Study on the correlation between the incidence of human brucellosis and natural and social factors in Northwest China
-
摘要:
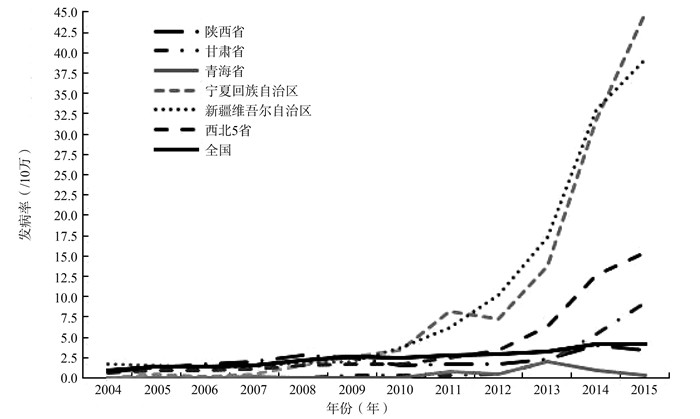
目的 描述西北地区布鲁氏菌病(简称布病)的流行特征,探索其发病率与自然和社会因素的相关性。 方法 收集全国2004—2015年布病监测数据、西北5省2004—2015年布病报告数据及自然和社会因素资料,描述布病的时间分布特征,采用主成分回归分析探索各因素对发病率的影响。 结果 2004—2015年间西北5省布病发病率逐年升高,且整体高于全国水平。每年5—8月为发病高峰。牧业总产值、地区生产总值、牛肉牛奶产量与布病发病率呈正相关,牛期末数量与布病发病率呈负相关。 结论 西北地区布病发生率较全国同期水平高,地区生产总值、牧业总产值、牛肉牛奶产量等社会因素对发病率有影响,春夏回暖季尽早防控,控制养殖规模,对于控制布病疫情具有重要意义。 Abstract:Objective To describe the epidemiology of Brucellosis in northwest China and to explore the association of incidence with natural and social factors. Methods The national surveillance data of brucellosis from 2004 to 2015, the report data of brucellosis from five Provinces in Northwest China from 2004 to 2015 and the data of natural and social factors were collected to describe the temporal distribution characteristics of brucellosis. The principal component regression analysis was used to explore the influence of various factors on the incidence of brucellosis. Results From 2004 to 2015, the incidence of brucellosis in northwest five Provinces increased year by year, and was higher than the national level. The incidence peak was from May to August every year. The total value of livestock production, regional GDP and the yield of beef and milk were positively correlated with the incidence of disease, while the number of cattle at the end of the period was negatively correlated with the incidence of disease. Conclusions The incidence of brucellosis in Northwest China is higher than that in the same period of the country. Social factors such as regional GDP, the total value of livestock production, beef and milk production have an impact on the incidence of brucellosis. Prevention and control of brucellosis as early as possible in spring and summer warm season and control of breeding scale are of great significance for the control of brucellosis epidemic. -
Key words:
- Brucellosis /
- Natural factors /
- Social factors /
- Correlation study
-
表 1 2004—2015年中国西北地区人间布病发病率与自然因素和社会因素相关分析
Table 1. Correlation analysis results of human brucellosis incidence and natural and social factors in Northwest China from 2004 to 2015
发病率影响因素 陕西省 甘肃省 宁夏回族自治区 青海省 新疆维吾尔自治区 r值 P值 r值 P值 r值 P值 r值 P值 r值 P值 平均气温(0.1 ℃) - - - - - - - - - 降水量(0.1 mm) - - - - 0.598 0.040 - - - - 平均风速(0.1 m/s) - - - - - - - - - - 牛期末数量(万头) - - - - 0.839 0.001 - - - - 牛肉产量(万吨) - - 0.713 0.009 0.807 0.002 - - 0.864 <0.001 牛奶产量(万吨) 0.641 0.025 - - 0.875 0.000 - - - - 牧业总产值(亿元) 0.592 0.042 0.807 0.002 0.806 0.002 0.688 0.013 0.878 <0.001 农业用水总量(亿立方米) 0.682 0.015 - - -0.646 0.023 - - 0.776 0.003 地区生产总值(亿元) 0.625 0.030 0.719 0.008 0.811 0.001 0.651 0.022 0.865 <0.001 表 2 中国西北地区2004—2015年布病发病率影响因素主成分提取结果
Table 2. Principal component extraction results of influencing factors of brucellosis incidence in Northwest China from 2004 to 2015
因子载荷 陕西省 甘肃省 青海省 宁夏回族自治区 新疆维吾尔自治区 成分1 牛期末数量-0.966牛肉产量0.926 牛肉产量0.951牛奶产量0.912 地区生产总值0.946牛奶产量0.942牧业总产值0.931 地区生产总值0.979牧业总产值0.977牛肉产量0.963牛奶产量0.961 地区生产总值0.957牧业总产值0.957牛肉产量0.926 成分2 平均风速-0.778降水量0.773 平均气温0.884平均风速0.865 平均风速0.912农业用水总量-0.934 平均气温0.863 牛奶产量0.856平均气温0.776平均风速0.748 成分3 - 农业用水总量0.881 牛肉产量0.864 - - 表 3 中国西北地区2004—2015年布病发病率与影响因素拟合模型
Table 3. Fitting model of brucellosis incidence and influencing factors in Northwest China from 2004 to 2015
地区 变量 β值 sx值 S(β)值 t值 R2 P值 陕西省 成分1 0.689 0.193 0.765 3.575 0.588 0.006 甘肃省 成分1 1.908 0.690 0.679 2.767 0.518 0.024 青海省 成分1 0.256 0.142 0.491 1.801 0.405 0.109 宁夏回族自治区 成分1 11.183 1.837 0.796 6.087 0.846 <0.001 新疆维吾尔自治区 成分1 11.991 1.514 0.921 7.917 0.878 <0.001 -
[1] 赵媛, 郭忠琴, 赵建华, 等. 2012—2016年宁夏人间布鲁菌病与自然环境因素的相关性[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2020, 24(4): 434-437, 443. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.04.013.Zhao Y, Guo ZQ, Zhao JH, et al. Correlation between human Brucellosis and natural environmental factors in Ningxia from 2012 to 2016[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2020, 24(4): 434-437, 443. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.04.013. [2] 刘维量, 寇增强, 陈保立, 等. 山东省2014-2016年布鲁氏菌病空间分布特征和空间自相关分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(9): 897-901. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.007.Liu WL, Kou ZQ, Chen BL, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and spatial autocorrelation analysis of Brucellosis in Shandong Province during 2014-2016[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(9): 897-901. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.09.007. [3] Alanazi A, Al Najjar S, Madkhali J, et al. Acute brucellosis with a guillain-barre syndrome-like presentation: a case report and literature review[J]. Infect Dis Rep, 2021, 13(1): 11-10. DOI: 10.3390/IDR13010001. [4] Zhai MM, Li WH, Tie P, et al. Research on the predictive effect of a combined model of ARIMA and neural networks on human brucellosis in Shanxi Province, China: a time series predictive analysis[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2021, 21(1): 280. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-05973-4. [5] 盛宗华. 浅析布鲁氏菌病疫情上升的原因与防控建议[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2014, 44(5): 49-50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2014.05.028.Sheng ZH. Analysis of the causes of brucellosis epidemic rise and suggestions for prevention and control[J]. Chin Qinghai J Animal Veterinary Sci, 2014, 44(5): 49-50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2014.05.028. [6] Ran XH, Cheng JJ, Wang MM, et al. Brucellosis seroprevalence in dairy cattle in China during 2008-2018: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Acta Tropica, 2019, 189: 117-123. DOI: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.10.002. [7] Ran XH, Chen XH, Wang MH, et al. Brucellosis seroprevalence in ovine and caprine flocks in China during 2000-2018: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Veterinary Research, 2018, 14(1): 393. DOI: 10.1186/s12917-018-1715-6. [8] Wang YB, Xu CJ, Zhang SK, et al. Temporal trends analysis of human brucellosis incidence in mainland China from 2004 to 2018[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 15901. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-33165-9. [9] 昝林森, 梁宏伟, 田万强, 等. 西北地区草食畜牧业发展现状及趋势[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2004, 25(2): 23-26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5190.2004.02.015.Zan LS, Liang HW, Tian WQ, et al. Present situation and trend of herbivorous animal husbandry in northwest China[J]. Animal Husb Feed Sci, 2004, 25(2): 23-26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5190.2004.02.015. [10] 朱岱, 张士义. 我国西部大开发地区布氏菌病现状分析[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2001, 16(1): 61-63. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1889.2001.01.031.Zhu D, Zhang SY. Analysis of brucellosis status in western developing region of China[J]. Chin J Control Endem Dis, 2001, 16(1): 61-63. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1889.2001.01.031. [11] 杨丽, 毕振旺, 寇增强, 等. 山东2005-2012年布鲁氏菌病流行病学特征[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2015, 31(1): 14-17. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws2015-31-01-05.Yang L, Bi ZW, Kou ZQ, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of Brucellosis in Shandong province from 2005 to 2012[J]. Chin J Public Heal, 2015, 31(1): 14-17. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws2015-31-01-05. [12] 李金萍, 徐雪华, 朱金宝, 等. 2012-2015年莱州市布鲁氏菌病流行特征和疾病负担分析[J]. 预防医学论坛, 2019, 25(3): 186-189. DOI: 10.16406/j.pmt.issn.1672-9153.2019.03.009.Li JP, Xu XH, Zhu JB, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and disease burden of Brucellosis in Laizhou City from 2012 to 2015[J]. Prev Med Trib, 2019, 25(3): 186-189. DOI: 10.16406/j.pmt.issn.1672-9153.2019.03.009. [13] 林代华, 肖方震, 韩腾伟, 等. 福建省2018-2019年人间布鲁氏菌病监测结果分析[J]. 海峡预防医学杂志, 2021, 27(1): 24-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYF202101011.htmLin DH, Xiao FZ, Han TW, et al. Analysis of human brucellosis surveillance results from 2018 to 2019 in Fujian Province[J]. Strait J Prev Med, 2021, 27(1): 24-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYF202101011.htm [14] 林代华, 韩腾伟, 肖方震, 等. 福建省2004-2018年人间布鲁氏菌病疫情特征及防控对策[J]. 海峡预防医学杂志, 2020, 26(2): 1-3, 30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYF202002001.htmLin DH, Han TW, Xiao FZ, et al. Characteristics and prevention and control measures of brucellosis in humans in Fujian Province from 2004 to 2018[J]. Strait J Prev Med, 2020, 26(2): 1-3, 30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYF202002001.htm [15] 孙英伟, 毛玲玲, 李鑫, 等. 辽宁省2001-2011年布鲁氏菌病流行特征分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2012, 23(3): 268-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMSK201203035.htmSun YW, Mao LL, Li X, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of Brucellosis in Liaoning Province from 2001 to 2011[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2012, 23(3): 268-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMSK201203035.htm [16] 康育慧, 崔咏梅, 曹文君. 2011-2017年我国人间布鲁氏菌病发病的长期趋势和季节性研究[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2018, 35(6): 895-897. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201806024.htmKang YH, Cui YM, Cao WJ. Long-term trend and seasonality of human brucellosis in China from 2011 to 2017[J]. Chin J Health Stat, 2018, 35(6): 895-897. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT201806024.htm [17] 邹明远, 邢智锋, 尹世辉, 等. 黑龙江省2010-2017年人间布鲁氏菌病流行特征及防控重点问题分析[J]. 中国公共卫生管理, 2018, 34(1): 71-73, 76. DOI: 10.19568/j.cnki.23-1318.2018.01.020.Zou MY, Xing ZF, Yin SH, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and key problems of brucellosis prevention and control in Heilongjiang Province from 2010 to 2017[J]. Chin J PHM, 2018, 34(1): 71-73, 76. DOI: 10.19568/j.cnki.23-1318.2018.01.020. [18] Zhao YQ, Li RD, Qiu J, et al. Prediction of Human Brucellosis in China Based on Temperature and NDVI[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2019, 16(21)4289. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16214289. [19] Dadar M, Shahali Y, Fakhri Y. A primary investigation of the relation between the incidence of brucellosis and climatic factors in Iran[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2020, 139: 103858. DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103858. [20] Cao LT, Liu HH, Li J, et al. Relationship of meteorological factors and human brucellosis in Hebei Province, China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2020, 703: 135491. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135491. [21] 王勋铭. 西北地区畜牧业经济发展战略研究[J]. 西北民族大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 1993, (1): 15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBMZ199301005.htmWang XM. Study on development Strategy of economy of animal husbandry in Northwest Region[J]. J Northwest Minzu Univ Philos Soc Sci Edition, 1993, (1): 15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBMZ199301005.htm [22] 李鹏媛, 陈盈, 吴迪迪, 等. 社会经济因素对布鲁氏菌病流行的影响[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2020, 20(4): 465-468. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3619.2020.04.010.Li PY, Chen Y, Wu DD, et al. Influence of socio-economic factors on brucellosis epidemic[J]. J Trop Med, 2020, 20(4): 465-468. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3619.2020.04.010. [23] 岑彩凤, 崔远圣. 人间布鲁氏菌病的常见传播途径与预防[J]. 当代畜禽养殖业, 2013, (10): 47-48. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5959.2013.10.004.Cen CF, Cui YS. Common transmission routes and prevention of human brucellosis[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry, 2013, (10): 47-48. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5959.2013.10.004. [24] 赵媛, 郭忠琴, 赵建华, 等. 宁夏回族自治区2012-2018年人间布鲁氏菌病发病时空分布及与家畜存栏数的相关性研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(6): 872-876. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20190925-00701.Zhao Y, Guo ZQ, Zhao JH, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution of brucellosis and its correlation with livestock population in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region from 2012 to 2018[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2020, 41(6): 872-876. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20190925-00701. -





 下载:
下载: