Association between maternal exposure to phosphate fertilizers during pregnancy and the risk of preterm birth
-
摘要:
目的 了解农村化肥施用量与早产发生风险的关系,为提高出生人口素质提供参考。 方法 利用山西省平定县2007年10月1日至2012年9月30日的出生人口监测数据,随访获得155例早产新生儿,从同时期出生、无任何体表缺陷、孕周≥37周、正常出生体重(2 500~4 000 g)的新生儿中,随机选择204例作为对照组。采用分层多因素Logistic回归分析模型和结构方程模型分析方法,探索早产发生风险与母亲孕期化肥暴露之间的关联及多种暴露因素对早产风险的贡献。 结果 分层多因素Logistic回归分析模型结果显示,调整混杂因素后,暴露于村级化肥施用量≥100 t的妇女早产发生风险大于村级化肥施用量<50 t的妇女(aOR=2.51, 95% CI:1.23~5.12);妇女家庭施用磷肥是早产发生的危险因素(aOR=2.54, 95% CI:1.23~5.22);结构方程模型检验发现,村级化肥施用量是对妇女早产发生风险贡献较大的环境因素。 结论 妇女孕期暴露于化肥,特别是磷肥与早产发生风险存在关联,建议农村妇女孕期尽量避免暴露于化肥施用环境。 Abstract:Objective To explore the association between consumption of chemical fertilizers and the risk of preterm birth, to provide references for improvement of birth outcomes. Methods Using the birth population monitoring data from October 1, 2007 to September 30, 2012 in Pingding County, Shanxi Province, 155 cases of preterm birth were followed up, and 204 newborns with normal birth weight (2 500~4 000 g) born at the same time without any surface defects and gestational age ≥37 weeks were randomly selected as the control group. Stratified multivariate Logistic regression model and structural equation model were used to investigate the associations between the risk of preterm birth and maternal exposure to chemical fertilizers during pregnancy. Results The results of the stratified multivariate Logistic regression analysis model showed that after adjusting for confounding factors, women exposed to village-level fertilizer application ≥100 t had a higher risk of preterm birth than women who had village-level fertilizer application < 50 t (aOR=2.51, 95% CI: 1.23-5.12). Household consumption of phosphorus fertilizer was a risk factor for premature birth (aOR=2.54, 95% CI: 1.23-5.22). The findings of structural equation model indicated that maternal exposure to phosphate fertilizer during pregnancy may be an important environmental factor for the risk of premature birth. Conclusions Women's exposure to chemical fertilizers during pregnancy, especially phosphate fertilizers, is associated with the risk of preterm birth, so it is recommended that rural women should try to avoid exposure to chemical fertilizers during pregnancy. -
Key words:
- Preterm birth /
- Chemical fertilizer /
- Phosphate /
- Pregnancy /
- Women /
- Association
-
表 1 山西省平定县早产新生儿组和健康新生儿组的人口学分布特征和暴露因素[n(%)]
Table 1. Demographic distribution characteristics and exposure factors of premature delivery case group and healthy control group in Pingding County, Shanxi Province [n(%)]
变量 早产新生儿组(n=155) 健康新生儿组(n=204) χ2值 P值 妇女年龄(岁) 9.974 0.007 <25 48(30.97) 83(40.69) 25~<30 33(21.29) 57(27.94) ≥30 74(47.74) 64(31.37) 妇女职业a 4.210 0.240 企事业 7(4.61) 7(3.48) 商业和服务业 20(13.16) 43(21.39) 农业和工业 56(36.84) 65(32.34) 家务或待业 69(45.39) 86(42.79) 妇女教育程度b 12.842 0.002 小学及以下 34(22.08) 18(8.87) 初中 93(60.39) 150(73.89) 高中及以上 27(17.53) 35(17.24) 产次(次)c 9.385 0.009 1 67(43.23) 103(50.74) 2 58(37.42) 83(40.89) ≥3 30(19.35) 17(8.37) 家庭年人均收入(元)d 8.852 0.031 <2 300 23(14.84) 38(18.72) 2 300~<5 000 55(35.48) 52(25.62) 5 000~<8 000 53(34.19) 60(29.56) ≥8 000 24(15.48) 53(26.11) 孕前BMI(kg/m2)e 3.184 0.204 <18.5 8(5.16) 10(4.93) 18.5~<24.0 86(55.48) 131(64.53) ≥24.0 61(39.35) 62(30.54) 孕期感染性疾病f 0.885 0.347 无 141(91.56) 192(94.12) 有 13(8.44) 12(5.88) 注:a早产新生儿组和健康新生儿组各有3例缺失;b早产新生儿组和健康新生儿组各有1例缺失;c、d、e健康新生儿组皆有1例缺失;f早产新生儿组有1例缺失。 表 2 山西省平定县早产新生儿组和健康新生儿组家庭及村级层面农业环境暴露因素[n(%)]
Table 2. Agricultural exposure factors at family and village level of premature delivery case group and healthy control groupin Pingding County, Shanxi Province [n(%)]
变量 早产新生儿组(n=155) 健康新生儿组(n=204) χ2值 P值 家庭层面 家庭耕地 4.611 0.100 无耕地 67(43.23) 107(52.45) 两亩及以内 35(22.58) 30(14.71) 两亩以上 53(34.19) 67(32.84) 家庭磷肥施用 8.334 0.004 无 122(78.71) 183(89.71) 有 33(21.29) 21(10.29) 家庭氮肥施用 0.460 0.498 无 138(89.03) 186(91.18) 有 17(10.97) 18(8.82) 家庭复合肥施用 0.691 0.406 无 107(69.03) 149(73.04) 有 48(30.97) 55(26.96) 村级层面 村用电量(万度) 0.753 0.386 <100 122(78.71) 168(82.35) ≥100 33(21.29) 36(17.65) 村级化肥施用量(t) 9.685 0.008 <50 71(45.81) 125(61.27) 50~<100 44(28.39) 48(23.53) ≥100 40(25.81) 31(15.20) 村级经济总收入(万元) 3.480 0.323 <2 500 45(29.03) 67(32.84) 2 500~<5 000 24(15.48) 43(21.08) 5 000~<10 000 39(25.16) 44(21.57) ≥10 000 47(30.32) 50(24.51) 村级粮食总产量(t) 6.660 0.036 <150 29(18.71) 56(27.45) 150~<500 69(44.52) 96(47.06) ≥500 57(36.77) 52(25.49) 表 3 早产发生风险与妇女农业环境暴露因素关联的分层多因素Logistic回归分析模型结果
Table 3. The results of stratified multivariate Logistic regression analysis model between the risk of preterm birth and agricultural environmental exposure factors
变量 cOR(95% CI)值a aOR(95% CI)值b 村级化肥施用量(t) <50 1.00 1.00 50~<100 1.61(0.98~2.67) 1.30(0.67~2.53) ≥100 2.27(1.31~3.95) 2.51(1.23~5.12) 家庭磷肥施用 无 1.00 1.00 有 2.34(1.30~4.24) 2.54(1.23~5.22) 注:a cOR即crude odds ratio, 粗比值比;b aOR即adjusted odds ratio, 调整比值比。 表 4 早产危险因素效应分析
Table 4. Effect analysis of risk factors for preterm birth
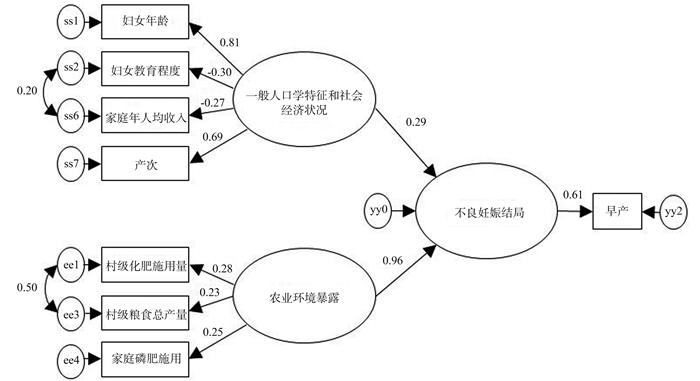
影响因素 因子载荷系数 总效应 效应排序 村级化肥施用量 0.275 0.263 1 妇女年龄 0.813 0.237 2 家庭磷肥施用 0.247 0.236 3 村级粮食总产量 0.227 0.217 4 产次 0.691 0.201 5 妇女教育程度 0.299 0.087 6 家庭年人均收入 0.274 0.080 7 -
[1] Beck S, Wojdyla D, Say L, et al. The worldwide incidence of preterm birth: a systematic review of maternal mortality and morbidity [J]. Bull World Health Organ, 2010, 88(1): 31-38. DOI: 10.2471/BLT.08.062554. [2] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 中国妇幼卫生事业发展报告[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国卫生部, 2011.Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. Report on the development of maternal and child health in China [R]. Beijing: Minister of Health of the People's Republic of China, 2011. [3] Rappazzo KM, Warren JL, Davalos AD, et al. Maternal residential exposure to specific agricultural pesticide active ingredients and birth defects in a 2003-2005 north Carolina birth cohort [J]. Birth Defects Res, 2019, 111(6): 312-323. DOI: 10.1002/bdr2.1448. [4] Magnus P, Jaakkola JJ, Skrondal A, et al. Water chlorination and birth defects [J]. Epidemiology, 1999, 10(5): 513-517. http://ir.cmu.edu.tw/handle/310903500/9989 [5] 陈晓辉. 中国种植业结构演变及其资源环境代价研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10019-1018065407.htmChen XH. Resource and environmental costs of cropping structure change in China [D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2018. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10019-1018065407.htm [6] 黄青青, 刘星, 张倩, 等. 磷肥中镉的环境风险及生物有效性分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(2): 156-161. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2016.02.029.Huang QQ, Liu X, Zhang Q, et al. Evaluating the environmental risk and the bioavailability of Cd in phosphorus fertilizers [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 39(2): 156-161. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2016.02.029. [7] 姚业峰. 基于田口方法的磷肥中三氯乙醛的检测方法及标准化研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10288-2010097745.htmYao YF. Study on measurement and standardization of chloral in phosphate based on Taguchi design [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10288-2010097745.htm [8] Bolognesi C, Bruzzone M, Ceppi M, et al. The lymphocyte cytokinesis block micronucleus test in human populations occupationally exposed to vinyl chloride: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Mutat Res, 2017, 774: 1-11. DOI: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2017.07.003. [9] 刘树堂, 赵永厚, 孙玉林, 等. 25年长期定位施肥对非石灰性潮土重金属状况的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(1): 164-167. DOI: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2005.01.041.Liu ST, Zhao YH, Sun YL, et al. Effects of 25 years long-term located fertilization on status of heavy metals in non-calcareous fluro-aquic soil [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2005, 19(1): 164-167. DOI: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2005.01.041. [10] 昝亚玲. 氮磷对旱地冬小麦产量、养分利用及籽粒矿质营养品质的影响[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10712-1013149926.htmZan YL. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer rate on yield, nutrient utilization and grain mineral nutrient quality of wheat in dryland [D]. Xianyang: Northwest Agriculture & Forest University, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10712-1013149926.htm [11] Thomas E, Omueti J. The effect of phosphate fertilizer on heavy metal in soils and Amaranthus caudatus [J]. Agric & Bio J of Nor Amer, 2012, 3(4): 145-149. DOI: 10.5251/abjna.2012.3.4.145.149. [12] 贾丽, 乔玉辉, 陈清, 等. 中国设施菜田土壤重金属含量特征与影响因素[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(2): 263-274. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1027.Jia L, Qiao YH, Chen Q, et al. Characteristics and affecting factors of heavy metals content in greenhouse vegetable soils in China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(2): 263-274. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1027. [13] Tumanyan AF, Shcherbakova NA, Tusaint F, et al. Heavy metal contents in soils and vegetables of southern Russia [J]. Chem Tech Fuels Oil, 2019, 54(6): 766-770. DOI: 10.1007/s10553-019-00985-y. [14] Yang J, Ma S, Zhou J, et al. Heavy metal contamination in soils and vegetables and health risk assessment of inhabitants in Daye, China [J]. J Int Med Res, 2018, 46(8): 3374-3387. DOI: 10.1177/0300060518758585. [15] 刘宁. 山西妇女经济地位的现状及提升对策——以第三期中国妇女社会地位调查山西省数据为蓝本[J]. 中共山西省委党校学报, 2013, 36(6): 91-93. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1203.2013.06.029.Liu N. The status quo of Shanxi women's economic status and the countermeasures to improve it-based on the data of Shanxi Province in the third survey of Chinese women's social status [J]. Journal of Shanxi Provincial Committee Party School of C.P. C, 2013, 36(6): 91-93. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1203.2013.06.029. -





 下载:
下载: