The mediating role of depression in the relationship between social engagement and cognitive function in older persons
-
摘要:
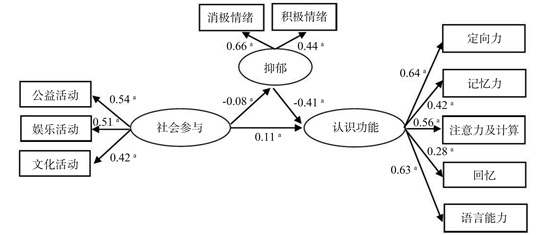
目的 分析抑郁在老年人社会参与和认知功能间的中介作用。 方法 基于2018年中国健康与养老追踪调查数据,筛选出符合标准的研究对象7 403人,采用结构方程模型分析抑郁在老年人社会参与和认知功能间的中介作用。 结果 患认知功能障碍的老年人有2 332(31.50%)人。社会参与和认知功能呈正相关(r=0.103, P < 0.001);社会参与和抑郁呈负相关(r=-0.050, P < 0.001);抑郁与认知功能呈负相关(r=-0.242, P < 0.001)。结构方程模型各项拟合指标结果显示:χ2=4.094,P < 0.001,渐进残差均方和平方根(root mean square error of approximation, RMSEA)=0.020,比较拟合指数(comparative fit index, CFI)=0.985,塔克-刘易斯指数(Tucker-Lewis Index, TLI)=0.979,增量拟合指数(incremental fit index, IFI)=0.985,模型拟合较好。社会参与对认知功能的直接效应为0.380(95% CI: 0.292~0.467),以抑郁为中介的间接效应为0.050(95% CI: 0.027~0.073)。 结论 社会参与与老年人认知功能正相关,抑郁与老年人认知功能负相关,抑郁在社会参与和认知功能关系中起部分中介作用。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the mediating effect of depression on the relationship between social engagement and cognitive function in older persons. Methods Based on data from the 2018 China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study, 7 403 participants were screened for meeting the criteria. Structural Equation Model was used to verify the mediating effect of depression on the relationship between social engagement and cognitive function in older persons. Results There were 2 332 (31.50%) subjects with cognitive dysfunction among older persons. Social engagement was positively correlated with cognitive function (r=0.103, P < 0.001), social engagement was negatively correlated with depression (r=-0.050, P < 0.001), and depression was negatively correlated with cognitive function (r=-0.242, P < 0.001). The results of each fitting index of structural equation model showed that: χ2=4.094, P < 0.001, root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA)=0.020, comparative fit index (CFI)=0.985, Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI)=0.979, incremental fit index (IFI)=0.985, indicated the model fits well. The direct effect of social engagement on cognitive function was 0.380 (95% CI: 0.292-0.467), the indirect effect mediated by depression was 0.050 (95% CI: 0.027-0.073). Conclusion Social engagement positively affects cognitive functioning in older persons, depression negatively affects cognitive functioning in older persons, and depression has a partly mediating effect on the relationship between social engagement and cognitive functioning. -
Key words:
- Cognitive function /
- Social engagement /
- Depression
-
表 1 研究对象认知功能的基本情况[n(%)]
Table 1. Basic information on the cognitive function of the participants [n(%)]
变量 n(%) (x±s) t/F值 P值 变量 n(%) (x±s) t值 P值 性别 16.188 < 0.001 饮酒状况 -11.454 < 0.001 男 4 131 (55.80) 23.14±4.20 无 4 753(64.20) 21.93±4.70 女 3 272 (44.20) 21.42±4.89 有 2 650(35.80) 23.19±4.29 年龄(岁) 7.189 < 0.001 吸烟状况 -3.882 < 0.001 ≤70 4 430 (59.84) 22.69±4.49 无 5 034(68.00) 22.24±4.70 > 70 2 973 (40.16) 21.91±4.72 有 2 369(32.00) 22.68±4.35 居住地 343.421 < 0.001 收入状况 -6.576 < 0.001 城市 1 739 (23.49) 24.49±3.97 无 6 287(84.93) 22.23±4.65 城镇 543 (7.33) 24.05±4.03 有 1 116(15.07) 23.21±4.22 农村 5 121 (69.17) 21.49±4.58 养老金 -1.036 0.300 教育程度 516.378 < 0.001 无 2 249(30.38) 22.30±4.46 小学以下 3 058 (41.31) 19.79±4.49 有 5 154(69.62) 22.42±4.66 小学 1 923 (25.98) 23.05±3.93 退休 -7.680 < 0.001 初中 1 491 (20.14) 24.64±3.39 否 4 022(54.33) 22.01±4.52 高中 795 (10.74) 25.81±2.89 是 3 381(45.67) 22.83±4.65 大专及以上 136 (1.84) 26.33±2.80 抑郁 18.893 < 0.001 婚姻状况 44.022 < 0.001 否 4 766(64.37) 23.11±4.42 已婚 5 875 (79.36) 22.65±4.52 是 2 637(35.62) 21.05±4.62 离异或分居 359 (4.85) 22.50±4.41 社会参与 -7.814 < 0.001 丧偶 1 133 (15.30) 21.00±4.79 无 3 498(47.25) 21.94±4.64 未婚 36 (0.49) 20.39±4.98 有 3 905(52.75) 22.77±4.53 表 2 老年人社会参与、抑郁与认知功能相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation analysis of social engagement, depression and cognitive function in older persons
变量 认知功能 社会参与 抑郁 认知功能 1.000 社会参与 0.103 a 1.000 抑郁 -0.242 a -0.050 a 1.000 注:a P < 0.001。 表 3 抑郁在老年人社会参与和认知功能之间中介效应的Bootstrap分析
Table 3. Bootstrap analysis of mediating effect of depression on social engagement and cognitive function in older persons
效应 效应值 Boot标准误 Boot 95% CI值 相对效应占比(%) 总效应 0.430 0.048 0.335~0.525 直接效应 0.380 0.045 0.292~0.467 88.37 间接效应 0.050 0.116 0.027~0.073 11.63 -
[1] 刘东祺, 李荣梅, 张美琪, 等. 沈阳市社区老年人认知功能障碍现状及影响因素分析[J]. 护理研究, 2020, 34(13): 2390-2393. DOI: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2020.13.027.Liu DQ, Li RM, Zhang MQ, et al. Status of cognitive dysfunction among the elderly in Shenyang communities and its influencing factors[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2020, 34(13): 2390-2393. DOI: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2020.13.027. [2] 聂晓璐, 吕晓珍, 卓琳, 等. 2001-2015年中国轻度认知功能障碍患病率的Meta分析[J]. 中华精神科杂志, 2016, 49(5): 298-306. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7884.2016.05.006.Nie XL, Lyu XZ, Zhuo L, et al. Prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in China: A meta-analysis of studies in 2001-2015[J]. Chin J Psychiatry, 2016, 49(5): 298-306. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7884.2016.05.006. [3] 张冲, 张丹. 城市老年人社会活动参与对其健康的影响: 基于CHARLS 2011年数据[J]. 人口与经济, 2016, (5): 55-63. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4149.2016.05.006.Zhang C, Zhang D. The Influences of social activities on urban elderly people's health: based on CHARLS 2011[J]. Popul Econ, 2016, (5): 55-63. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4149.2016.05.006. [4] 赵丹, 余林. 社会交往对老年人认知功能的影响[J]. 心理科学进展, 2016, 24(1): 46-54. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00046.Zhao D, Yu L. Influence of social interaction on cognitive functions in the elderly[J]. Adv Psychol Sci, 2016, 24(1): 46-54. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2016.00046. [5] Amagasa S, Fukushima N, Kikuchi H, et al. Types of social participation and psychological distress in Japanese older adults: a five-year cohort study[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): e0175392. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175392. [6] 马明娟, 樊春凯. 老年急性脑梗死患者认知功能障碍与焦虑、抑郁情绪的关系[J]. 国际精神病学杂志, 2020, 47(4): 749-753. DOI: 10.13479/j.cnki.jip.2020.04.031.Ma MJ, Fan CK. Correlation between cognitive dysfunction and anxiety/depression in elderly patients with acute cerebral infarction[J]. Journal of International Psychiatry, 2020, 47(4): 749-753. DOI: 10.13479/j.cnki.jip.2020.04.031. [7] 陈铭灵, 李为翊, 何丽华, 等. 体力活动与老年认知功能: 抑郁的中介作用[J]. 老年医学与保健, 2018, 24(2): 205-210. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8296.2018.02.032.Chen ML, Li WY, He LH, et al. Physical activity and cognitive function of the elderly: a mediating role of depression[J]. Geriatr Heal Care, 2018, 24(2): 205-210. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8296.2018.02.032. [8] Lam BCP, Haslam C, Steffens NK, et al. Longitudinal evidence for the effects of social group engagement on the cognitive and mental health of Chinese retirees[J]. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci, 2020, 75(10): 2142-2151. DOI: 10.1093/geronb/gbz134. [9] Folstein MF, Folstein SE, Mchugh PR. "Mini-mental state". A parctical method for g-arding the cognitive state of patients for clinician[J]. J Psychiatr Res, 1975, 12(3): 189-198. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [10] 李格, 沈漁邨, 陈昌惠, 等. 老年痴呆简易测试方法研究-MMSE在城市老年居民中的测试[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 1988, 2(1): 13-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXWS198801003.htmLi G, Shen YC, Chen CH, et al. Preliminary application of MMSE in the aged of urban population in Beijing[J]. Chin Ment Heal J, 1988, 2(1): 13-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXWS198801003.htm [11] Andresen EM, Malmgren JA, Carter WB, et al. Screening for depression in well olde-r adults: Evaluation of a short form of the CES-D[J]. Am J Prev Med, 1994, 10(2): 77-84. DOI: 10.1016/S0749-3797(18)30622-6. [12] Shiba K, Kondo N, Kondo K, et al. Retirement and mental health: dose social participation mitigate the association? A fixed-effects longitudinal analysis[J]. BMC Public Health, 2017, 17(1): 526. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-017-4427-0. [13] 任俊威, 王志中. 应对方式在老年心血管病患者依恋和健康赋权间的中介效应[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(S1): 95-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX2020S1028.htmRen JW, Wang ZZ. Mediating effect of medical coping style on the relationship between attachment and health empowerment among elderly patients of cardiovascular disease[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2020, 23(S1): 95-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX2020S1028.htm [14] 黄文, 李金, 陈奇峰. 老年人认知功能损害的影响因素分析[J]. 预防医学, 2020, 32(11): 1130-1133. DOI: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2020.11.011.Huang W, Li J, Chen QF. Influencing factors of cognitive impairment in the elderly[J]. Prev Med, 2020, 32(11): 1130-1133. DOI: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2020.11.011. [15] 李月, 陆杰华, 成前, 等. 我国老年人社会参与与抑郁的关系探究[J]. 人口与发展, 2020, 26(3): 86-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCRK202003008.htmLi Y, Lu JH, Cheng Q, et al. Association between social participation and depression among older adults in China[J]. Popul Dev, 2020, 26(3): 86-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCRK202003008.htm [16] Sibalija J, Savundranayagam MY, Orange JB, et al. Social support, social participation, & depression among caregivers and non-caregivers in Canada: A population health perspective[J]. Aging Ment Heal, 2020, 24(5): 765-773. DOI: 10.1080/13607863.2018.1544223. [17] 曾毅, 顾大男, Jama Purser, 等. 社会、经济与环境因素对老年健康和死亡的影响-基于中国22省份的抽样调查[J]. 中国卫生政策研究, 2014, 7(6): 53-62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2982.2014.06.010.Zeng Y, Gu DN, Jama P, et al. Associations of environmental factors with health and mortality among Chinese elderly: a sample survey in 22 provinces in China[J]. Chin J Heal Policy, 2014, 7(6): 53-62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2982.2014.06.010. [18] Butler M, McCreedy E, Nelson VA, et al. Does cognitive training prevent cognitive decline?: a systematic review[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2018, 168(1), 63-68. DOI: 10.7326/M17-1531. [19] Small GW, Moody TD, Siddarth P, et al. Your brain on google: Patterns of cerebral activation during internet searching[J]. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry, 2009, 17(2): 116-126. DOI: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e3181953a02. [20] 王珊珊. 个体老年期认知能力及其影响因素分析: 基于生物医学-心理-社会模式的分析框架[J]. 老龄科学研究, 2017, 5(6): 59-70. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5898.2017.06.007.Wang SS. Analysis the influencing factors of cognitive ability in the elderly-an analytical framework based on the biopsychosocial model[J]. Sci Res Aging, 2017, 5(6): 59-70. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5898.2017.06.007. [21] Mackie DM, Worth LT. Processing deficits and the mediation of positive affect in persuasion[J]. J Pers Soc Psychol, 1989, 57(1): 27-40. DOI: 10.1037//0022-3514.57.1.27. [22] 胡维明, 庞楠, 惠李, 等. 睡眠障碍、抑郁和焦虑情绪对医护人员认知功能的影响[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2019, 28(7): 586-591. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6554.2019.07.003.Hu WM, Pang N, Hui L, et al. Influence of sleep disturbance, depression and anxiety on cognitive function of medical staff[J]. Chin J Behav Med Brain Sci, 2019, 28(7): 586-591. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6554.2019.07.003. [23] 江雯红, 杨青梅, 闫桂虹. 2型糖尿病患者发生认知功能障碍危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理教育, 2019, 16(3): 165-172. DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.1672-9234.2019.03.001.Jiang WH, Yang QM, Yan GH. A meta-analysis of risk factors of cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Chin J Nurs Educ, 2019, 16(3): 165-172. DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.1672-9234.2019.03.001. -





 下载:
下载: