Combined effect of adult neck circumference and waist circumference on diabetes mellitus
-
摘要:
目的 探索成人颈围(neck circumference, NC)现状及其与糖尿病关系,并分析颈围和腰围(waist circumference, WC)对糖尿病患病风险的联合效应。 方法 根据中国成人慢性非传染性疾病与营养监测方案,在天津市调查4 136名成人,收集其NC、WC数据,并采集静脉血检测空腹血糖、服用无水葡萄糖2 h后血糖和糖化血红蛋白。将男性成人NC < 37 cm或女性成人NC < 33 cm者划分为NC1组,其余为NC2组。分析调查人群NC的分布状况及不同NC分组的糖尿病患病率情况,用WC将人群分为WC正常、中心型肥胖前期、中心型肥胖组,在此基础上分析其与NC对糖尿病患病率及患病风险的联合效应。 结果 调查人群平均NC为36.3 cm,男性平均NC高于女性,且与年龄呈正相关(β=0.271, t=3.452, P=0.001);NC2组糖尿病患病率为27.7%,高于NC1组的17.9%;在WC正常组和中心型肥胖组中,NC2组糖尿病患病率均高于NC1组;多因素logistic回归分析模型分析结果显示,与WC正常组+NC1组相比,随着WC、NC的增加罹患糖尿病的风险也随之增大,其中中心型肥胖组+NC2组罹患糖尿病的风险最高(OR=2.939, 95%CI: 2.227~3.880, P<0.001)。 结论 天津市颈围较大成人糖尿病患病率较高,WC和NC对糖尿病患病风险的联合效应较强,未来需要进一步研究NC与糖尿病患病的生物学机制,以便应用于大人群筛查达到早期发现、控制糖尿病的效果。 Abstract:Objective To explore the current situation of neck circumference (NC) and its relationship with diabetes among adults, and to analyze the combined effect of NC and waist circumference (WC) on risk of diabetes. Methods According to the Chinese adult chronic disease and nutrition surveillance program, a total of 4 136 inhabitants aged 18 and above were enrolled from Hexi, Nankai, Hongqiao, Wuqing, Jinnan, Baodi and Jizhou district of Tianjin. Except for measuring NC and WC, venous blood was collected to detect fasting blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin and blood glucose after taking sugar for 2 h. Those whose male adult NC < 37 cm or female adult NC < 33 cm were divided into NC1 group and the rest were NC2 group. Investigate the distribution of NC and the prevalence of diabetes in different NC groups. Divide the surveyed population into three groups with WC: normal, pre-central obesity and central obesity, on this basis, analyze the combined effect with NC on the prevalence rate and diabetes risk. Results The average NC of the investigated population in Tianjin was 36.3 cm, which was higher in males than in females, and was positively correlated with age(β=0.271, t=3.452, P=0.001). The prevalence rate of diabetes in NC2 group was 27.7%, which was significantly higher than that in NC1 group (17.9%). In WC normal group and central obesity group, the prevalence rate of diabetes in NC2 group was significantly higher than that in NC1 group. The multivariate logistic regression showed that compared with normal WC + NC1 group, the risk of diabetes increased with the increase of WC and NC, and the central obesity + NC2 group had the highest risk of diabetes (OR=2.939, 95%CI: 2.227-3.880, P < 0.001). Conclusions The prevalence rate of diabetes is high among higher NC people (large neck circumference) in Tianjin adults, and the combined effect of WC and NC on the risk of diabetes is strong. In the future, it is necessary to further study the biological mechanism of NC and diabetes, so that it can be applied to large population screening to achieve the effect of early detection and control of diabetes. -
Key words:
- Neck circumference /
- Waist circumference /
- Diabetes /
- Central obesity /
- Glycosylated hemoglobin
-
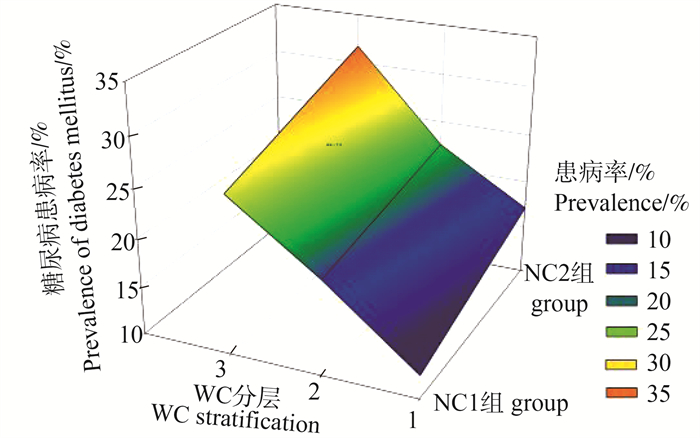
图 1 调查人群WC、NC与糖尿病患病率的关联
WC:腰围;NC: 颈围;WC分层: 1=WC正常组,2=中心型肥胖前期组,3=中心型肥胖组;NC1组:男性成人NC < 37 cm或女性成人NC < 33 cm;NC2组:男性成人NC≥37 cm或女性成人NC≥33 cm。
Figure 1. Correlation between WC, NC and prevalence of diabetes mellitus in participants
WC: waist circumference; NC: neck circumference; WC stratification: 1=normal WC group, 2=pre-central obesity group, 3=central obesity group; NC1 group: male adult NC < 37 cm or female adult NC < 33 cm; NC2 group: male adult NC≥37 cm or female adult NC≥33 cm.
表 1 调查对象基本情况及NC状况
Table 1. Basic information and NC of the investigated population
分组 group 调查人数
Number of people surveyedNC/cm ① NC1组人数(占比/%) ②
Number of NC1 group people(proportion/%) ②NC2组人数(占比/%) ③
Number of NC2 group people (proportion/%) ③性别 Gender 男性 Male 1 827 38.4±3.5 539(29.5) 1 288(70.5) 女性 Female 2 309 34.5±3.0 565(24.5) 1 744(75.5) t/χ2值 value 50.337 13.201 P值 value < 0.001 < 0.001 地区 Region 城镇 Town 3 043 36.6±3.8 682(22.4) 2 361(77.6) 农村 Rural 1 093 35.4±3.5 422(38.6) 671(61.4) t/χ2值 value 15.828 107.817 P值 value < 0.001 < 0.001 年龄组/岁 Age group/years 18~ < 45 660 35.8±4.2 209(31.7) 451(68.3) 45~ < 60 1 338 36.3±3.7 315(23.5) 1 023(76.5) ≥60 2 138 36.4±3.7 580(27.1) 1 558(72.9) t/χ2值 value 22.686 15.337 P值 value < 0.001 < 0.001 合计 Total 4 136 36.3±3.8 1 104(26.7) 3 032(73.3) 注:NC,颈围。
①以x±s表示。②NC1组,男性成人NC < 37 cm或女性成人NC < 33 cm。③NC2组,男性成人NC≥37 cm或女性成人NC≥33 cm。
Note: NC: neck circumference.
①x±s; ②NC1 group, male adult NC < 37 cm or female adult NC < 33 cm; ③NC2 group, male adult NC≥37 cm or female adult NC≥33 cm.表 2 年龄与NC趋势性检验分析
Table 2. Trend test and analysis of age and NC
指标 Index β值
valuesx t值
valueP值
value常数项 Constant term 35.612 0.194 183.500 < 0.001 年龄/岁 Age/years 0.271 0.079 3.452 0.001 注:NC,颈围。
Note: NC, neck circumference.表 3 不同NC调查对象的糖化血红蛋白及糖尿病患病情况
Table 3. Glycosylated hemoglobin and diabetes mellitus prevalence in different NC investigated populations
分组
GroupHbAlc 糖尿病
Diabetes mellitus人数
Number of people均值±标准差
(x±s)人数
Number of people患病率/%
Prevalence/%NC1组 group 1 100 5.5±0.7 197 17.9 NC2组 group 3 027 5.8±1.0 839 27.7 t/χ2值 value 76.440 41.632 P值 value < 0.001 < 0.001 合计 Total 4 127 5.7±0.9 1 036 25.1 注:NC,颈围; HbA1c, 糖化血红蛋白; NC1组,男性成人NC < 37 cm或女性成人NC < 33 cm;NC2组,男性成人NC≥37 cm或女性成人NC≥33 cm。
Note: NC: neck circumference; HbA1c, Glycosylated hemoglobin; NC1 group, male adult NC < 37 cm or female adult NC < 33 cm; NC2 group, male adult NC≥37 cm or female adult NC≥33 cm.表 4 WC分层基础上增加不同NC情况的糖尿病患病率
Table 4. Prevalence rate of diabetes mellitus along with different NC based on WC stratification
变量
VariableWC分层WC stratification 分层内总人数
Number of people within stratificationWC正常 ①
WC normal ①分层内总人数
Number of people within stratification中心型肥胖前期 ①
Precentral obesity ①分层内总人数
Number of people within stratification中心型肥胖 ①
Central obesity ①NC1 NC2 NC1 NC2 NC1 NC2 男性 Male 437 35(13.7) 43(23.6) 348 27(23.1) 54(23.4) 1 042 51(30.5) 289(33.0) χ2值 value 7.100 0.004 0.395 P值 value 0.008 0.950 0.529 女性 Female 603 32(11.1) 42(13.3) 445 24(16.9) 66(21.8) 1 261 28(20.6) 345(30.7) χ2值 value 0.641 1.428 5.917 P值 value 0.424 0.232 0.015 城镇 Town 750 51(14.6) 74(18.5) 567 38(24.2) 99(24.2) 1 726 53(30.3) 517(33.3) χ2值 value 2.074 0.000 0.660 P值 value 0.169 1.000 0.446 农村 Rural 290 16(8.3) 11(11.2) 226 13(12.8) 21(16.9) 577 26(20.3) 117(26.1) χ2值 value 0.642 0.769 1.764 P值 value 0.522 0.456 0.203 18~ < 45岁years 252 7(5.6) 8(6.3) 144 3(6.7) 11(11.1) 264 5(12.8) 32(14.2) χ2值 value 0.055 0.696 0.054 P值 value 1.000 0.549 1.000 45~ < 60岁years 330 9(5.8) 26(14.9) 268 17(21.0) 27(14.4) 740 21(26.6) 192(29.1) χ2值 value 7.102 1.767 0.209 P值 value 0.011 0.210 0.695 ≥60岁 years 458 51(19.5) 51(26.0) 381 31(23.3) 82(33.1) 1 299 53(28.7) 410(36.8) χ2值 value 2.783 3.950 4.600 P值 value 0.112 0.059 0.038 合计 Total 1 040 67(12.4) 85(17.1) 793 51(19.7) 120(22.5) 2 303 79(26.1) 634(31.7) χ2值 value 4.607 0.797 3.898 P值value 0.032 0.372 0.048 注:WC,腰围;NC,颈围;NC1组,男性成人NC < 37 cm或女性成人NC < 33 cm;NC2组,男性成人NC≥37 cm或女性成人NC≥33 cm。
①以糖尿病患病人数(糖尿病患病率/%)表示。
Note: WC, waist circumference. NC, neck circumference. NC1 group, male adult NC < 37 cm or female adult NC < 33 cm; NC2 group, male adult NC≥37 cm or female adult NC≥33 cm.
①Number of people with diabetes mellitus(prevalence rate of diabetes mellitus/%).表 5 NC与WC对糖尿病患病风险的联合效应
Table 5. Combined effects of NC and WC on risk of diabetes
分组 Group 糖尿病患病 Diabetes mellitus OR值value (95% CI) P值value WC正常+NC1 WC normal +NC1 1.000 WC正常+NC2 WC normal +NC2 1.493(1.048~2.126) 0.026 中心型肥胖前期+NC1 Pre-central obesity+NC1 1.702(1.135~2.554) 0.010 中心型肥胖前期+NC2 Pre-central obesity+NC2 1.984(1.423~2.767) < 0.001 中心型肥胖+NC1 Central obesity+NC1 2.293(1.586~3.315) < 0.001 中心型肥胖+NC2 Central obesity+NC2 2.939(2.227~3.880) < 0.001 注:WC,腰围;NC,颈围;NC1组,男性成人NC < 37 cm或女性成人NC < 33 cm;NC2组,男性成人NC≥37 cm或女性成人NC≥33 cm。
1.控制因素为性别、年龄、城乡。
Note: WC, waist circumference;NC, neck circumference; NC1 group, male adult NC < 37 cm or female adult NC < 33 cm; NC2 group, male adult NC≥37 cm or female adult NC≥33 cm.
1.The controlling factors are gender, age and town and rural areas. -
[1] 王莉. 糖化血红蛋白测定在糖尿病诊断和治疗中的应用研究[J]. 吉林医学, 2015, 36(14): 3076. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0412.2015.14.086.Wang L. Study on the application of glycosylated hemoglobin in the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus [J]. Jilin Med J, 2015, 36(14): 3076. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0412.2015.14.086. [2] 孙晓慧, 柳杰, 刘大娜, 等. 颈围用于筛选糖调节受损人群的临床价值研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2018, 18(20): 3980-3983. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2018.20.041.Sun XH, Liu J, Liu DN, et al. Analysis of the clinical value of neck circumference for screening the patients with impaired glucose regulation [J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine, 2018, 18(20): 3980-3983. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2018.20.041. [3] Britton KA, Massaro JM, Murabito JM, et al. Body fat distribution, incident cardiovascular disease, cancer, and all-cause mortality [J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2013, 62(10): 921-925. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.06.027. [4] Wang Y, Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, et al. Comparison of abdominal adiposity and overall obesity in predicting risk of type 2 diabetes among men [J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2005, 81(3): 555-563. DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/81.3.555. [5] 宋晴阳, 李翀, 郑连斌, 等. 颈围预测成人肥胖的可行性分析[J]. 解剖学报, 2021, 52(6): 986-991. DOI: 10.16098/j.issn.0529-1356.2021.06.024.Song QY, Li C, Zheng LB, et al. Feasibility of neck circumference in evaluating adult obesity [J]. Acta Acad Sin, 2021, 52(6): 986-991. DOI: 10.16098/j.issn.0529-1356.2021.06.024. [6] Luo Y, Ma X, Shen Y, et al. Neck circumference as an effective measure for identifying cardio-metabolic syndrome: a comparison with waist circumference [J]. Endocrine, 2017, 55(3): 822-830. DOI: 10.1007/s12020-016-1151-y. [7] Namazi N, Larijani B, Surkan PJ, et al. The association of neck circumference with risk of metabolic syndrome and its components in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2018, 28(7): 657-674. DOI: 10.1016/j.numecd.2018.03.006. [8] Limpawattana P, Manjavong M, Sopapong R. Can neck circumference predictmetabolic syndrome? An experience from a university community [J]. Endocr Pract, 2016, 22(1): 8-15. DOI: 10.4158/EP15902.OR. [9] Yang GR, Yuan MX, Wan G, et al. Association between neck circumference and the occurrence of cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes: Beijing community diabetes study 20 (BCDS-20) [J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019: 4242304. DOI: 10.1155/2019/4242304. [10] Khalangot M, Gurianov V, Okhrimenko N, et al. Neck circumference as a risk factor of screen-detected diabetes mellitus: community-based study [J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2016, 8: 12. DOI: 10.1186/s13098-016-0129-5. [11] Salmanroghani H, Salmanroghani R, Nourian M, et al. Evaluation of neck circumference as an easy and reliable predictor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2019, 30(2): 163-170. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2018.18004. [12] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 国家卫生和计划生育委员会通告(卫计生通〔2013〕4号) [J]. 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会公报, 2013, 118(5): 1. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGB201305002.htmThe National Health and Family Planning Commission of People′s Republic of China. Announcement No. 4 of the National Health and Family Planning Commission [J]. Gazette of the national health and family planning commission of People′s Republic of China, 2013, 118(5): 1. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGB201305002.htm [13] Ozkaya I, Yardimci B, Tunckale A, et al. Appropriate neck circumference cut-off points for metabolic syndrome in Turkish patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr, 2017, 64(10): 517-523. DOI: 10.1016/j.endinu.2017.07.006. [14] Cui T, Yan BH, Liu Z, et al. Neck circumference: a valuable anthropometric measurement to detect metabolic syndrome among different age groups in China [J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2018, 34(3). DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.2966. [15] Yan Q, Sun DM, Li X, et al. Neck circumference and incidence of type 2 diabetes in Chinese elderly individuals: a community-based cohort study [J]. Obes Facts, 2021, 14(5): 450-455. DOI: 10.1159/000514219. [16] Wan H, Wang Y, Xiang Q, et al. Associations between abdominal obesity indices and di-abetic complications: Chinese visceral adiposity index and neck circumference [J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2020, 19(1): 118. DOI: 10.1186/s12933-020-01095-4. [17] Cao W, Xu Y, Shen Y, et al. Neck circumference predicts the occurrence and remission of metabolic associated fatty liver disease: a longitudinal study of community-dwelling population [J]. Ann Nutr Metab, 2022, 78(5): 273-280. DOI: 10.1159/000526075. -





 下载:
下载: