chin J Vaccines Immun, 2020, 26(5): 493-497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM202005002.htm [15] 随海田, 李锦成, 王淼, 等. 2005―2015年中国水痘流行病学特征[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2019, 25(2): 155-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201902016.htmSui HT, Li JC, Wang M, et al. Varicella epidemiology in China, 2005-2015[J]. Chin J Vaccines Immun, 2019, 25(2): 155-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201902016.htm [16] World Health Organization. Rubella[EB/OL]. (2019-10-04)[2020-10-25]. https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact- sheets/detail/rubella. [17] 甘肃省卫生健康委员会. 关于做好学校风疹等传染病工作的通知[EB/OL]. (2019-06-19)[2020-10-25]. http://wsjk.gansu.gov.cn/single/10986/79205.html.Health Commission of Gansu Province. Notice on doing a good job in school rubella and other infectious diseases. [EB/OL]. (2019-06-19)[2020-10-25]. http://wsjk.gansu.gov.cn/single/10986/79205.html. -





 下载:
下载: