Evaluation of an item-specific physical activity scale for Chinese children and adolescents(I-PASCA)
-
摘要:
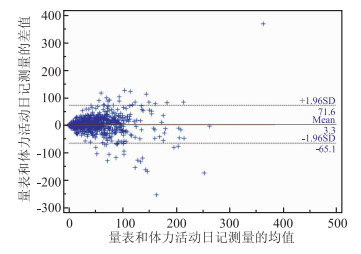
目的 评价我国儿童青少年专用体力活动量表的信效度,为在儿童及青少年人群中开展体力活动流行病学调查提供可靠的测量和评价工具。 方法 通过分层整群抽样,于2013年和2016年抽取南京市小学四年级至高中三年级的学生作为研究对象,采用体力活动日记和加速度计对量表进行信效度验证。依据中高强度体力活动时间,使用Cronbach α系数评价量表信度,采用Spearman相关系数和Bland-Altman图评价量表效度。 结果 使用体力活动日记进行验证的有效人数为815人,量表所测量的中高强度体力活动的Cronbach α系数为0.73,量表与体力活动日记测量值的相关系数为0.59。Bland-Altman一致性分析显示量表与体力活动日记对中高强度体力活动测量结果的一致性为95.8%。使用加速度计进行验证的有效人数为624人,Cronbach α系数分别为0.72,量表与加速度计测量值的相关系数为0.36。Bland-Altman分析显示量表与体力活动日记对中高强度体力活动测量结果的一致性为95.5%。 结论 该儿童青少年体力活动量表信效度良好,可用于人群水平的儿童青少年人群体力活动相关的流行病学研究。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the validity and reliability of an item-specific physical activity scale for Chinese children and adolescents(I-PASCA). Methods Students from Grade 4-12 in Nanjing were randomly selected using a multi-stage sampling approach, 7-days physical activity (PA) level was recorded by self-reported I-PASCA and PA log and were objectively measured with accelerometers. The total moderate and vigorous PA (MVPA) time was calculated. Cronbach α was calculated to estimate the reliability of I-PASCA. Pearson correlation coefficient and Bland-Altman were used to examine I-PASCA's validity. Results There were 815 students recruited in 2013 to evaluate the reliability and validity of I-PASCA using PA log. Cronbach α for I-PASCA was 0.73 regarding moderate and vigorous PA (MVPA). The Spearman correlation coefficients of the values of PA recorded by I-PASCA and PA log were 0.59 for MVPA, and the Bland-Altman coefficient was 95.8% for MVPA. 624 students were involved to examine the reliability and validity of I-PASCA using accelerometers. Cronbach α for I-PASCA was 0.72 regarding MVPA. The Spearman correlation coefficient was 0.36 for MVPA, while the Bland-Altman coefficient was 95.5% for MVPA. Conclusions The I-PASCA, the first physical activity questionnaire specific to Chinese children and adolescents, shows acceptable reliability and validity and can be used to evaluate Chinese students' physical activity level in population-based studies. -
Key words:
- Adolescents /
- Children /
- Physical activity /
- Scale /
- Reliability /
- Validity
-
表 1 儿童体力活动量表的效度
Table 1. Validity of an Item-specific Physical Activity Scale for Chinese Children and Adolescents(I-PASCA)
变量 MVPA P值 体力活动日记 总体效度系数 0.59 0.005 男生组效度系数 0.57 0.032 女生组效度系数 0.61 <0.001 加速度计 总体效度系数 0.36 <0.001 男生组效度系数 0.32 0.018 女生组效度系数 0.36 <0.001 表 2 量表与日记、加速度计测量绝对差值
Table 2. The absolute difference between I-PASCA to PA log and accelerometers
类别 差值(min/d) P值 I-PASCA量表与日记测量值 -3.26 0.021 I-PASCA量表与加速度计 16.50 <0.001 -
[1] US Department of Health and Human Services. Physical activity and health: A report of the Surgeon General[R]. Atlanta, GA, 1996, 20-144. DOI: 10.1067/mhc.2000.108190. [2] 何志文, 陈玮君. 对青少年学生体质健康状况下降的思考(之一)——青少年学生体质健康水平下降的原因调查[J]. 体育科技文献通报, 2008, 16(6): 13-16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0256.2008.06.006.He ZW, Chen WJ. Consideration on decline of physical fitness condition of junior students-investigation on the reasons for the decline of physical health level of adolescent students[J]. Bulletin Sport Science Technology, 2008, 16(6): 13-16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0256.2008.06.006. [3] Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC, et al. Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities[J]. Med Sci in Sports Exerc, 2000, 32(9): S498-504. DOI: 10.1249/00005768-199301000-00011. [4] Bland JM, Altman DG. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies[J]. Stat Methods Med Res, 1999, 8(2): 135-160. DOI: 10.1177/096228029900800204. [5] Wang Z, Xu F, Ye Q et al. Childhood obesity prevention through a community-based cluster randomized controlled physical activity intervention among schools in china: the health legacy project of the 2nd world summer youth olympic Games (YOG-Obesity study)[J]. Int J Obes (Lond), 2018, 42(4): 625-633. DOI: 10.1038/ijo.2017.243. [6] Cora L, Alison L, Marshall, et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity[J]. Med & Sci in Sports & Exerc, 2003, 35(18): 1381-1395. DOI: 10.1249/01.MSS.0000078923.96621.1. [7] Bull FC, Maslin TS, Armstrong T, et al. Global physical activity questionnaire(GPAQ): nine country reliability and validity study[J]. J Phys Act Health, 2009, 6(6): 790-804. DOI: 10.0000/PMID20101923 [8] 储文杰, 王志勇, 周海茸, 等. 儿童青少年体力活动量表的信度和效度分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2014, 18(11): 1079-1082. DOI:1674-3679(2014) 11-1079-04.Wang WJ, Wang ZY, Zhou HR, et al. The reliability and validity of a physical activity questionnaire in Chinese children[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2014, 18(11): 1079-1082. DOI:1674-3679(2014) 11-1079-04. [9] 李潮. 中国儿童青少年体力活动量表的信效度研究[J]. 健康教育与健康促进, 2017, 12(4): 296-299. DOI: 10.16117/j.cnki.31-1974/r.201704003.Li C. Study on Validity and Reliability of Chinese Children and Adolescent Physical Activity Questionnaire[J]. Health Education and Health Promotion, 2017, 12(4): 296-299. DOI: 10.16117/j.cnki.31-1974/r.201704003. [10] 刘爱玲, 马冠生, 张倩, 等. 小学生七天体力活动问卷信度和效度的评价[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2003, 24(10): 901-904. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2003.10.013.Liu AL, Ma GS, Zhang Q, et al. Reliability and validity of a 7-day physical activity questionnaire for elementary students[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2003, 24(10): 901-904. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2003.10.013. [11] 李海燕. 上海市青少年日常体力活动测量方法的研究与应用[D]. 上海: 上海体育学院, 2010.Li HY. Research and Application of the Measurement Method for Shanghai Adolescents Physical Activity[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Sport, 2010. [12] 黄雅君, 王香生. 香港小学生体力活动水平的评价: 问卷法的信度与效度研究[Z]. 第八届全国体育科学大会论文摘要汇编, 2007: 194.Hang YJ, Wang XS. Evaluation of Physical Activity on Hong Kong Primary School Students: Study on Validity and Reliability of Questionnaire[Z]. Summary of Papers of the Eighth National Congress of Sports Science, 2007: 194. [13] 陈卉. Bland-Altman分析在临床测量方法一致性评价中的应用[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2007, 24(3): 308-309. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3674.2007.03.029.Chen H. Apply of bland-altman in clinical measurement consistency evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal Health Statistics, 2007, 24(3): 308-309. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3674.2007.03.029. -





 下载:
下载: