Application of a dimensionality reduction strategy based on SIS and MDS and machine learning statistical modeling methods to breast cancer transcriptome data
-
摘要:
目的 探索以确定独立筛选(sure independence screening,SIS)与多维尺度变换(multi-dimensional scaling,MDS)为基础的2步降维策略,及以支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)、随机森林(random forest,RF)和梯度推进机(gradient boosting machine,GBM)构建乳腺癌淋巴结转移风险预测的统计模型,为高危人群识别及早期干预提供科学依据。 方法 采用SIS和MDS作为初步降维方法,并以套索算法(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO)为第2步降维方法,通过SIS+LASSO和MDS+LASSO的2步降维策略,将筛选的变量分别纳入SVM、RF和GBM 3种机器学习模型。使用受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic, ROC)曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC)作为衡量模型预测性能的评价指标。 结果 所有预测模型中,SIS+LASSO和MDS+LASSO 2步降维策略相对SIS和MDS单步策略在SVM、RF和GBM 3种预测模型下预测稳定性提升,运行时间和运行内存减少。MDS+LASSO 2步降维策略相对于MDS单步降维策略的预测精度提升。所有策略中,GBM的预测精度均高于SVM和RF。 结论 在SIS与MDS基础上加入LASSO的2步降维策略,从运算速度、内存消耗、建模方法选择、预测精度等方面弥补了SIS和MDS单步降维的不足。对于不同的降维策略,GBM的预测性能均比SVM和RF好。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to investigate the utility of a two-step dimensionality reduction strategy, incorporating sure independence screening (SIS) and multi-dimensional scaling (MDS), alongside machine learning algorithms, namely support vector machine (SVM), random forest (RF) and gradient boosting machine (GBM), for constructing a statistical model for breast cancer lymph node metastasis risk prediction. This model aims to provide a scientific basis for the identification of high-risk groups and early intervention. Methods SIS and MDS were used as the initial dimensionality reduction method and the last absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) was used as the second step of dimensionality reduction. The filtered variables were incorporated into three machine learning models, SVM, RF and GBM, respectively, by the two-step dimensionality reduction strategies of SIS+LASSO and MDS+LASSO. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) area under the curve (AUC) was used as an evaluation metric to measure the prediction performance of the models. Results Among all prediction models, the SIS+LASSO and MDS+LASSO two-step dimensionality reduction strategies have improved prediction stability and reduced running time and running memory relative to the SIS and MDS single-step strategies for the three prediction models SVM, RF, and GBM. The MDS+LASSO two-step dimensionality reduction strategy has improved prediction accuracy relative to the MDS single-step dimensionality reduction strategy. Among all strategies, GBM has higher prediction accuracy than SVM and RF. Conclusions The two-step dimensionality reduction strategy with LASSO added to SIS and MDS compensates for the shortcomings of SIS and MDS single-step dimensionality reduction in terms of computing speed, memory consumption, modeling method selection, and prediction accuracy. For different dimensionality reduction strategies, the prediction performance of GBM is better than that of SVM and RF. -
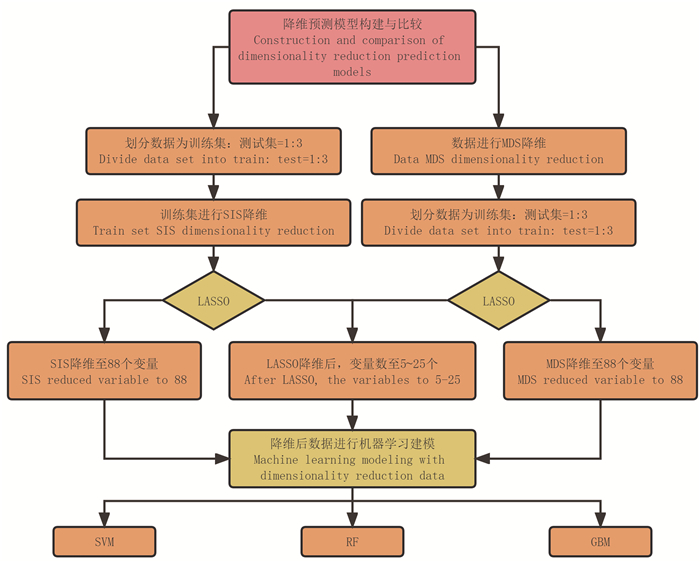
图 1 研究流程图
注:SIS, 确定独立性筛选;MDS, 多维缩放;LASSO, 最小绝对收缩和选择算法;SVM, 支持向量机;RF, 随机森林;GBM, 梯度推进机。
Figure 1. Research workflow
Note: SIS, sure independent screening; MDS, multidimensional scaling; LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; SVM, support vector machine; RF, random forest; GBM: gradient propulsion machine.
图 2 SIS与SIS+LASSO在不同统计建模方法下的预测性能
AUC:曲线下面积;SVM:支持向量机;RF:随机森林;GBM:梯度推进机;SIS:确定独立性筛选策略;LASSO: 套索算法; SIS+LASSO:确定独立性筛选和LASSO结合的策略。
Figure 2. Prediction performance of SIS and SIS+LASSO under different statistical modelling approaches
AUC: area under the curve; SVM: support vector machine; RF: random forest; GBM: gradient propulsion machine; SIS: sure independent screening strategies; LASSO: least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; SIS+LASSO: the strategy of combining Sure Independent Screening and LASSO.
图 3 MDS与MDS+LASSO在不同统计建模方法下的预测性能
AUC:曲线下面积;SVM:支持向量机;RF:随机森林;GBM:梯度推进机;MDS:多维缩放;LASSO: 套索算法; MDS+LASSO:多维缩放和LASSO结合的策略。
Figure 3. Prediction performance of MDS and MDS+LASSO under different statistical modelling approaches
AUC: area under the curve; SVM: support vector machine; RF: random forest; GBM: gradient propulsion machine; MDS: multidimensional scaling; LASSO: least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; MDS+LASSO: the strategy of combining multidimensional scaling and LASSO.
表 1 不同降维策略下的AUC以及时间和内存消耗
Table 1. AUC, time and memory consumption under different dimension reduction strategies
策略
StrategyAUC① 内存/KB
Memory/KB时间/s
Time/sSIS(88)+ SVM 0.879(0.822, 0.933) 0.020 189.233 RF 0.910(0.875, 0.952) 0.102 484.055 GBM 0.917(0.880, 0.967) 4.020 380.851 SIS+LASSO SVM 0.875(0.828, 0.928) 0.007 50.761 RF 0.888(0.855, 0.929) 0.057 402.752 GBM 0.895(0.861, 0.949) 3.833 97.875 MDS(88)+ SVM 0.735(0.684, 0.778) 0.018 210.714 RF 0.879(0.846, 0.928) 0.145 641.008 GBM 0.903(0.871, 0.947) 4.739 380.852 MDS+LASSO SVM 0.873(0.821, 0.919) 0.006 56.422 RF 0.885(0.860, 0.922) 0.108 608.742 GBM 0.900(0.858, 0.943) 4.160 105.042 注:1.AUC:曲线下面积;SIS: 确定独立筛选;LASSO: 套索算法; MDS:多维尺度变换;SVM:持向量机;RF:随机森林;GBM:梯度推进机。
2.SIS(88)、MDS(88)表示该方法筛选出的变量数为88;SIS+LASSO:确定独立性筛选和LASSO结合的策略;MDS+LASSO:多维缩放和LASSO结合的策略。
①以[M (P25, P75)]表示。
Note: 1. AUC: area under the curve; SIS:sure independence screening;LASSO: least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; MDS:multi-dimensional scaling;SVM:support vector machine;RF:random forest;GBM:gradient boosting machine.
2.SIS (88) and MDS (88) indicate that the number of variables screened by this method is 88; SIS+LASSO: The strategy of combining Sure Independent Screening and LASSO; MDS+LASSO: The strategy of combining multidimensional scaling and LASSO.
① [M (P25, P75)]. -
[1] Pfeiffer RM, Park Y, Kreimer AR, et al. Risk prediction for breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancer in white women aged 50 y or older: derivation and validation from population-based cohort studies[J]. PLoS Med, 2013, 10(7): e1001492. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001492. [2] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2021[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(1): 7-33. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21654. [3] Woolston C. Breast cancer: 4 big questions[J]. Nature, 2015, 527(7578): S120-S120. DOI: 10.1038/527S101a. [4] Oreski D, Oreski S, Klicek B. Effects of dataset characteristics on the performance of feature selection techniques[J]. Appl Soft Comput, 2017, 52: 109-119. DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.12.023. [5] Frank SM, Qi A, Ravasio D, et al. Supervised learning occurs in visual perceptual learning of complex natural images[J]. Curr Biol, 2020, 30(15): 2995-3000.e3. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.05.050. [6] Aflalo Y, Dubrovina A, Kimmel R. Spectral generalized multi-dimensional scaling[J]. Int J Vis, 2016, 118(3): 380-392. DOI: 10.1007/s11263-016-0883-8. [7] 刘妍琛, 张晓曙, 崔旭东, 等. 基于Group LASSO Logistic回归分析模型分析流行性乙型脑炎早期临床症状与预后的关联[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 25(8): 891-897, 934. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.08.005.Liu YC, Zhang XS, Cui XD, et al. Study on the relationship between early clinical symptoms and prognosis of Japanese encephalitis: based on Group LASSO Logistic regression model[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2021, 25(8): 891-897, 934. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.08.005. [8] Dai P, Chang W, Xin Z, et al. Retrospective study on the influencing factors and prediction of hospitalization expenses for chronic renal failure in China based on random forest and LASSO regression[J]. Front Public Health, 2021, 9: 678276. DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.678276. [9] Heo JN, Yoon JG, Park H, et al. Machine learning-based model for prediction of outcomes in acute stroke[J]. Stroke, 2019, 50(5): 1263-1265. DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.024293. [10] Jiang F, Jiang Y, Zhi H, et al. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future[J]. Stroke Vasc Neurol, 2017, 2(4): 230-243. DOI: 10.1136/svn-2017-000101. [11] Ellis K, Kerr J, Godbole S, et al. A random forest classifier for the prediction of energy expenditure and type of physical activity from wrist and hip accelerometers[J]. Physiol Meas, 2014, 35(11): 2191-2203. DOI: 10.1088/0967-3334/35/11/2191. [12] Natekin A, Knoll A. Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial[J]. Front Neurorobot, 2013, 7: 21. DOI: 10.3389/fnbot.2013.00021. [13] Chin K, DeVries S, Fridlyand J, et al. Genomic and transcriptional aberrations linked to breast cancer pathophysiologies[J]. Cancer Cell, 2006, 10(6): 529-541. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.009. -





 下载:
下载: