Analysis on the epidemic status and the burden of intestinal infectious diseases in Jining city from 2009 to 2016
-
摘要:
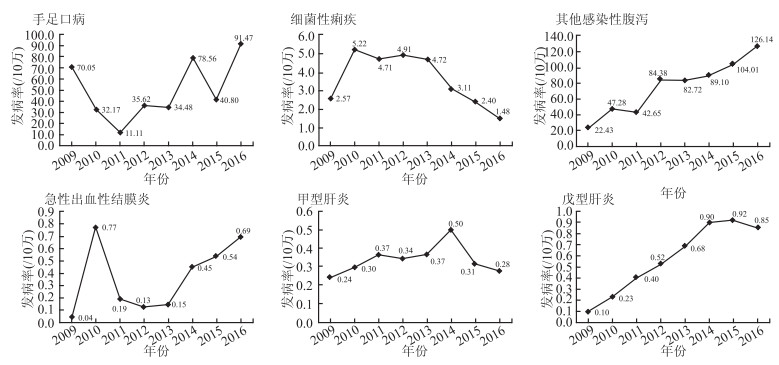
目的 对济宁市2009-2016年肠道传染病疾病负担进行分析,确定该地区的流行趋势和高危人群,为疾病防治提供依据。 方法 收集法定传染病上报系统济宁市2009-2016年肠道传染病资料,计算总体发病率、伤残生命年(years lived with disability,YLDs)和YLDs强度。 结果 2009-2016年济宁市肠道传染病年均发病率为128.81/10万,依次为其他感染性腹泻(74.74/10万)、手足口病(49.15/10万)、细菌性痢疾(3.65/10万)、戊型肝炎(0.57/10万)、急性出血性结膜炎(0.37/10万)和甲型肝炎(0.34/10万)。5~8月高发。总YLDs为593.04人年,男性372.31人年,女性220.73人年;依次为手足口病(326.88人年)、其他感染性腹泻(235.74人年)、戊型肝炎(10.65人年)、细菌性痢疾(10.09人年)、甲型肝炎(7.71人年)和急性出血性结膜炎(1.97人年),对应YLDs强度为0.489、0.353、0.016、0.015、0.012和0.003人年/10万。 结论 2009-2016年济宁市肠道传染病以手足口病和其他感染性腹泻为主,夏季高发,学龄前儿童和老年人是高发人群。提示疾病防控部门可根据人群和季节发病特点,采取措施加以防控。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the burden of intestinal infectious diseases in Jining city from 2009 to 2016, determine the epidemic trends and the high-risk groups in this area, so as to provide evidence for the prevention and control of intestinal infectious diseases. Methods The intestinal infectious diseases case information were collected from the Infectious Diseases Surveillance Information Reporting System. Based on these data, the incidence rate, the years lived with disability (YLDs) and the intensity of YLDs of intestinal infectious diseases was calculated. Results From 2009 to 2016, the annual incidence rate of intestinal infectious diseases in Jining city was 128.81/100 000, the annual incidence rate of subtype diseases in the descending order were other infectious diarrhea (74.74/100 000), hand-foot-and-mouth disease (49.15/100 000), bacillary dysentery (3.65/100 000), hepatitis E (0.57/100 000), acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (0.37/100 000) and hepatitis A (0.34/100 000). The highest incidence of intestinal infectious diseases was at May to August. The total YLDs caused by intestinal infectious diseases were 593.04 person-years, including 372.31 person-years for males and 220.73 person-years for females. The YLDs ranked in descending order were of hand-foot-mouth disease (326.88 person-years), other infectious diarrhea (235.74 person-years), hepatitis E (10.65 person-years), bacillary dysentery (10.09 person-years), hepatitis A (7.71 person-years), and acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (1.97 person-years), and the corresponding intensity of YLDs were 0.489, 0.353, 0.016, 0.015, 0.012, and 0.003 person-years/100 000, respectively. Conclusions The hand-foot-and-mouth disease and the other infectious diarrhea were the main intestinal infectious diseases subtypes prevailed in Jining city from 2009 to 2016, whose incidence was highest in the season of summer, and the preschool children and elderly people were the high-risk populations. According to its incidence characteristic, relevant government departments can take effective measures to prevent and control the intestinal infectious diseases in Jining city. -
表 1 济宁市2009-2016年不同性别肠道传染病发病率、YLDs及YLD强度
Table 1. Gender-specific incidence rate, YLDs and the intensity of YLDs of intestinal infectious diseases in Jining city from 2009 to 2016
年度(年) 男性 女性 合计 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 2009 119.71 44.79 1.046 69.62 23.98 0.595 95.43 68.77 0.827 2010 109.34 33.53 0.772 61.12 16.72 0.409 85.96 50.25 0.596 2011 72.74 19.48 0.446 45.28 10.58 0.258 59.42 30.07 0.355 2012 155.45 44.46 1.019 94.51 24.05 0.586 125.90 68.50 0.809 2013 142.67 39.43 0.933 102.34 25.01 0.629 123.12 64.44 0.785 2014 203.64 64.98 1.531 139.63 39.08 0.978 172.61 104.06 1.263 2015 164.04 46.06 1.078 132.98 32.33 0.803 148.98 78.39 0.945 2016 264.23 79.58 1.849 174.88 48.97 1.209 220.92 128.55 1.539 合计 153.74 372.31 1.082 102.32 220.73 0.682 128.81 593.04 0.888 表 2 济宁市2009-2016年不同年龄人群肠道传染病发病率、YLDs及YLD强度
Table 2. Age-specific incidence rate, YLDs and the intensity of YLDs of intestinal infectious diseases in Jining city from 2009 to 2016
年龄组(岁) 手足口病 细菌性痢疾 其他感染性腹泻 急性出血性结膜炎 甲型肝炎 戊型肝炎 合计 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 发病率(/10万) YLDs (人年) YLDs强度(人年/10万) 0~ 520.12 251.78 5.180 17.92 3.96 0.082 337.07 85.87 1.767 0.31 0.13 0.003 0.31 0.44 0.009 0.51 0.57 0.012 876.24 342.75 7.051 5~ 32.62 24.23 0.325 3.00 0.85 0.011 35.50 11.67 0.156 0.31 0.22 0.003 0.20 0.45 0.006 0.07 0.12 0.002 71.68 37.54 0.503 15~ 8.53 12.63 0.085 1.98 1.11 0.007 57.21 36.80 0.248 0.32 0.44 0.003 0.49 2.55 0.017 0.18 0.77 0.005 68.71 54.30 0.365 30~ 9.10 12.61 0.091 1.79 0.94 0.007 53.13 32.00 0.230 0.43 0.56 0.004 0.32 1.53 0.011 0.42 1.65 0.012 65.20 49.29 0.354 45~ 8.32 12.58 0.083 2.25 1.29 0.008 46.46 30.55 0.201 0.43 0.62 0.004 0.30 1.59 0.010 0.82 3.55 0.023 58.58 50.17 0.330 ≥60 12.48 13.06 0.124 4.34 1.94 0.018 75.49 38.85 0.370 0.34 0.34 0.003 0.30 1.13 0.011 1.34 4.00 0.038 94.30 59.32 0.565 合计 49.15 326.88 0.489 3.65 10.09 0.015 74.74 235.74 0.353 0.37 1.97 0.003 0.34 7.71 0.012 0.57 10.65 0.016 128.81 593.04 0.888 -
[1] 张洁, 钱序, 陈英耀. 疾病负担研究进展[J]. 中国卫生经济, 2005, 24(5): 69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0743.2005.05.025Zhang J, Qian X, Chen YY. Progress in disease burden researches[J]. Chinese Health Economics Magazine, 2005, 24(5): 69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0743.2005.05.025 [2] 方博, 靳文正, 宋桂香. 疾病负担研究进展[J]. 现代预防医学, 2009, 36(9): 1665-1668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF200909030.htmFang B, Jin WZ, Song GX. Progress in disease burden researches[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2009, 36(9): 1665-1668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF200909030.htm [3] The US burden of disease collaborators. The state of US health, 1990-2016: Burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors among US States[J]. JAMA, 2018, 319(14): 1444-1472. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.0158. [4] GBD causes of death collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980-2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390: 1151-1210. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9. [5] Sudhir Anand, Kara Hanson. Disability-adjusted life years: a critical review[J]. J Health Econ, 1997, 16: 685-702. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6296(97)00005-2 [6] 夏毅, 龚幼龙, 顾杏元, 等. 疾病负担的测量指标-DALY(一)[J]. 中国卫生统计, 1998, 15(3): 53-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT804.021.htmXia Y, Gong YL, Gu XY, et al. Index of disease burden-DALY (Ⅰ). Chin J Health Stati, 1998, 15(3): 53-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT804.021.htm [7] 夏毅, 龚幼龙, 顾杏元, 等. 疾病负担的测量指标-DALY(二)[J]. 中国卫生统计, 1998, 15(4): 56-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT804.021.htmXia Y, Gong YL, Gu XY, et al. Index of disease burden-DALY (Ⅱ). Chin J Health Stati, 1998, 15(3): 56-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT804.021.htm [8] 夏毅, 龚幼龙, 顾杏元, 等. 疾病负担的测量指标-DALY(三)[J]. 中国卫生统计, 1998, 15(5): 60-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT804.021.htmXia Y, Gong YL, Gu XY, et al. Index of disease burden-DALY (Ⅲ). Chin J Health Stati, 1998, 15(3): 60-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWT804.021.htm [9] Paalman M, Bekedam H, Hawken L, et al. A critical review of priority setting in the health sector: the methodology of the 1993 world development report[J]. Health Policy Plan, 1993, 13(1): 13-31. http://heapol.oxfordjournals.org/content/13/1/13.abstract [10] 马玉秀. 2006-2015年济南市槐荫区法定传染病流行趋势及预测分析[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2016.Ma YX. The analysis and predicting of trend of notifiable infectious diseases in Jinan Huaiyin district from 2006 to 2015[D]. Jinan: Shandong University. 2016. [11] 高风华, 冯谦谨, 江丽凤, 等. 中国大陆2002-2010年法定传染病疫情分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2013, 40(4): 756-759, 761. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF201304072.htmGao FH, Feng QJ, Jiang LF, et al. Analysis of legal infectious diseases epidemic situation from 2002 to 2010 in mainland China. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2013, 40(4): 756-759, 761. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF201304072.htm [12] 仲连发, 张志诚, 赵继军. 基于年龄结构的中国大陆手足口病流行特征的分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2015, 19(7): 651-654, 687. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2015.07.002.Zhong LF, Zhang ZC, Zhao JJ. Age-structured model and analysis of hand foot and mouth disease in China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2015, 19(7): 651-654, 687. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2015.07.002. [13] 王凌燕. 长春市2011-2015年手足口病疫情特征分析及趋势预测[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.Wang LY. Epidemiological characteristics and trend prediction of hand foot mouth disease in Changchun, 2011-2015[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. [14] 郭建欣, 张海艳, 徐文彩, 等. 2008-2013年北京市东城区细菌性痢疾流行病学特征[J]. 首都公共卫生, 2014, 8(3): 117-119. DOI: 10.16760/j.cnki.sdggws.2014.03.014.Guo JX, Zhang HY, Xu WC, et al. Epidemiological study of bacillary dysentery in Beijing Dongcheng district from 2008- 2013[J]. Capital Journal of Public Health, 2014, 8(3): 117-119. DOI: 10.16760/j.cnki.sdggws.2014.03.014. [15] 常昭瑞, 孙强正, 裴迎新, 等. 2012年中国大陆地区细菌性痢疾疫情特点与监测结果分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2014, 29(7): 528-532. DOI:10.3784/j.issn. 1003-9661.2014.07.006.Chang ZR, Sun QZ, Pei YX, et al. Surveillance for bacillary dysentery in China, 2012[J]. Disease Surveillance, 2014, 29(7): 528-532. DOI:10.3784/j.issn. 1003-9661.2014.07.006. [16] 徐也晴, 崔富强, 张国民, 等. 中国2007-2011年甲型和戊型病毒性肝炎以及细菌性痢疾流行病学特征分析[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2013, 19(6): 501-505. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201306006.htmXu YQ, Cui FQ, Zhang GM, et al. Epidemiological characteristic analysis of hepatitis A, hepatitis E, bacillary dysentery in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization, 2013, 19(6): 501-505. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJM201306006.htm [17] 白衫. 沈阳市2011-2016年病毒性肝炎流行特征分析[J]. 基层医学论坛, 2018, 22(11): 1549-1550. DOI: 10.19435/j.1672-1721.2018.11.074.Bai S. Epidemiological analysis of viral hepatitis in Shenyang 2011-2016[J]. The Medical Forum, 2018, 22(11): 1549-1550. DOI: 10.19435/j.1672-1721.2018.11.074. -





 下载:
下载: